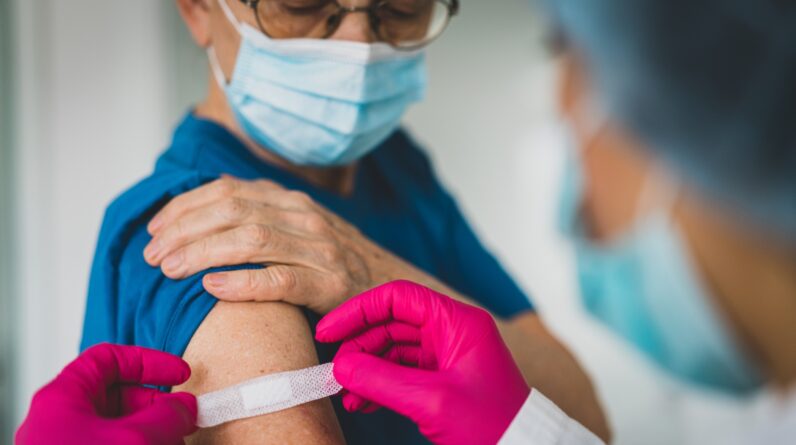
Health authorities are suggesting that some groups get more than one upgraded COVID-19 vaccine dosage this year.
(Image credit: Jasmin Merdan through Getty Images)
Grownups 65 and older and individuals with weakened body immune systems ought to get 2 dosages of the recently upgraded COVID-19 vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) suggests.
Individuals in these groups need to seek their 2nd dosage a minimum of 6 months after getting their very first dosage, the CDC stated Wednesday (Oct. 23). This suggestion likewise unlocks for individuals with moderate to extreme immunosuppression to get 3 dosages, or perhaps more, the company included. Clients can speak to their medical company about whether they might take advantage of getting 3 or more dosages.
“The recommendation acknowledges the increased risk of severe disease from COVID-19 in older adults and those who are immunocompromised,” the CDC mentioned. It likewise acknowledges that, unlike the seasonal influenzaCOVID-19 flows year-round, so particular clients might take advantage of getting an increase in resistance more than when a year.
“Receiving recommended 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccines can restore and enhance protection against the virus variants currently responsible for most infections and hospitalizations in the United States,” the CDC stated. “COVID-19 vaccination also reduces the chance of suffering the effects of Long COVID.”
Related: Infection that triggers COVID-19 utilizes a secret’back entrance’to contaminate the brain
Everybody 6 months and older is advised to get at least one dosage of a 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccine. There are 3 vaccines readily available, made by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and Novavax. The very first 2 shots usage mRNAa hereditary particle, as their base, while the Novavax vaccine consists of infection proteins and a compound to accelerate the body immune system.
The CDC does not suggest one kind of vaccine over another, other than to keep in mind that Novavax is just authorized for individuals ages 12 and up, while the others can be provided to kids as young as 6 months. Young kids might be suggested to get one to 3 dosages of the vaccine, depending upon which brand name they get this year and whether they’ve been immunized for COVID-19 formerly. Those information are defined on the CDC site
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
The 2024-2025 vaccines vary from previous shots because they’ve been upgraded to defend against brand-new variations of the coronavirus that have actually just recently emerged. The Pfizer and Moderna shots target a branch of the omicron ancestral tree called KP.2, which started acquiring supremacy in June. The Novavax shot was created to target an earlier alternativecalled JN.1, which KP.2 overtook.
Because summertime, brand-new versions have actually emerged, with one called KP.3.1.1 getting traction in August and staying on the top since mid-October. The infection continues to develop, lab tests recommend that all 3 2024-2025 vaccines produce antibodies versus a wide variety of JN.1 descendents, consisting of KP.2, KP.3 and their close loved ones.
The CDC hopes that, by advising extra dosages to high-risk groups, individuals can be much better secured from the infection year-round.
You can discover more about where to get a COVID-19 vaccine on the CDC site
This post is for educational functions just and is not suggested to provide medical recommendations.
Ever question why some individuals develop muscle more quickly than others or why freckles come out in the sunSend us your concerns about how the body works to community@livescience.com with the subject line “Health Desk Q,” and you might see your concern responded to on the site!
Nicoletta Lanese is the health channel editor at Live Science and was formerly a news editor and personnel author at the website. She holds a graduate certificate in science interaction from UC Santa Cruz and degrees in neuroscience and dance from the University of Florida. Her work has actually appeared in The Scientist, Science News, the Mercury News, Mongabay and Stanford Medicine Magazine, to name a few outlets. Based in NYC, she likewise stays greatly associated with dance and carries out in regional choreographers’ work.
The majority of Popular
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.