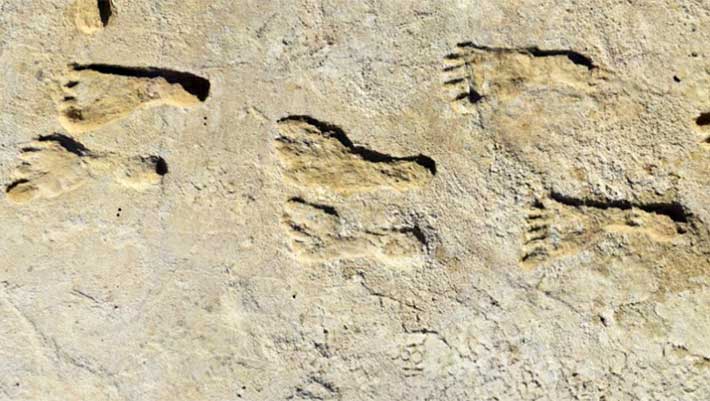
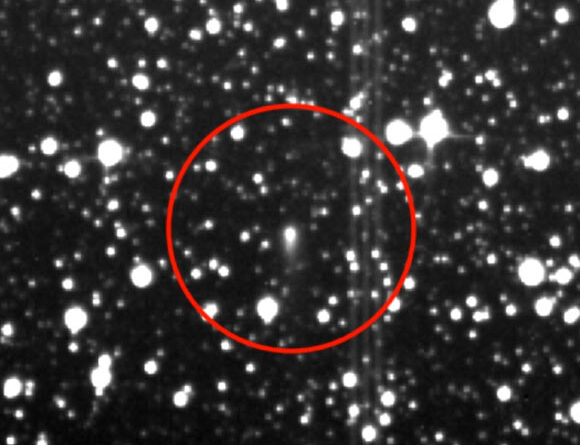
Discovery of human footprints at White Sands, New Mexico, dated to in between 21,000 and 23,000 years earlier, was a significant action in comprehending the preliminary peopling of the Americas, however that work was met criticism concentrated on the dependability of the products utilized in the radiocarbon dating: seeds of the typical water plant Ruppia cirrhosa and conifer pollen grains. A brand-new research study led by University of Arizona scientist Vance Holliday marks the 3rd kind of product– ancient mud in paleolake Otero– utilized to date the footprints, and reveals that the mud is in between 20,700 and 22,400 years of ages.
The ancient human footprints discovered at White Sands National Park in New Mexico, the United States. Image credit: Bennett et aldoi: 10.1126/ science.abg7586.
Generally, researchers thought that people gotten here in North America around 16,000 to 13,000 years earlier.
The footprints at White Sands revealed human activity in the location took place in between 23,000 and 21,000 years back– a timeline that would overthrow our understanding of when cultures established in North America.
It would make the prints about 10,000 years older than stays discovered 90 years earlier at a website near Clovis, New Mexico, which provided its name to an artifact assemblage long comprehended by archaeologists to represent the earliest recognized culture in North America.
Critics have actually invested the last 4 years questioning the 2 previous research studies, mainly arguing that the ancient seeds and pollen in the soil utilized to date the footprints were undependable markers.
“It’s an extremely constant record. You specify where it’s actually tough to discuss all this away,” Dr. Holliday stated.
“As I state in the paper, it would be serendipity in the severe to have all these dates offering you a constant image that’s in mistake.”
Millennia back, White Sands was a series of lakes that ultimately dried up.
Wind disintegration stacked the plaster into the dunes that specify the location today.
The footprints were excavated in the beds of a stream that streamed into one such ancient lake.
“The wind disintegration damaged part of the story, so that part is simply gone. The rest is buried under the world’s greatest stack of plaster sand,” Dr. Holliday stated.
For the most recent research study, Dr. Holliday and coworkers went back to White Sands in 2022 and 2023 and dug a brand-new series of trenches for a better take a look at the geology of the lake beds.
“It’s an odd sensation when you head out there and take a look at the footprints and see them personally,” stated Jason Windingstad, a doctoral prospect at the University of Arizona.
“You recognize that it essentially opposes whatever that you’ve been taught about the peopling of North America.”
The authors acknowledge that their research study does not resolve a concern they spoke with critics considering that 2021: Why exist no indications of artifacts or settlements left by those who made the footprints?
“It’s a reasonable concern. A few of the footprints discovered for the 2021 research study belonged to trackways that would have taken simply a couple of seconds to stroll,” they stated.
“It’s completely affordable to presume that hunter-gatherers would beware not to leave any resources in such a brief time frame.”
“These individuals live by their artifacts, and they were far from where they can get replacement product.”
“They’re not simply arbitrarily dropping artifacts. It’s not rational to me that you’re visiting a particles field.”
The group’s brand-new outcomes appear in the journal Science Advances
_____
Vance T. Holliday et al2025. Paleolake geochronology supports Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) age for human tracks at White Sands, New Mexico. Science Advances 11 (25 ); doi: 10.1126/ sciadv.adv4951
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.