Paleontologists have actually assumed for years that a significant animal group called Ecdysozoa needs to be older than the Cambrian duration, however previously its origins have actually stayed enigmatic. The discovery of Uncus dzaugisi fixes up a significant space in between forecasts based upon molecular information and the absence of explained ecdysozoans prior to the abundant Cambrian fossil record and contributes to our understanding of the advancement of animal life, according to a research study group headed by University of California– Riverside’s Professor Mary Droser.
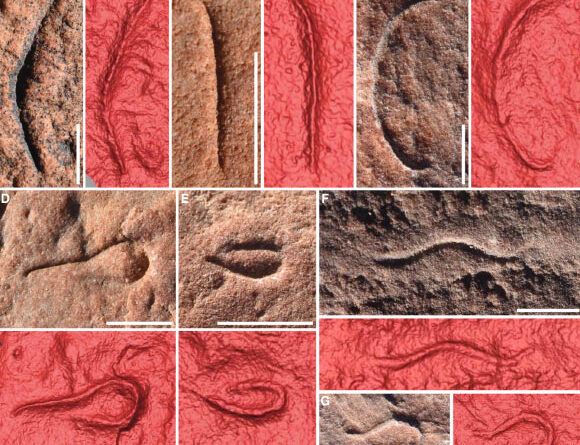
Digital pictures and 3D laser scans of Uncus dzaugisi body fossils. Scale bars– 10 mm. Image credit: Hughes et aldoi: 10.1016/ j.cub.2024.10.030.
Ecdysozoa is the biggest and most species-rich animal group in the world, including majority of all animals.
Identified by their cuticle– a hard external skeleton that is regularly shed– the group makes up 3 subgroups: nematodes, which are tiny worms; arthropods, that include bugs, spiders, and shellfishes; and scalidophora, a diverse group of little, flaky marine animals.
“Like numerous modern-day animal groups, ecdysozoans prevailed in the Cambrian fossil record and we can see proof of all 3 subgroups right at the start of this duration, about 540 million years earlier,” stated Ian Hughes, a college student in marine biology at Harvard University.
“We understand they didn’t simply appear out of no place, therefore the forefathers of all ecdysozoans should have existed throughout the preceding Ediacaran duration (635-539 million years ago).”
“DNA-based analyses, utilized to anticipate the age of animal groups by comparing them with their closest living family members, have actually supported this hypothesis.”
“Yet ecdysozoan fossil animals have actually stayed concealed amongst ratings of animal fossils paleontologists have actually found from the Ediacaran duration.”
The newly-described Ediacaran ecdysozoan, Uncus dzaugisiwas simply a couple of centimeters in length.
An assemblage of 82 Uncus dzaugisi specimens was discovered in the Nilpena Ediacara National Park in South Australia.
“Nilpena is possibly the very best fossil website for comprehending early animal development worldwide since the fossils take place throughout a duration of increased variety and we have the ability to excavate comprehensive layers of rock that protect these photos,” stated Florida State University’s Dr. Scott Evans.
“The layer where we discovered Uncus dzaugisi is especially interesting due to the fact that the sediment grains are so little that we truly see all the information of the fossils maintained there.”
“We were delighted to discover proof of what researchers had actually long anticipated– that ecdysozoans existed in the Ediacaran duration,” Hughes stated.
“It’s likewise actually crucial for our understanding of what these early animal groups would have appeared like and their way of life, particularly as the ecdysozoans would actually concern control the marine environment in the Cambrian.”
The discovery is reported in a paper in the journal Existing Biology
_____
Ian V. Hughes et alAn Ediacaran bilaterian with an ecdysozoan affinity from South Australia. Existing Biologyreleased online November 18, 2024; doi: 10.1016/ j.cub.2024.10.030
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.