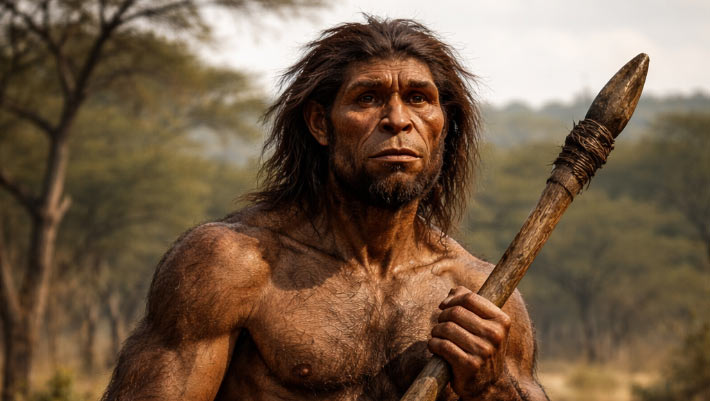
The hominin fossils found in the Grotte à Hominidés at Thomas Quarry I in Casablanca, Morocco, are supplying brand-new proof about the deep origins of Humankindrecommending that the ancestral family tree of modern-day human beings was currently present in Africa almost 800,000 years earlier. The fossils are comparable in age to Homo antecessor from Spain however reveal a mix of primitive characteristics and obtained functions similar to Eurasian antiquated hominins and later Humankind
Restoration of Homo erectus
Previously, paleoanthropologists have actually discussed where the last typical forefather of contemporary people, Neanderthals and Denisovans lived.
Hereditary proof recommends that this forefather existed in between about 765,000 and 550,000 years earlier, however the fossil record has actually stayed unsure.
Some researchers had actually proposed a Eurasian origin, based in part on 950,000- to 770,000-year-old fossils from Atapuerca, Spain.
The brand-new hominin fossils– partial mandibles, teeth, vertebrae and a piece of a thigh– from the Grotte à Hominidés reinforce the case for Africa.
An analysis of the surrounding sediments reveals that the Moroccan fossils are from a time near a significant shift in the Earth’s electromagnetic field, about 773,000 years back, providing a comparable age to Homo antecessor
The brand-new fossils are morphologically various from Homo antecessorrecommending that local distinction in between Europe and North Africa was currently present by the late Early Pleistocene (around 1.8 million to 780,000 years ago).
The Moroccan fossils integrate ancient functions seen in types such as Homo erectus with more contemporary qualities discovered in Humankind and Neanderthals.
Their molar size patterns look like those of early Humankind and Neanderthals, whereas their mandible shape is better to those of Homo erectus and other African antiquated people.
The Moroccan fossils might not be the last typical forefathers to modern-day human beings, Neanderthals and Denisovans, however might be close forefathers.
“The Moroccan stays most likely represent a progressed type of Homo erectus in North Africa, however one that sits near the evolutionary split in between African and Eurasian family trees,” the scientists stated.
“Our findings highlight the Maghreb as an essential area for comprehending the development of our types, enhancing the case for an African instead of a Eurasian origins of Humankind“
The outcomes were released today in the journal Nature
_____
JJ. Hublin et alEarly hominins from Morocco basal to the Humankind family tree. Naturereleased online January 7, 2026; doi: 10.1038/ s41586-025-09914-y
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.