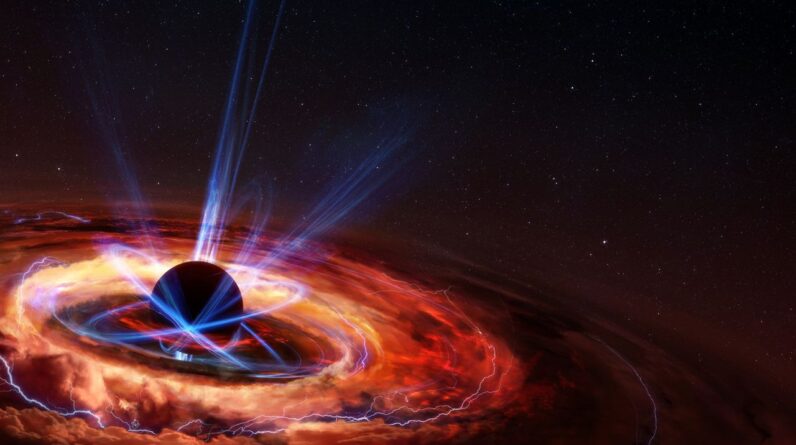
Mars likely as soon as held plentiful water. Previously, observations have actually revealed that a lot of climatic water loss happens throughout the Red Planet’s southern summer season, when warmer, dustier conditions enable water vapor to increase to high elevations without condensing and get away into area. In brand-new research study, planetary researchers recognized a formerly unacknowledged path for water loss– observed, for the very first time, throughout the opposite season. Their outcomes reveal that a strong, localized and temporary dust storm in Martian Year 37 (August 2023) drove a rise of water vapor up throughout the northern summertime.
This close-up color picture of a small dust storm on Mars was gotten by the HRSC instrument on ESA’s Mars Express in April 2018. Image credit: ESA/ DLR/ FU Berlin/ CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO.
“Our findings expose the effect of this kind of storm on earth’s environment development and opens a brand-new course for comprehending how Mars lost much of its water gradually,” stated Dr. Adrián Brines, a scientist at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía and the University of Tokyo.
While dust storms have actually long been acknowledged as essential for Mars’ water escape, previous conversations have actually primarily concentrated on big, planet-wide dust occasions.
On the other hand, Dr. Brines and his coworkers reveals that smaller sized, local storms can likewise highly improve water transportation to high elevations, where it can be more quickly lost to area.
Previous research study has actually focused on the warm, vibrant summertimes of the southern hemisphere, considering that it is normally the primary duration of water loss on Mars.
The existing research study spotted an uncommon boost in water vapor in the center environment of Mars throughout the northern hemisphere summer season in Martian Year 37, brought on by an anomalous dust storm.
Diagram highlighting the climatic action to a localized dust storm in the northern hemisphere throughout the regional summertime season; high dust concentrations considerably increase the absorption of solar radiation, causing higher climatic warming, particularly in the center environment; moreover, the increased climatic flow connected with the dust storm improves the vertical transportation of water vapor from the lower environment, promoting water injection at greater elevations and increasing hydrogen escape from the exobase. Image credit: Brines et aldoi: 10.1038/ s43247-025-03157-5.
At these elevations, the quantity of water depended on 10 times higher than normal, a phenomenon not observed in previous Martian years and not anticipated by existing environment designs.
Quickly later, the quantity of hydrogen in the exobase (an area where the environment combines with area) increased substantially to 2.5 times that of the previous years throughout the very same season.
Among the secrets to comprehending just how much water Mars has actually lost is determining just how much hydrogen has actually gotten away into area, given that this component is easily launched when water breaks down in the environment.
“These outcomes include an essential brand-new piece to the insufficient puzzle of how Mars has actually been losing its water over billions of years, and reveals that brief however extreme episodes can play an appropriate function in the environment development of the Red Planet,” stated Dr. Shohei Aoki, a scientist at the University of Tokyo and Tohoku University.
The outcomes appear today in the journal Communications: Earth & & Environment
_____
A. Brines et al2026. Out-of-season water escape throughout Mars’ northern summer season activated by a strong localized dust storm. Commun Earth Environ 7, 55; doi: 10.1038/ s43247-025-03157-5
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.