(Image credit: simon2579 through Getty Images)
Research study has long pointed to a link in between bad gum health and a greater threat of heart disease– and now, a brand-new trial recommends that dealing with serious gum illness might minimize the constricting of a significant artery in time in otherwise healthy individuals.
Likely by minimizing swellingthis regular oral health treatment might be an unrecognized method of decreasing decreases in capillary working.
“I was very overwhelmed when I looked at the data the first time,” research study co-author Dr. Marco Orlandia medical research study periodontist at University College London, informed Live Science.
Around 40 % of U.S. grownups ages 30 and older have some level of gum illness, called periodontitisa persistent inflammatory condition whose development results in unsteady teeth, missing teeth and consistent foul breath. As the illness aggravates, little pockets around the teeth that can not be reached by a tooth brush or floss broaden and fill with plaque and germs.
There is now an abundance of research study connecting periodontitis to a greater danger of different health results, consisting of Alzheimer’s illness colon cancer and rheumatoid arthritisA crucial location with installing proof is the association in between extreme gum illness and heart diseasewith previous research studies discovering that the management of gum illness is connected to enhanced capillary function.
Now, a medical trial released Aug. 19 in the European Heart Journal has actually discovered that dealing with periodontitis slows the thickening of the inner 2 layers of the carotid arteries, discovered on each side of the neck, in otherwise healthy grownups. The density of those artery walls is a crucial marker for heart disease threat
Related: Keratin drawn out from sheep’s wool repair work teeth in development
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
By targeting swelling instead of other artery health elements, like cholesterol, “the impact of what we are doing comes without going through the classic risk pathway” for heart disease, Orlandi stated.
To evaluate whether dealing with periodontitis in fact triggers the carotid arteries to thicken less in time, Orlandi and his group of periodontists and cardiologists performed a gold-standard trial at an oral medical facility in main London. The trial was randomized, implying individuals were arbitrarily positioned in a treatment group or a contrast group that didn’t get the extensive gum treatment.
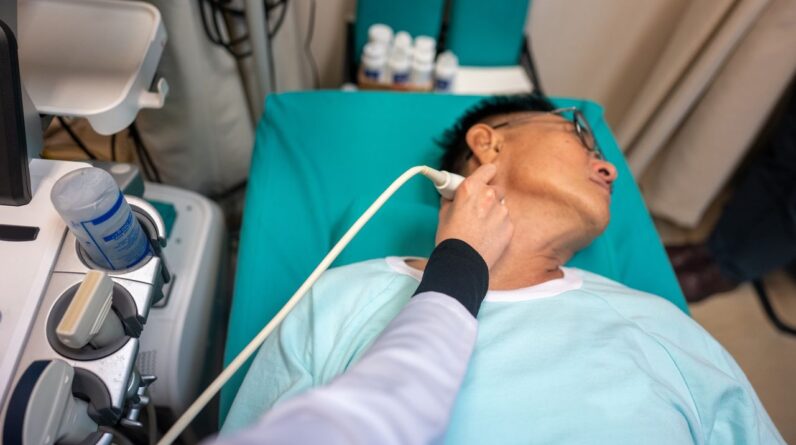
An ultrasound screen revealing the 2D picture of the typical carotid sector. The main black location is the channel within the carotid capillary, and the more specified layers on each side of this main channel are the artery walls. The periphery of the image reveals the soft tissues surrounding the artery. (Image credit: Marco Orlandi)The scientists took ultrasounds of the carotid arteries of 135 individuals with extreme periodontitis, to develop a standard level of density. They likewise determined just how much the arteries dilated when blood circulation increased– a step of capillary operating– and took blood samples to identify markers of inflammatory and oxidative tensionAll of the people were healthy besides having gum illness.
Next, the individuals were arbitrarily divided into either the treatment group or the control group. Care was required to guarantee there was an approximately even divided in between the 2 groups in regards to the individuals’ periodontitis seriousness, smoking cigarettes status and household history of heart disease.
In the treatment group, clients got extensive periodontitis treatment: a comprehensive tidy of the entire mouth and a deep tidy listed below the gumline to get rid of plaque and tartar. The control group got a basic scale and polish, more similar to a routine oral cleansing that does not consist of a deep tidy of the gums.
The individuals were then followed for 2 years, and they each got even more oral treatments at routine periods throughout that time. The scientists likewise reassessed the carotid artery at the 1 year and two-year marks, and took blood samples and determined blood-vessel function at 5 time points.
They discovered that the density of the carotid arteries’ inner linings was lower for people who got extensive treatment than for those in the control group. This distinction was “comparable to what has been seen with lifestyle interventions and some pharmacological agents in similar populations,” research study co-author Dr. Francesco D’Aiutoa medical research study periodontist at University College London, informed Live Science in an e-mail.
The cured clients likewise had much better capillary function and lower levels of inflammatory and oxidative tension markers in their blood, which are understood to add to the constricting of artery walls– a condition called atherosclerosis
Lots of elements drive atherosclerosis, “our results reinforce the view that untreated periodontitis is a modifiable risk factor for vascular ageing and possibly cardiovascular events,” D’Aiuto stated.
An essential constraint of the research study is that it was performed in just one area, so there is an opportunity that the findings partially come down to peculiarities of the area or the individuals in the sample, Orlandi stated.
Another restriction, stated Dr. Maurizio Tonettia scientific and research study periodontist at the University of Hong Kong who was not associated with the research study, is that all of the individuals in the trial were healthy besides having periodontitis. These outcomes must not be analyzed as proof that if somebody with atherosclerosis has their gum illness dealt with, the health of their arteries will enhance, he informed Live Science.
However, the findings “are bringing the concept of these [intensive gum disease] interventions into the preservation of wellness,” Tonetti stated.
“For many, many years, dentists have been focusing on the teeth, forgetting the rest of the body, and physicians have been focusing on the body, forgetting that there are teeth,” he stated. “They are really two worlds that have been separated and need to go back together for the benefit of patients.”
This short article is for informative functions just and is not suggested to provide medical recommendations.
Sophie is a U.K.-based personnel author at Live Science. She covers a vast array of subjects, having actually formerly reported on research study covering from bonobo interaction to the very first water in deep space. Her work has actually likewise appeared in outlets consisting of New Scientist, The Observer and BBC Wildlife, and she was shortlisted for the Association of British Science Writers’ 2025 “Newcomer of the Year” award for her freelance work at New Scientist. Before ending up being a science reporter, she finished a doctorate in evolutionary sociology from the University of Oxford, where she invested 4 years taking a look at why some chimps are much better at utilizing tools than others.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.