The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has actually taken a photo of the disallowed spiral nebula NGC 337.
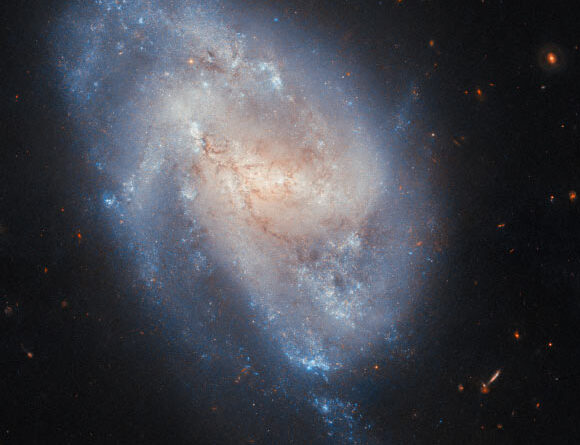
This Hubble image reveals NGC 337, a disallowed spiral nebula some 60 million light-years away in the constellation of Cetus. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ Hubble/ C. Kilpatrick.
NGC 337 lies roughly 60 million light-years far from Earth in the constellation of Cetus.
Understood as LEDA 3572 or IRAS 00573-0750, this disallowed spiral galaxy has a size of 60,400 light-years.
It was found on September 10, 1785 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel.
NGC 337 is the biggest and brightest member of the NGC 337 group (likewise referred to as LGG 15), a little group that consists of a minimum of 3 other galaxies.
The brand-new picture of the galaxy was made from different direct exposures taken in the noticeable and near-infrared areas of the spectrum with Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS).
2 filters were utilized to sample numerous wavelengths. The color arises from appointing various colors to each monochromatic image connected with a specific filter.
“This image integrates observations made at 2 wavelengths, highlighting the galaxy’s golden center and blue borders,” the Hubble astronomers stated in a declaration.
“The golden main radiance originates from older stars, while the shimmering blue edges get their color from young stars.”
“If Hubble had actually observed NGC 337 about a years earlier, the telescope would have found something amazing amongst the hot blue stars along the galaxy’s edge: a fantastic supernova,” they included.
“Labeled SN 2014cx, this supernova is amazing for having actually been found almost all at once in 2 greatly various methods: by a respected supernova hunter, Koichi Itagaki, and by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN).”
“ASAS-SN is an around the world network of robotic telescopes that scans the sky for unexpected occasions like supernovae.”
According to the astronomers, SN 2014cx is categorized as a Type IIP supernova.
“The Type II category implies that the taking off star was a supergiant a minimum of 8 times as huge as the Sun,” the scientists stated.
“The ‘P’ represents plateau, suggesting that after the light from the supernova started to fade, the level reached a plateau, staying at the exact same brightness for a number of weeks or months before fading additional.”
“This kind of supernova takes place when an enormous star can no longer produce adequate energy in its core to fend off the squashing pressure of gravity.”
“SN 2014cx’s progenitor star is approximated to have actually been 10 times more enormous than the Sun and numerous times as broad.”
It has actually long given that dimmed from its preliminary luster, the astronomers are still keeping tabs on the residue of SN 2014cx.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.