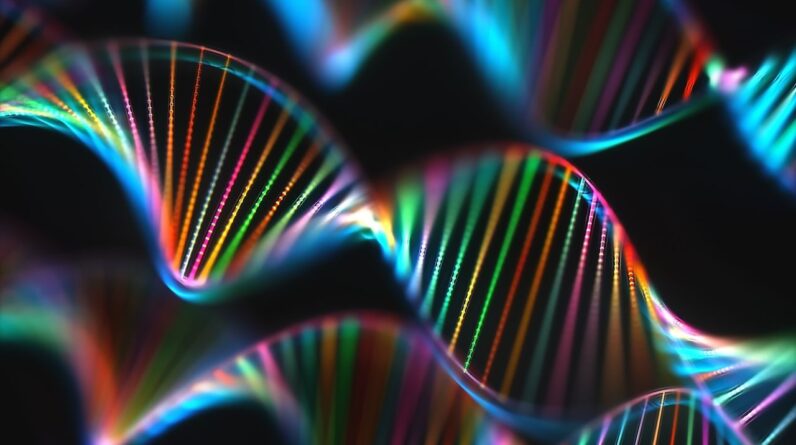
(Image credit: KTSDESIGN/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY by means of Getty Images )
Quick truths about genes
Where genes are discovered: In the chromosomes in the nuclei of cells and in the mitochondria
Variety of genes human beings bring: More than 20,000
Resemblance of your genes: All human beings share about 99.9 %of the very same genes
What makes everyone special? Part of the response remains in our genes.A lot of genes are discovered in the nuclei of cells in the body. There, they are arranged in threadlike structures called chromosomeswhich are made from particles called deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA. Human cells usually consist of 23 sets of chromosomes, and the body includes more than 20,000 genesin overall. All of the hereditary info in an organism is called a genome.
By sending out guidelines to structures in cells called ribosomes, genes trigger the cells to make particular proteins. This allows your cells to duplicate, fix themselves, and carry out specialized jobs.
Whatever you require to understand about genes
What is DNA?
DNAwhich is brief for “deoxyribonucleic (dy-AHK”-see-RY’-boh-noo-KLAY-ik) acid,” is the particle that comprises chromosomes. It holds the whole user’s manual for an organism. DNA particles appear like zany ladders, with 2 long hairs signed up with by “rungs” at the center and twisted into a 3D shape called a double helix. The sides of the ladder are sugars and phosphates. The ladder’s rungs are paired mixes of 4 particles called nucleotides: adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine (A, C, G and T). These are the “letters” that comprise DNA’s code.
There are around 3 billion of these letters in the human genome, and they are organized in various sets and in various series. These series equate into guidelines for making proteins, which, in turn, impact particular characteristics. These series are called genes.
In between genes are other DNA areas that do not consist of protein-making directions. These bits are called noncoding DNAwhich assists cells work in other methods; for example, the noncoding DNA might turn other genes “up” or “down.” About 98% to 99% of our DNA is noncoding
Helping DNA in its work is RNAor ribonucleic acid, which is likewise discovered in every cell. RNA are copies of DNA series that check out and bring DNA’s directions out of the nucleus and into the cell. RNA is needed to make proteinsand it likewise helps in stimulating chain reactions and managing genes.
The majority of DNA is nuclear DNA, indicating it’s situated in the cells’ nuclei in chromosomes. Some DNA is in the fluid surrounding the nucleus, discovered in structures called mitochondria. This mitochondrial DNAor mtDNA, assists mitochondria produce energy for cells; that’s why the mitochondria are referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell. Unlike nuclear DNA, which comes from both moms and dads, mtDNA is typically acquired just from the mom.
How comparable is human DNA and animal DNA?
All living things have DNA, and all DNA particles consist of series of nucleotides– A, C, G and T– that code for proteins. Distinctions in between types originated from the order and length of those DNA series. Researchers study these distinctions by comparing the portion of DNA series that types share.
