( Image credit: Illustration by Dane Johnson/Museum of the Rockies)
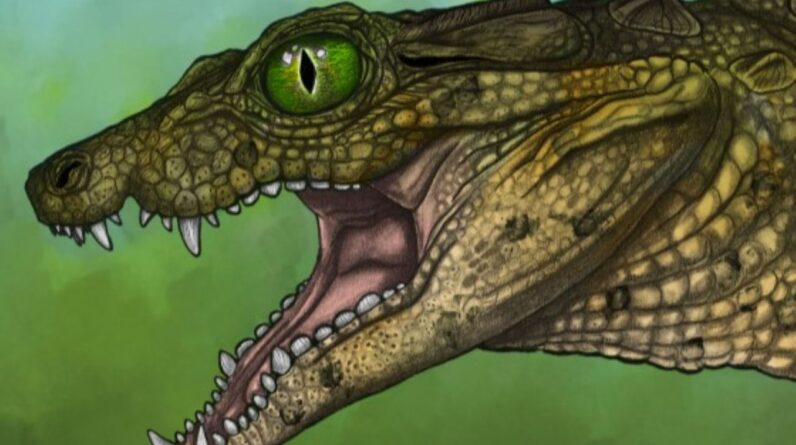
Around 95 million years back, little crocodile-like animals with unusual, sheathed teeth burrowed along the coasts of the Western Interior Seaway in what is now southwest Montana, a brand-new research study recommends.
The brand-new research study explains the very first such animal ever found– a teenage croc nicknamed Elton that determined about 2 feet(60 centimeters)long from nose to tail idea. Elton’s fossilized remains were found in 2021 throughout an arranged dig in the Blackleaf geological development, which dates to the middle of the Cretaceous duration (145 million to 66 million years ago).
The very first fossil Allen saw was Elton’s skull, which was simply 2 inches (5 cm) long and ingrained in rock, according to the declaration. Allen revealed the mini skull to David Varricchioa teacher of paleobiology, taphonomy and ichnology at Montana State University, who instantly comprehended the fossil’s significance.
“After the dig, Dr. Varricchio told me why he was so excited the day I found the initial specimen,” Allen stated. “It has so much visible anatomy to explore, and he could see it was a tiny, tiny croc skull, fully articulated and preserved — it was a special thing.”
It ends up, Elton came from a now-extinct household of crocodile-like animals, or crocodyliforms, that scientists formerly didn’t understand existed. This household, called Wannchampsidae, sits within the family tree Neosuchia, that includes all contemporary crocodilians and their closest extinct loved ones. Its members resided in North America throughout the Cretaceous, and they were much smaller sized than other neosuchian crocs are; had Elton made it through till the adult years, he would have grown to simply 3 feet (90 cm) long, according to the declaration.
Neosuchians are usually semi-aquatic or marine predators with easy, cone-shaped teeth– however not Elton. He and fellow members of the newly found types, called Thikarisuchus xenodenteshad a selection of in a different way formed teeth, consisting of sheathed and other specialized fangs, which they utilized to feast on plants and pests, according to the declaration.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Elton and his kind likewise survived on land, and they likely made burrows in the ground, based upon how largely jam-packed Elton’s bones were when Allen and his associates evaluated them, the declaration stated.
Quickly after discovering Elton’s skull, Allen went back to gather bagfuls of the surrounding sediment to browse it for more hints about the animal. He invested hours sorting through the dirt, drawing out pieces of bone and rebuilding the Thikarisuchus skeleton bit by bit. He dealt with his schoolmate Dane Johnsonnow a paleontology laboratory and field professional at the Museum of the Rockies in Montana– typically to the tune of Elton John’s 1972 tune “Crocodile Rock,” which influenced the name Elton.
To get a clear image of the fossils, Allen then made CT scans, which assisted him compare the bones and portions of rock that were still stayed with Elton’s remains. “Harrison worked super hard to digitally reconstruct the animal, and it came out beautifully,” Varricchio, who is a co-author of the brand-new research study, stated in the declaration.
An in-depth description and photos of T. xenodentesin addition to a conversation of the newly found types’ position in the evolutionary tree, are consisted of in the research study, released Sept. 22 in the Journal of Vertebrate PaleontologyEspecially, the scientists highlight a household of ancient crocodyliforms called Atopasauridae that was formerly discovered in Eurasia and appears like Elton, with a little body size and comparable oral functions.
“It suggests that during the same time period, we’re seeing convergent evolution between two distantly related groups due to similar environmental conditions, prey availability and who-knows-what that prompted crocs on opposite sides of the planet to develop similar features,” Allen stated.
Sascha is a U.K.-based personnel author at Live Science. She holds a bachelor’s degree in biology from the University of Southampton in England and a master’s degree in science interaction from Imperial College London. Her work has actually appeared in The Guardian and the health site Zoe. Composing, she takes pleasure in playing tennis, bread-making and searching pre-owned stores for covert gems.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.