(
FAST FACTS
Turning point: Discovery of penicillin
Date: Sept. 28, 1928
Where: St Mary’s Hospital, London
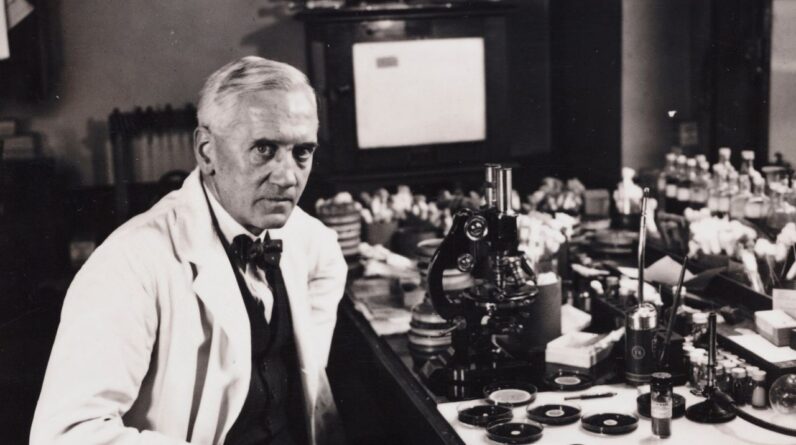
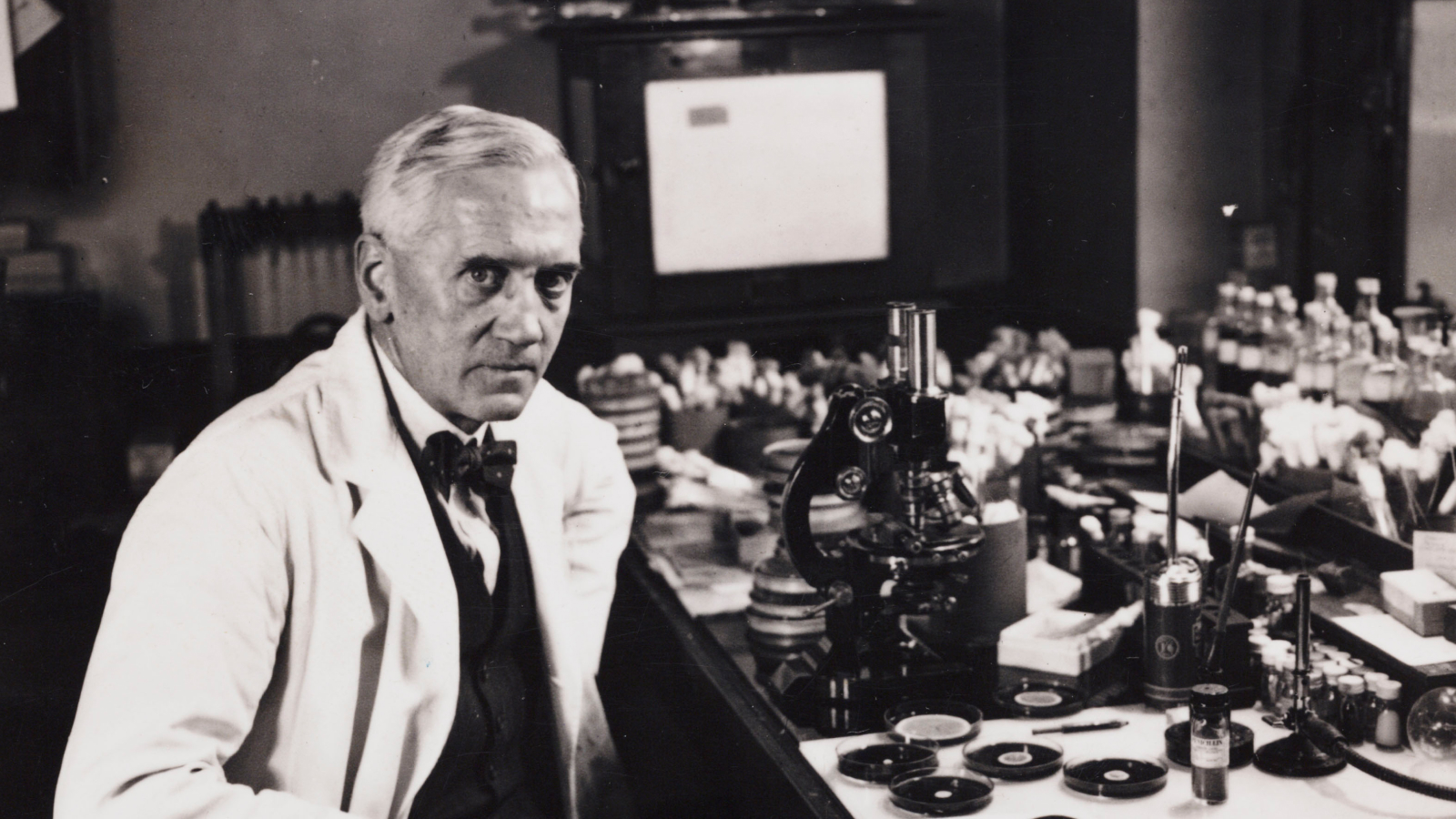
Who: Scottish microbiologist Alexander Fleming
On Sept. 28, 1928, Alexander Fleming awakened to examine his experiments examining bacterial development– and inadvertently found the world’s very first antibiotic.The discovery of penicillin took place when Fleming returned from a two-week break. He took a look at his plates of Staphylococcus aureus that had actually been cultured from a contaminated injury On among the plates, Fleming observed a spot of green mold converging the golden-yellow bacterial nests, according to an account from his assistant, V.D. Allison. Near the green spot, the germs were clear, colorless and dead. The compound that eliminated the germs would form the basis of the very first antibiotic, though the term wasn’t created up until 1941
“When I woke up just after dawn on September 28, 1928, I certainly didn’t plan to revolutionize all medicine by discovering the world’s first antibiotic, or bacteria killer,” Fleming later on stated. “But I suppose that was exactly what I did.”
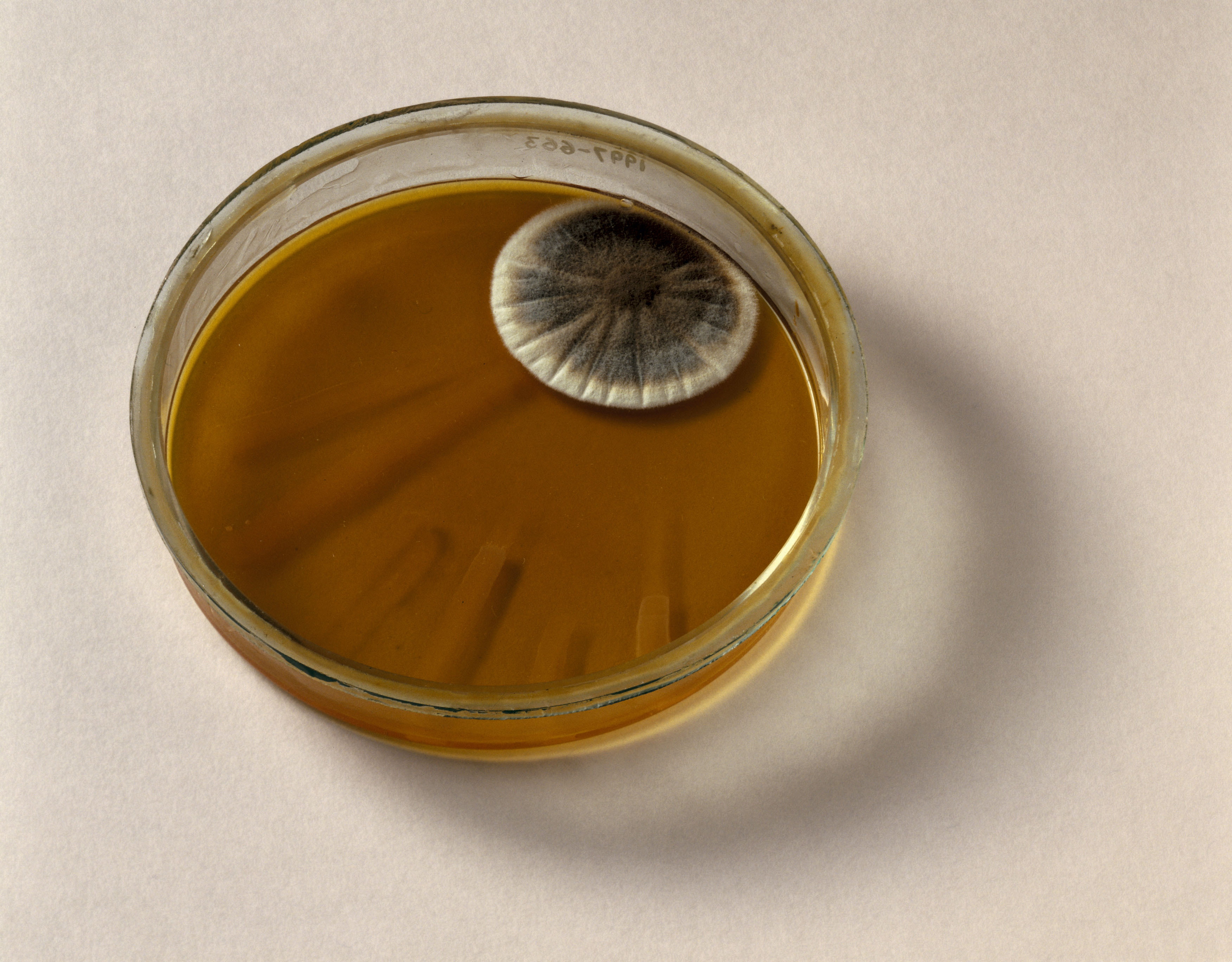

A petri meal which contains bacterial nests with the mold P. notatum growing in the upper right-hand corner. A chemical produced by the fungi would form the basis of the drug penicillin. (Image credit: SSPL/Getty Images)Fleming identified that the “mold juice” originated from a fungal types he ultimately recognized as PenicilliumWhen he explained