From one human to the next, our genomes have to do with 99.9% alike. As an outcome of developmentthe plan of hereditary directions in our DNA is likewise really comparable to that of other animals.
Earth’s very first life is believed to have actually appeared a minimum of 3.77 billion years agoOver billions of years, progressively intricate types of life progressed and gave their DNA. Animal types that are carefully associated to each other– and therefore closer to the very same shared forefather– bring comparable hereditary guidelines. Even if they look really various, outwardly, the genomes of carefully associated types are more comparable than those of distantly associated types.
manateeslikewise referred to as sea cows, have bodies that are structured for residing in water. Even though manatees might look rather like seals and walruses, they are really more carefully associated to elephantsAnd the closest land-animal loved ones of seals and walruses are bears
Other than for modern-day human beings (Humankindall types on the human ancestral tree are long extinct. Our closest living family members are primates– particularly, chimpanzees (Pan troglodytesand bonobos (Pan paniscus. Till just recently, researchers had actually proposed that chimps and people shared 98.8% of their DNA. Scientists just recently recommended that this portion leaves out crucial parts of the 2 genomes that are more difficult to compare. After thinking about these other little bits of the human and chimp genomes, their general resemblance might be closer to 90%
Animals that aren’t primates still have numerous genes in typical with people. Mice and human beings are both mammals and vertebrates (animals with foundations). Typically, the protein-coding parts of the mouse and human genomes have to do with 85% comparableBy contrast, we share simply 70% of our genome with zebrafish, another animal typically studied in the laboratory.
As scientists continue to map the genomes of much more animal types, they will discover more about development, genetics and genes throughout the tree of life.
An illustration revealing hairs of DNA, which includes the directions for developing proteins that assist your body function. 2 hairs of DNA type a double-helix shape that appears like a twisted ladder. The sides of this “ladder” are made from sugars and phosphates. The “rungs” in the middle are base sets; each consists of 2 of 4 substances– adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine– in various mixes. (Image credit: Science Picture Co by means of Alamy)
Who was Gregor Mendel?
The field of contemporary genes is rooted in plant experiments carried out by pioneering researcher Gregor Johann Mendel ( 1822-1884 ). In 1865, Mendel started studying genetics by explore pea plants (Pisum sativum. Physical characteristics in pea plants are simple to see. The peas can be smooth or old and wrinkly, the flowers can be purple or white, and the plants can be high or brief.
Mendel picked 7 attributes to observe in the plants. To study how these characteristics were acquired, he developed hybrids by passing pollen in between pea plants with various characteristics. He then observed which characteristics in hybrids were given to the next generation of plants and which were not acquired or would avoid generations.
At the time, the majority of researchers believed offspring’s qualities arised from a mixing of their moms and dads’ qualitiesBy that reasoning, plants with brilliant purple flowers that were reproduced with plants with white flowers would produce hybrids with lilac flowers. To put it simply, the qualities of each moms and dad brought equivalent weight when adding to the offspring.
Mendel’s experiments showed otherwise. He revealed that some characteristics were dominant and would bypass other hereditary guidelines for the characteristic. If simply one moms and dad had a dominant characteristic, such as purple flowerstheir offspring would have it, too. By contrast, recessive qualities need that both moms and dads have a characteristic in order for it to be observable in their offspring.
(Although Mendel discovered these essential concepts of genes, it’s crucial to keep in mind that researchers did not comprehend how qualities were formed by DNA and genes till the 1940s)
Mendel invested 9 years on his pea plant task. He reproduced and observed about 28,000 plantsproducing hybrid pressures that integrated various characteristics. The pattern of dominant and recessive qualities used to all of the qualities that Mendel checked.
While his clinical accomplishments were not acknowledged throughout his life time, Mendel is now called “the father of genetics.” His research study provided an easy view of how qualities work. Ever since, the field of genes has actually revealed more complicated systems that manage characteristics, consisting of the impact of an organism’s environment.

