(Image credit: Scenics & Science by means of Alamy Stock Photo)
An insect called the fall armyworm has actually spread out around the world, threatening food security in more than 80 nationsNow, brand-new research study has actually exposed Australian fungis that consume the worms from the within out– and might be the secret to stopping the insects’devastating spread.
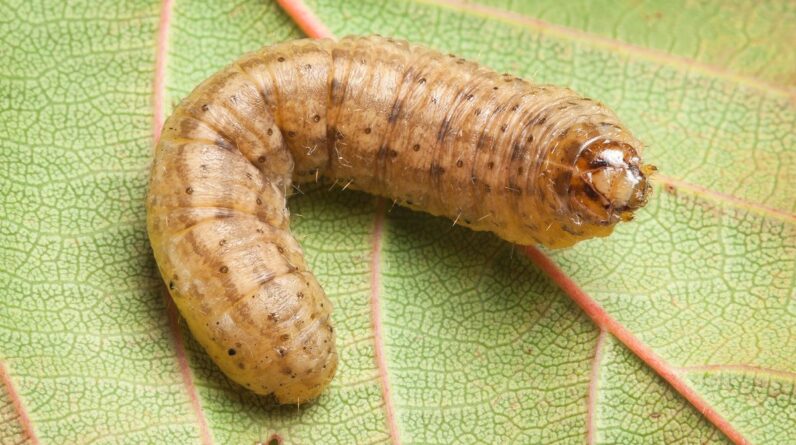
Fall armyworms (Spodoptera frugiperda ) are a kind of grey moth belonging to tropical locations of Central and South America, and recently, they have actually turned into one of the world’s most disastrous corn crop bugs. The adult moths can move fars away helped by worldwide trade and by windsand they are now present in Europe, Asia, Africa and Australia.
The longest taped armyworm flight was from Mississippi to southern Canada, covering 870 miles (1,400 kilometers) in simply 30 hours, Johnnie van den Berga zoologist at North-West University in South Africa who was not included with the brand-new research study, informed Live Science in an e-mail.
One fertile S. frugiperda woman can lay 1,000 to 2,000 eggs in her life time. And the offspring establish quickly: After eggs are laid on corn plants, the larvae are huge enough to trigger major leaf damage in about a week, van den Berg stated. The worm-like larvae are likewise hard to spotas they are little and tough to find– frequently, farmers may not identify fall armyworms till crop damage has actually currently started.
Related: What’s the distinction in between a moth and a butterfly?
These bugs mainly consume corn however can feed upon a big range of other cropsdestructive wheat, cotton, sugarcane and veggies.
Farmers have actually attempted to manage the spread of armyworms with pesticides, however the insects can rapidly establish a resistance to chemical pesticides. Researchers and farmers have actually checked out options for handling the armyworm issue, such as presenting infections that assault the wormsusing botanical extracts and engineering crops to be resistantThese approaches differ both in their practicality on a big scale and in their expense efficiency.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Now, brand-new research study from Australia’s Department of Primary Industries (DPI) reveals an appealing development: Fungi belonging to Australia that assault the fall armyworm.
The scientists have actually recognized 5 kinds of fungis that can eliminate fall armyworms within 24 hours of direct exposure. The fungi Nomuraea rileyi connects to the armyworm’s skin, covering it, before spreading out inside the larva’s body. It then consumes the armyworm from the within out.
The scientists shared their findings in a conference on fall armyworm management kept in March, and with Australian reportersThey have actually not yet been released in a peer-reviewed journal.
In different research study, another group of researchers found extra kinds of fungis that have the ability to eliminate fall armyworms, together with some kinds of germs. Some stress of the fungi Beauveria bassiana eliminated about 75% of armyworms within 48 hours. The germs Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) was Discovered to be reliable in eliminating fall armyworms.
This research study group still does not completely comprehend how the B. bassiana fungi eliminates armyworms, research study co-author Wee Tek Taya biologist at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in Australia, informed Live Science in an e-mail. It’s much better comprehended how the germs Bt works: it produces holes in cells of the armyworms’ gut, which eventually starves them, sets off blood poisoning, or both.
The CSIRO scientists state their work is still in the early phases, and more research study is required to approach application for insect management.
“The use of biological control agents … can be very effective,” Tay kept in mind. Releasing the fungis would “require careful resistance management planning,” he stated, because similar to standard insecticides, misusing fungis might cause resistance.
The fungis his group checked are typically discovered in the natural surroundings and routinely come across by pests, he included, so they do not prepare for the fungis having bad environmental effects if they were utilized to manage fall armyworms.
The DPI researchers, on the other hand, are now working to get N. rileyi authorized for sale as an insect control step, so it can be provided to farmers.
Before the fungis can get in massive usage, the prospective danger and unexpected effects the fungis may have on the environment should be examined, van den Berg stated. Compared to the effect of chemical insecticides, the effect of germs and fungis tend to be much less hazardous to the environment, he stated.
Editor’s note: This story was upgraded on April 11, 2025, to supply info about Bacillus thuringiensis and to clarify how it impacts armyworms.
Olivia Ferrari is a New York City-based freelance reporter with a background in research study and science interaction. Olivia has actually lived and operated in the U.K., Costa Rica, Panama and Colombia. Her composing concentrates on wildlife, ecological justice, environment modification, and social science.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.