the discovery to his fellow physicians at a fulfilling the next year, he was consulted with practically overall disinterest. Separating the evasive “mold juice” Shown tough, so the discovery suffered for a years, Allison composed in individual recollections.
In 1939, researchers Howard Florey and Ernst Chain took an interest in the compound. They produced a research study group and, together with researchers such as Margaret Jennings, Edward Abraham and Norman Heatley, handled to separate penicillin from the mold, test it and utilize the yellowy, grainy compound to treat a handful of clients. The substance was still fairly impure.
In 1942, Fleming was dealing with a young client who was seriously ill with meningitisHe discovered the powder eliminated the client’s bacterial infection, and he telephoned Florey and Chain for a few of their stash, although it was not cleansed. After Fleming injected it into the young boy’s spine, the client recuperated.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
After this amazing healing, Fleming was persuaded that penicillin required to be mass-produced. He pitched it to the federal government, and quickly there was a collaboration in between the U.S. and the U.K. to mass-produce the compound. By 1945, the very first antibiotic was extensively readily available.
By the 1940s, penicillin was being standardized. Here, a male extracts a dosage of penicillin utilizing a glass syringe.
(Image credit: Anthony Potter Collection/Getty Images)Fleming, Florey and Chain would win the 1945 Nobel Prize in medication for their deal with the discovery, seclusion and production of penicillin. In 1964, Dorothy Hodgkin would make the Nobel Prize in chemistry for illuminating its crystal structure, which assisted chemists style later on prescription antibiotics.
It’s approximated that considering that its discovery, penicillin has actually conserved 500 million lives and, together with its derivatives, is still an essential in the treatment of myriad diseases, consisting of ear infections, strep throatand urinary system infections.
Penicillin likewise resulted in the advancement of numerous various prescription antibioticsPrevalent usage and abuse of these marvel drugs have actually implied that numerous bacterial pressures have developed resistance versus typical prescription antibioticsconsisting of penicillin. In the arms race versus superbugs, researchers are now discovering absolutely brand-new methods to eliminate germs, from utilizing the power of infections to assault germs to utilizing the gene-editing tool CRISPR to develop brand-new drugs.
Tia is the handling editor and was formerly a senior author for Live Science. Her work has actually appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com and other outlets. She holds a master’s degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science composing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia belonged to a group at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that released the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won numerous awards, consisting of the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.