A painting of Gregor Mendel operating in the garden where he performed his fundamental pea plant experiments. (Image credit: Bettmann by means of Getty Images)
How does DNA expose your origins?
Hereditary origins screeninglikewise referred to as hereditary genealogy, is a method to trace household history through DNA. Gradually, hereditary variations appear in groups of individuals. These variations are given through generations and are distinct to those geographical areas. Having a specific kind of variation in your DNA might indicate that your forefathers stemmed from a location worldwide where other individuals share that variation.
Commercially readily available sets can assist to determine an individual’s hereditary origins. Users send their DNA in saliva samples, which are then sent out to labs and compared to other DNA samples in a big database. Tests might try to find hereditary variations in the Y chromosome — the sex chromosome normally brought by males– to check out origins in the direct male family tree. They might look for matches in mitochondrial DNA, which shows maternal family tree. Other tests examine variations called single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which are distinctions in single “letters” within an offered gene and hence appear in the whole genome.
DNA can even inform you if you have Neanderthals in your ancestral tree. Neanderthals H. sapien‘s closest extinct family members, passed away out about 40,000 years earlier. For thousands of years before that, Neanderthals mated with H. sapiens in parts of Europe and Asia. Traces of Neanderthal DNA remain in the genomes of individuals whose forefathers originated from those continents.
Still, origins represents just a partial photo of what qualities you wind up with. Genes alone might form particular qualities, such as eye and hair color, or vulnerability to particular kinds of illness. An individual’s environment, way of life and other aspects likewise impact their total health and look, and differentiate one specific from another.
Is cancer hereditary?
Specific health issue are brought on by hereditary problems. These coding mistakes in DNA might be an anomaly in a single gene, or missing out on or duplicated product in chromosomes.
Some hereditary mistakes are acquired. The signs of genetic conditions in some cases appear early in life, however this is not constantly the case. In Tay-Sachs illnesswhich impacts nerves in the brain and spine, signs usually emerge at 3 to 6 months old. By contrast, Huntington’s illnessa neurodegenerative condition, generally does not establish up until the adult years.
Ecological aspects and way of life options might likewise integrate with genetics to trigger illness. These health conditions are called multifactorial conditions due to the fact that they come from a complicated mix of elements.
Cancer, in which cells in various parts of the body increase or grow frantically, is one such condition. There are more than 200 kinds of cancerand hereditary anomalies can increase the threat of some cancers. In some cases, these anomalies are triggered by external elements that damage DNA and trigger mistakes in cell duplication, like sun damage or direct exposure to toxic substances. Some hereditary anomalies that increase the threat of cancer are genetic, acquired from an individual’s moms and dads. Particular acquired anomalies in genes called BRCA1 and BRCA2 are connected to an increased danger of breast cancer and ovarian cancer
Acquired gene anomalies have actually been connected to more than 2 lots kinds of cancersconsisting of cancers of the thyroid, stomach, prostate and pancreas. Just about 5% to 10% of cancer cases are brought on by genetic anomalies alone.
