19459003]fetchpriority=”high” data-component-name=”Image”>
19459003]fetchpriority=”high” data-component-name=”Image”>
(Image credit: buradaki by means of Getty Images )
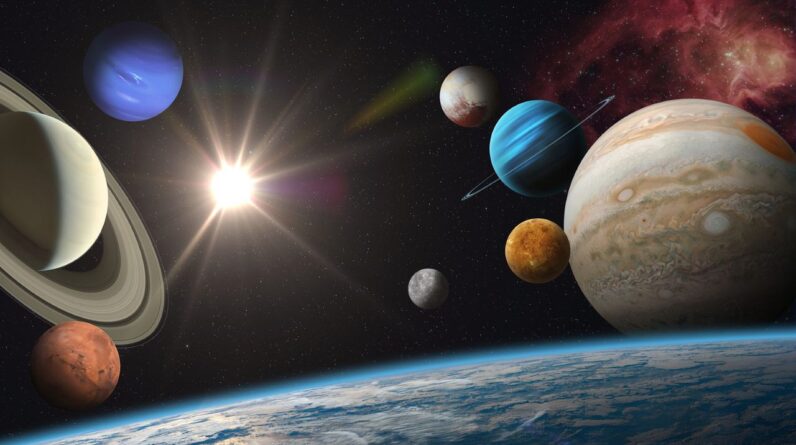
Worlds go through various life phases: They form, progress and ultimately satisfy an end. The timelines for these procedures vary extensively in between Earth-like worlds and worlds that orbit less-powerful stars.
How long do most worlds last?[
Register for our newsletter
(Image credit: Marilyn Perkins/ Future)
Register for our weekly Life’s Little Mysteries newsletter to get the current secrets before they appear online.
“Planets start off as microscopic dust grains in disks orbiting young stars, and eventually grow by a huge amount through a series of collisions,” Sean Raymondan astrophysicist at the University of Bordeaux in France, informed Live Science in an e-mail.
Gas giants, like Jupiter and Saturn, begin as enormous rocky and icy cores, and after that record gas from the disk to end up being giants. Rocky worlds like Earth go through a late stage of huge crashes with other growing worlds and smaller sized things after the gas disk from the sun had actually dissipated, Raymond stated. There is still some argument amongst researchers about the order in which worlds formed.
Specifying the “end” of a world, nevertheless, is more complex. “You could say a planet lasts until it’s destroyed,” Matthew Reinholda planetary researcher at Stanford University, informed Live Science. Or, you might specify a world’s ending to be when it no longer runs under the exact same conditions. “You could say, ‘This was a world that had these conditions at some point, but now it has changed and has these very different conditions,” Reinhold stated. “Because I prefer those previous conditions; I consider this planet as having ended.'”
Let’s take Earth as an example. Like lots of others, our world’s life expectancy is connected to the development of the sunThe sun presently develops heat and light through nuclear blend at its core– a procedure in which hydrogen changes into helium. In about 5 billion yearsthe sun will lack hydrogen, at which point it will broaden into a red giant and ultimately collapse into itself.
An illustration of Proxima b, a dim red dwarf that is the closest star to the sun. Worlds that orbit red dwarf stars tend to have long lives.
(Image credit: MARK GARLICK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY by means of Getty Images)”Our Earth will ‘die’ in multiple ways,” Raymond stated. “First, the slowly-brightening Sun will make conditions on the Earth unlivable by vaporizing the oceans. Then, Earth may be swallowed by the Sun when it becomes a red giant. Finally, Earth (if it’s still around) will be tossed into interstellar space.”
According to these computations, Earth’s overall life expectancy will have to do with 9.5 billion years.
Earth most likely will not live as long as the majority of worlds, he kept in mind. That’s because, unlike the sunwhich is a yellow dwarf star most stars are red overshadows that are smaller sized and cooler than our sun, and they burn fuel a lot more gradually. “They can last for trillions of years,” Reinhold stated.
Because case, it may not be the death of the star, however rather an internal procedure that causes these worlds’ death.
In his work, Reinhold has actually designed what may take place to a theoretical habitable world orbiting a red dwarf star. Active geology, such as plate tectonics, is thought about important for habitability since it permits nutrients to move in between the world’s mantle and surface area and drives the carbon-silicate cycle.
“We want a planet that can stabilize its climate,” Reinhold stated, and the carbon-silicate cycle is Earth’s natural thermostat.
Reinhold discovered that mantle convection will last someplace in between 30 billion and 90 billion years, while mantle melting may last someplace in between 16 billion and 23 billion years. These number varieties are too big to be significant, Reinhold stated, they recommend that any Earth-like worlds orbiting a red dwarf will pass away of an internal procedure long before their stars get close to the ends of their lives. And even on the quickest timelines, many rocky worlds orbiting red overshadows will keep their conditions for billions of years.
Larger stars have much shorter life-spans, due to the fact that they consume their nuclear fuel quicker. The fate of an inner world orbiting an A-type white star, for circumstances, would be connected up to the star’s life expectancy of 100 million to 1 billion years.
It’s likewise possible for gas giants to lose their environments due to the extreme light from their star, Reinhold stated, ending up being rocky worlds. This procedure depends upon how close a world is to its star, just how much energetic radiation the star discharges, and how strong a world’s gravity is. “The stronger their gravity, the better they are at holding onto their atmospheres, and the more radiation they get from their star, the more intense the stripping power,” Reinhold discussed. Depending upon those aspects, this can take anywhere from millions to billions of years.
Completion of deep spaceEven when a world’s conditions alter gradually, the rock itself still exists. Over big timescales, there are various possibilities for its fate as the possibility of uncommon occasions boosts. It might hit another world, or be tossed out of its orbit.
“In all of this mayhem over quadrillions of years, the planets that have been kicked away from their stars will be kicked out of the galaxy to wander for eternity in the void,” Reinhold stated. “What actually seals [its] fate really comes down to the nature of the end of the universe,” stated Reinhold.
Planetary system test: How well do you understand our cosmic community?
Sara Hashemi is a reporter and fact-checker covering ecological justice, environment and the crossway in between science and society. Her work has actually appeared in Sierra, Smithsonian Magazine, Maisonneuve and more. She has a master’s degree in science journalism from NYU.
You need to validate your show and tell name before commenting
Please logout and after that login once again, you will then be triggered to enter your screen name.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.