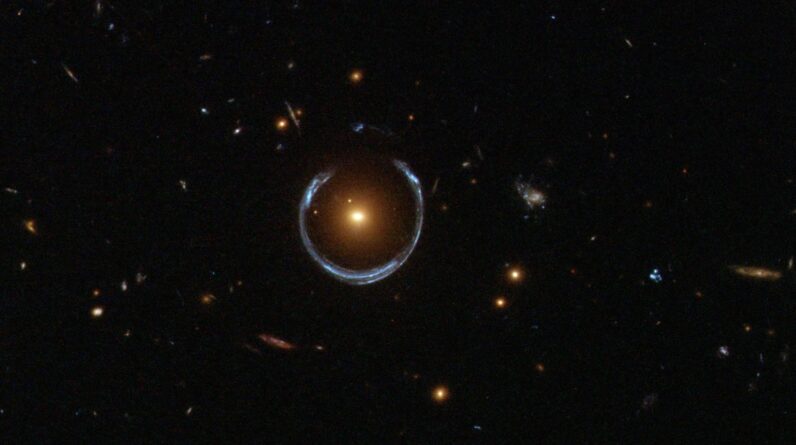
Astronomers have actually found a massive great void the size of 36 billion suns prowling within the “Cosmic Horseshoe.” The leviathan item is among the biggest great voids ever spotted.
Found in 2007, the Cosmic Horseshoe is a system of 2 galaxies situated in the constellation Leo. Pictures of the system reveal a halo of light surrounding the foreground galaxy, LRG 3-757. This phenomenon, called an Einstein ringtakes place when the substantial mass of the galaxy warps and amplifies light from a lot more far-off galaxy behind it.
This kind of zoom is called gravitational lensing and was very first forecasted by Albert Einstein in 1915. Now, brand-new research study has actually exposed simply how LRG 3-757 gets the mass needed to flex light: from a monstrous ultramassive black hole sitting in its. The scientists released their findings Feb. 19 on the preprint server arXiv, so they have actually not been peer-reviewed.
Einstein’s theory of basic relativity explains the method huge items warp the material of deep space, called space-time. GravityEinstein found, isn’t produced by a hidden force however by space-time curving and misshaping in the existence of matter and energy.
This curved area, in turn, sets the guidelines for how energy and matter relocation. Despite the fact that light journeys in a straight line, light taking a trip through an extremely curved area of space-time, such as the location around an enormous galaxy, likewise takes a trip in a curve– flexing around the galaxy and splaying out into a halo.
Related: Strange ‘Green Monster’ prowling in James Webb image of supernova residue is lastly discussed
To discover proof for the great void prowling within the Cosmic Horseshoe, the astronomers utilized information gathered from the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer spectrograph in Chile’s Atacama Desert, together with images collected by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
By examining the effective gravitational lensing by LRG 3-757– a galaxy with 100 times the mass of the Galaxy — along with the speed and way at which stars move it, the scientists concluded that the existence of an ultramassive great void “is necessary to fit both datasets simultaneously.”
This detection puts LRG 3-757’s great void amongst the biggest to ever exist. The most significant, called Ton 618, is approximated to weigh in at 66 billion times the mass of our sun and extend as much as 40 times the range in between Neptune and the sun. The black hole at the centre of the Holm 15A galaxy cluster is 44 billion solar masses and covers as much as 30 times the Neptune to sun range.
An ultramassive secret
Astronomers have not yet checked out precisely how LRG 3-757’s huge great void formed. The stars moving around it are fairly sluggish, and their motions are less random than would be anticipated for a black hole of its size.
This might be due to the fact that a few of the stars near it were ejected by previous galaxy mergers, or due to the fact that the great void as soon as had effective jets that satiated star developmentOr maybe the great void rapidly demolished a number of its surrounding stars previously in its life.
The astronomers anticipate to discover a few of the responses to these concerns from the Euclid area telescopewhich is one year into its six-year objective to brochure a 3rd of the whole night sky by catching countless wide-angle images. All informed, Euclid will record light from more than a billion galaxies that depend on 10 billion years of ages, according to the European Space Agency.
As soon as this is done, astronomers will utilize Euclid’s images to develop 2 maps: one made up of lots of other Einstein rings, and the other revealing shock waves called baryon acoustic oscillations. These maps must assist scientists trace dark matter and dark energy — strange elements of deep space thought to comprise the majority of its matter and trigger its speeding up growth, respectively.
“The Euclid mission is expected to discover hundreds of thousands of lenses over the next five years,” the authors composed in the research study. “This new era of discovery promises to deepen our understanding of galaxy evolution and the interplay between baryonic [regular matter] and [dark matter] components.”
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.