Genes glossary
Genes images
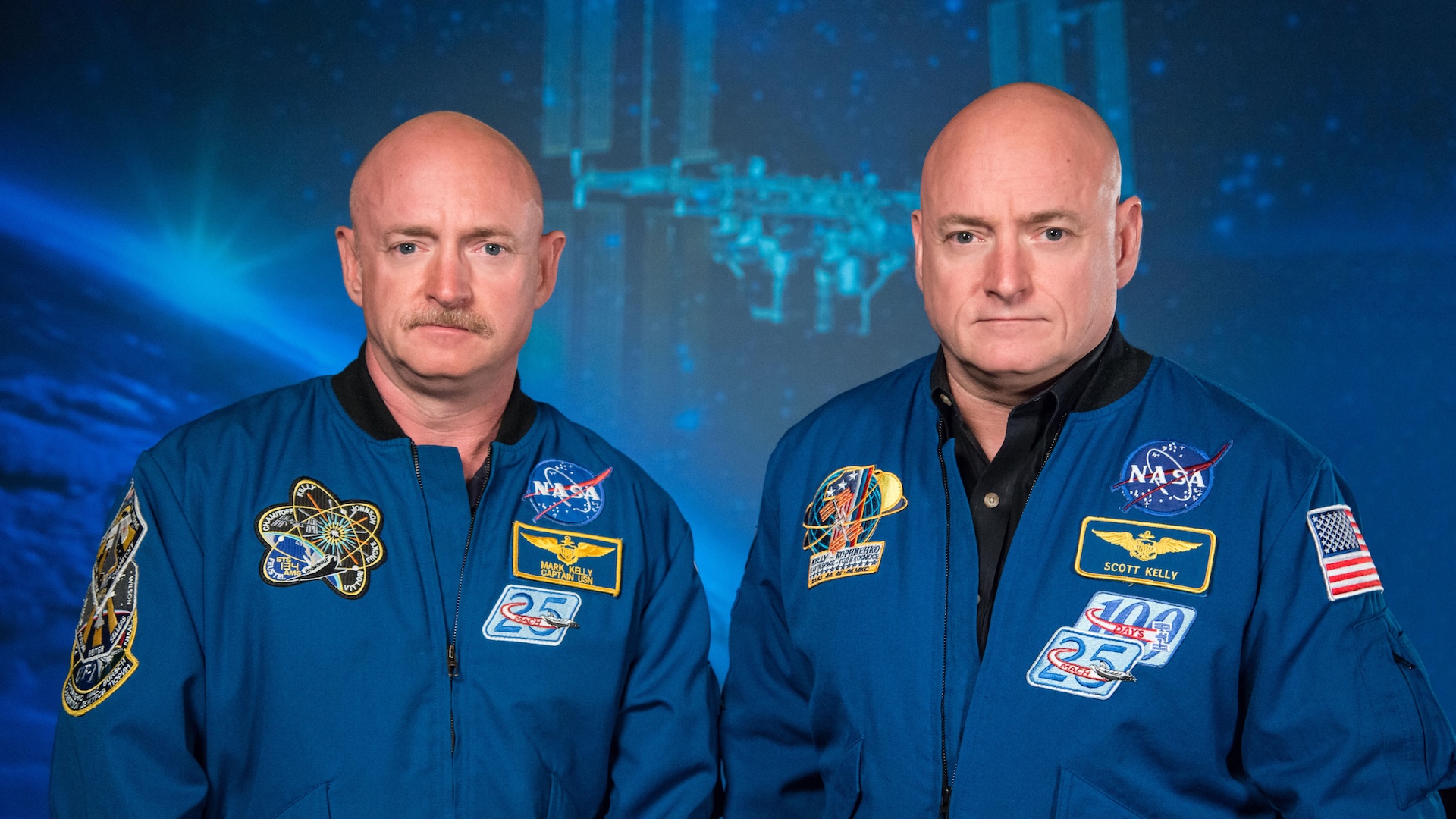

Twins
Astronaut Scott Kelly(left) and his sibling, previous astronaut Mark Kelly(ideal), equal twins. Research study groups collected information from the 2 bros while Scott Kelly remained in area and Mark Kelly was on Earth. The Kellys’hereditary resemblance is assisting researchers to much better comprehend how spaceflight alters the body.
Discover more about genes
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Mindy Weisberger is a science reporter and author of “Rise of the Zombie Bugs: The Surprising Science of Parasitic Mind-Control” (Hopkins Press). She previously modified for Scholastic and was a channel editor and senior author for Live Science. She has actually reported on basic science, covering environment modification, paleontology, biology and area. Mindy studied movie at Columbia University; prior to LS, she produced, composed and directed media for the American Museum of Natural History in NYC. Her videos about dinosaurs, astrophysics, biodiversity and development appear in museums and science centers worldwide, making awards such as the CINE Golden Eagle and the Communicator Award of Excellence. Her writing has actually likewise appeared in Scientific American, The Washington Post, How It Works Magazine and CNN.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.