(Image credit: Tim Platt through Getty Images )
Unlike human beings, frogs and other amphibians do not require to depend on their lungs to breathe; their special skin assists them exchange oxygen and beverage. How do frogs breathe and consume through their skin?
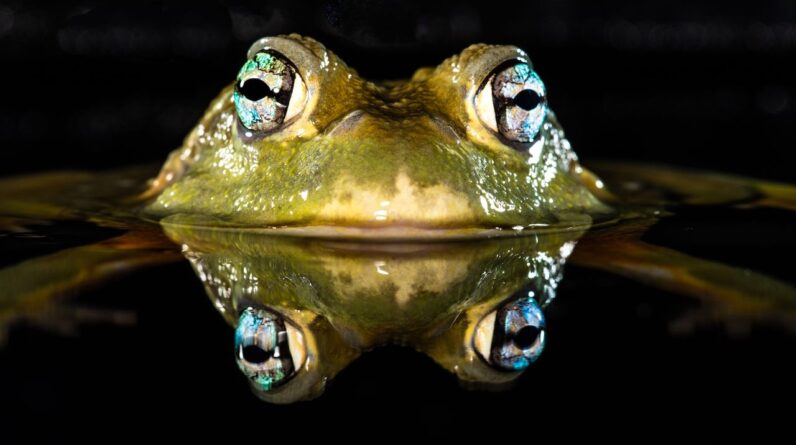
Frog skin is complex: It’s thin, covered in glands that produce mucous to keep the skin moist, and permeable sufficient to enable air particles to penetrate.
“[Their skin] is designed to allow both oxygen to get into the skin, and water to be absorbed,” Christopher Raxworthya manager and herpetologist at the American Museum of Natural History in New York, informed Live Science.
A network of little capillary best beneath the skin soaks up oxygen straight from water or the air, and likewise permits co2 to be eliminated of the body in a procedure called cutaneous respiration, discussed Kurt Schwenkan evolutionary biologist at the University of Connecticut who has actually studied the breathing systems of frogs and tadpoles. “It’s really almost identical to a lung system,” Raxworthy included.
Frogs can likewise breathe through their lungs and the lining of their mouth, cutaneous respiration enables frogs to endure undersea and through long hibernations. “Almost without trying, just having skin that’s moist, and having some blood vessels in it, they’re going to exchange gas and water through their skin, whether they like it or not,” Schwenk stated, although not all frogs depend upon cutaneous respiration similarly.
Tadpoles do not have actually established gills yet, so they require to breathe in air from the surface area to endure. When they’re hatchlings, they’re too little to break water’s surface area stress. Rather, they develop their own air bubbles. In a 2020 research studySchwenk and his coworker observed the tadpoles swim right listed below the surface area, where they rapidly absorb air, forming a bubble. They press the air bubble into their lungs.
Related: Can turtles truly breathe through their butts?
Frogs’ permeable skin is likewise how they consume. “That water is getting into all those spaces in the skin, and is then being absorbed across cell membranes into cells and into the bloodstream,” Schwenk included. Numerous frogs even have an extremely vascularized location on their skin called a “drinking patch,” through which they can soak up a big quantity of water.
Some frogs discovered in dry locations– like the trilling frog and the water-holding frogs residing in Australian deserts — are specifically proficient at taking in water throughout rainy seasons. “They store it, and then they go into burrows, into the ground, and sometimes they might even put an extra layer of mucus around them, and then they can survive on that water that they stored internally for months or even years until the next rains come,” Raxworthy discussed.
A West African bullfrog, immersed in shallow water, can utilize its skin to both breathe and consume. (Image credit: Brian Mckay by means of Getty Images)
It’s a helpful tool, their skin’s permeability likewise suggests frogs and other amphibians are specifically susceptible to toxins and environment modificationSchwenk stated. Research studies have actually revealed that the permeability of frog skin regularly exposes the animals to industrial chemical items and microplasticsAnd since frogs require to keep their skin moist to endure, the increased dry spells and warmer weather condition researchers forecast from environment modification might diminish frog environments, specifically in the Amazon jungle and the Atlantic rain forest in Brazil, Argentina and Paraguay.
“Amphibians tend to be some of the first groups that you start seeing declining or disappearing, and that usually is an indication of a problem within the environment,” Raxworthy stated. Losing frogs, in turn, modifications the balance of a community since of their position on the food cycle: They keep insect populations under control and are victim for snakes and birds.
Time will inform if some frog types will adjust to an altering environment. “A question that runs through all climate change biology is whether any particular species is subject to climate change, which is all of us, can adapt fast enough,” Schwenk stated. “In most cases, climate change is happening much faster than animals can adapt.”
Animal test: Test yourself on these enjoyable animal trivia concerns
Sara Hashemi is a reporter and fact-checker covering ecological justice, environment and the crossway in between science and society. Her work has actually appeared in Sierra, Smithsonian Magazine, Maisonneuve and more. She has a master’s degree in science journalism from NYU.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.