A brand-new analysis of archival information from the Near Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (NIMS) on board NASA’s Galileo spacecraft has actually exposed the very first proof of ammonia-bearing substances on Jupiter’s icy moon Europa, providing brand-new ideas about its subsurface ocean and current geological activity.
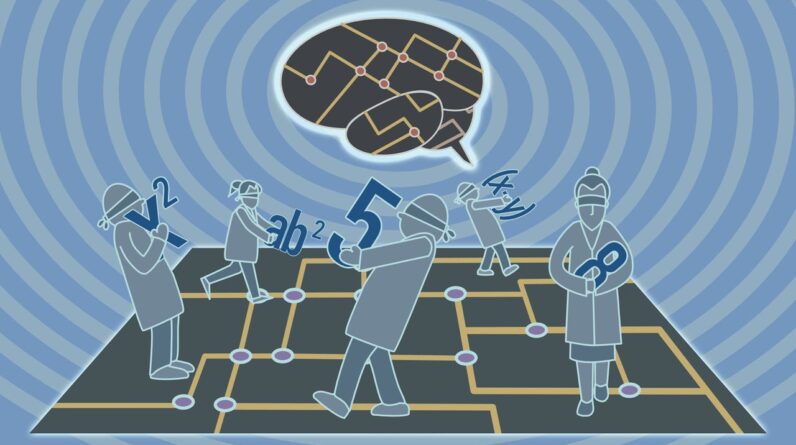
In this composite image, red pixels mark places on Europa’s surface area where ammonia-bearing substances were discovered; purple shows no such detection. Image credit: NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
“The detection of ammonia(NH3or ammonia-bearing parts (ammonia hydrate, salts, or minerals) on icy planetary bodies in the Solar System is of substantial interest for comprehending their geology, possible habitability, and astrobiological importance,” stated research study author Dr. Al Emran, a scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
“On Jupiter’s moon Europa, the existence of ammonia or ammoniated types is especially essential for constraining ocean chemistry, examining habitability, and rebuilding the moon’s early environment.”
“Ammonia serves as an antifreezer; a plentiful existence of this can decrease the freezing point of liquid water by as much as 100 K and might allow retention of subsurface oceans for icy bodies.”
“Although it stays uncertain whether Europa’s subsurface ocean is straight linked to its surface area, the detection of ammonia substances might recommend such a connection, as these products are unsteady in area radiation.”
In his brand-new paper released in the Planetary Science JournalDr. Emran reports the detection of a particular ammonia absorption function at 2.20 microns in near-infrared spectra of Europa’s surface area.
The signal was recognized in observations from Galileo’s NIMS instrument, which surveyed Europa throughout flybys in the 1990s.
Ammonia hydrate and ammonium chloride are the most possible products accountable for the discovered function.
Ammonia is unsteady under extreme area radiation, a residential or commercial property that makes its existence on Europa’s surface area considerable.
According to the paper, the survival of ammonia-bearing products recommends they were carried from Europa’s underground ocean or shallow subsurface to the surface area in the moon’s current geological past, perhaps through gushing cryovolcanism or a comparable system.
The analysis likewise indicates wider ramifications for Europa’s internal structure.
The existence of ammoniated substances follows a thinner ice shell and a chemically minimized, high-pH subsurface ocean.
Ammonia functions as an antifreezing representative, efficient in reducing the freezing point of water ice and assisting sustain liquid oceans underneath icy crusts.
“Hidden in the information were faint signals of ammonia near fractures on the moon’s frozen surface area, through which liquid water consisting of liquified ammonia substances would be anticipated to increase,” Dr. Emran stated.
“The substances might have reached the surface area through geologically current cryovolcanism.”
“That’s since ammonia considerably reduces the freezing point of water, functioning as a sort of antifreeze.”
While ammonia-bearing types have actually been determined on other icy bodies in the external Solar System– consisting of Pluto, Charon, a number of Uranian moons, and Saturn’s moon Enceladus– previous efforts to validate their existence on Europa had actually produced undetermined or conflicting outcomes.
“The detection of ammonia-bearing parts in this research study offers the very first proof of nitrogen-bearing types on Europa, an observation of significant astrobiological significance due to nitrogen’s fundamental function in the molecular basis of life,” Dr. Emran stated.
_____
A. Emran. 2026. Detection of an NH3 Absorption Band at 2.2 μm on Europa. World. Sci. J 6, 255; doi: 10.3847/ PSJ/ae1291
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.