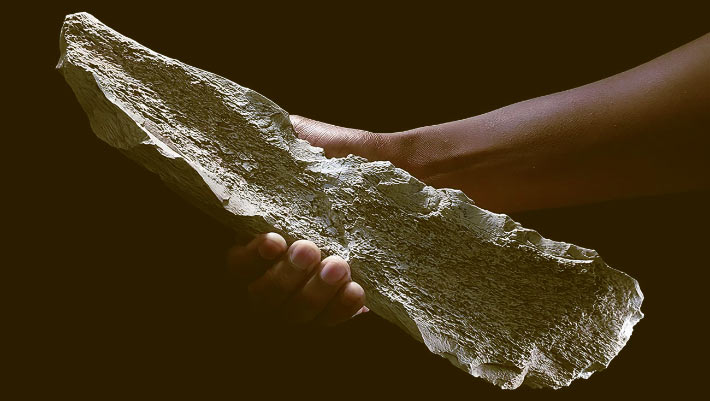
Paleoanthropologists have actually recorded a bone tool assemblage from a single horizon dated to 1.5 million years earlier at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. These bone tools precede other proof of methodical bone tool production by more than 1 million years and sheds brand-new light on the nearly unidentified world of early hominin bone innovation.
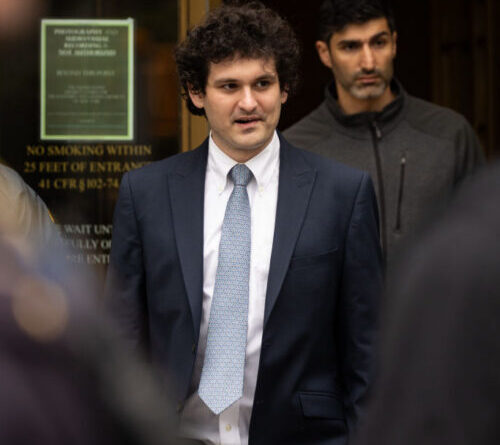
The 1.5-million-year-old elephant humerus that has actually been knapped into a tool. Image credit: CSIC.
Early hominins had actually currently been making tools out of stone in some capability for a minimum of a million years, however there’s been little proof of prevalent tool-making out of bones before about 500,000 years back.
The hominins who formed the newly-discovered bone tools did so in a way comparable to how they made tools out of stone, by cracking away little flakes to develop sharp edges– a procedure called knapping.
This transfer of strategies from one medium to another reveals that the hominins who made the bone tools had an innovative understanding of tool-making, which they might adjust their methods to various products, a considerable intellectual leap.
It might suggest that human forefathers at that time had a higher level of cognitive abilities and brain advancement than researchers believed.
“This discovery leads us to presume that early people substantially broadened their technological alternatives, which till then were restricted to the production of stone tools and now enabled brand-new basic materials to be included into the collection of prospective artifacts,” stated Dr. Ignacio de la Torre, a scientist at the CSIC-Spanish National Research Council.
“At the very same time, this growth of technological possible suggests advances in the cognitive capabilities and psychological structures of these hominins, who understood how to integrate technical developments by adjusting their understanding of stone work to the adjustment of bone stays.”
“The tools reveal proof that their developers thoroughly worked the bones, breaking off flakes to develop beneficial shapes,” stated Dr. Renata Peters, a scientist at University College London.
“We were thrilled to discover these bone tools from such an early timeframe.”
“It implies that human forefathers can moving abilities from stone to bone, a level of intricate cognition that we have not seen somewhere else for another million years.”
The 1.5-million-year-old bone tools were found at the T69 Complex website in the Frida Leakey Korongo West Gully at Olduvai Gorge, in northern Tanzania, a website prominent for its long history of essential historical discoveries exposing the origins of human beings.
The research study authors found a collection of 27 bones that had actually been formed into tools at the website. The bones primarily originated from big mammals, mainly elephants and hippos.
The tools are solely made from the animals’ limb bones, as these are the most thick and strong.
The extremely earliest stone tools originate from the Oldowan age which extended from about 2.7 million years ago to 1.5 million years earlier. It utilizes an easy technique for making stone tools, by cracking one or a couple of flakes off a stone core utilizing a hammerstone.
The bone tools reported in the present research study were from the time that the ancient human forefathers were advancing into the Acheulean age which started as far back as about 1.7 million years earlier.
The Acheulean innovation is best identified by the usage of more complex handaxes that were thoroughly formed by knapping– enabling the production of tools through more standardized ways.
The bone tools reveal that these advanced methods were rollovered and embraced for usage on bones too, something formerly hidden in the fossil record for another million years, much later on into the Acheulean age.
Prior to this discover, bones formed into tools had actually just been recognized sporadically in unusual, separated circumstances in the fossil record and never ever in a way that suggested that human forefathers were methodically producing them.
It’s uncertain exactly what the tools were utilized for, since of their total shape, size and sharp edges, it’s most likely that they might have been utilized to process animal carcasses for food.
It’s likewise uncertain which types of human forefather crafted the tools.
No hominin stays were discovered together with the collection of bone artifacts, though it’s understood that, at the time, Homo erectus and Paranthropus boisei were occupants of the area.
“Because these tools were such an unanticipated discovery, we hope that our findings will trigger archaeologists to re-examine bone discoveries worldwide in case other proof of bone tools has actually been missed out on,” the scientists stated.
Their paper appears today in the journal Nature
_____
I. de la Torre et alMethodical bone tool production at 1.5 million years earlier. Naturereleased online March 5, 2025; doi: 10.1038/ s41586-025-08652-5
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.