(Image credit: Antonio Busiello/Getty Images)
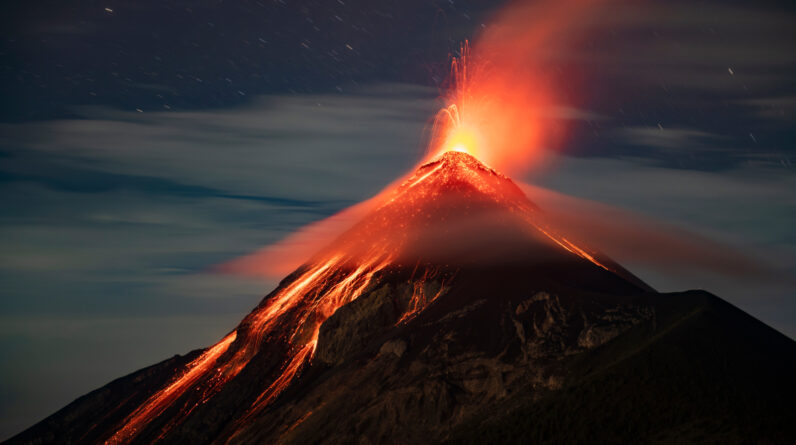
Volcanoes do not run on human timescales. They might go peaceful for centuries, just to rumble to life with ravaging eruptions. Their eruptions might last for days or years, and it’s typically tough to forecast beforehand the length of time an occasion will last.
Formally, volcanologists think about a volcano active if it has actually emerged at some point throughout the Holocene Epochwhich began 11,700 years earlier at the end of the last glacial epochA volcano that hasn’t appeared in the Holocene is thought about extinct.
This geologic-timescale-based difference is rather approximate, Ben Kennedya volcanologist at the University of Canterbury in New Zealand, informed Live Science. Volcanoes do not understand or care when the Holocene began. There is a great, physical factor to think about a volcano extinct after it’s been peaceful for more than 11,000 years, Kennedy stated.
That time duration is “probably roughly on the same timescale as you could keep a magma chamber underground filled with some liquid in it that could erupt,” he stated. After many years, many lava chambers and the volcanic pipes feeding them will have taken shape into strong rock, he stated, making them incapable of eruption.
Related: ‘This might be the origin of the Atlantis legend’: Mountain that sank below the waves found off Canary Islands
There is an exception, nevertheless: large “supervolcanoes” with huge lava chambers. These are frequently plainly active volcanic systems that have not emerged in the Holocene. The Yellowstone Calderafor instance, has moving lava underpinning it, triggering little earthquakes and heating various warm springs and geysers. The last active eruption was 70,000 years back, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.[
(Image credit: Holger Leue/Getty Images)
“We often call those systems ‘restless,'” Kennedy stated. “It’s staying hot, there’s a little bit of magma there and it’s doing something. It’s not necessarily erupting.”
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
What are’ inactive ‘volcanoes?
An even fuzzier term is “dormant.” This phrasing is more colloquial than clinical, Kennedy stated, due to the fact that inactive might describe an active volcano that isn’t presently appearing however might rumble to life any minute. Or it might describe an older volcano that’s most likely never ever going to emerge once again, however hasn’t passed the 11,000-year limit to main termination. “I think we use ‘dormant’ as that overlapping term, but it’s not useful,” Kennedy stated.
Lots of active volcanoes have long inactive durations. Mount St. Helens in Washington, for instance, emerged in between 1800 and 1857, then went peaceful before considerably blowing its top in 1980. The oft-snowcapped Mount Taranaki in New Zealand hasn’t appeared considering that 1800 however is anticipated to do so once again– the mountain’s geological history recommends it experiences big eruptions every 500 years approximately, with smaller sized eruptions every 90 years, according to the nation’s geological research study institute, GNS Science
Possibly among the most remarkable current volcanic awakenings happened in Iceland on the Reykjanes Peninsula starting in December 2023. The Sundhnúkur crater row in western Iceland, which had not been active for 800 years, all of a sudden started to open a series of rifts, launching intense lava streamsBased upon the geologic history of the area, volcanologists anticipate that the volcanic system will continue to emerge for centuries.
Stephanie Pappas is a contributing author for Live Science, covering subjects varying from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and habits. She was formerly a senior author for Live Science however is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and frequently adds to Scientific American and The Monitor, the month-to-month publication of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie got a bachelor’s degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science interaction from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
Many Popular
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.