the brain, to find out more about how the organ types in the womb.
(Image credit: Yu, D., Jain, S., Wangzhou, A. et al. Nature (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09362-8)
Immune cells in the human brain might be crucial to managing the organ’s advancement in the womb since they activate a significant boost in an essential kind of afferent neuron, brand-new research study recommends.
Price quotes recommend that these essential cells, referred to as repressive interneurons, comprise some 25 % to 50 % of the nerve cells in the adult cortex, the old and wrinkly tissue that covers the surface area of the brain. The human cortex brings more than double the variety of interneurons as the mouse cortex does.
These interneurons pass on signals in between other brain cells and assist keep that signaling in talk to a chemical messenger called GABAAs the brain’s primary “inhibitory” messenger, GABA assists reject brain activity by making nerve cells less most likely to fire, hence canceling the “excitatory” signals that enhance brain activity. Numerous conditions have actually been connected to issues with interneurons, consisting of epilepsy autism and schizophrenia
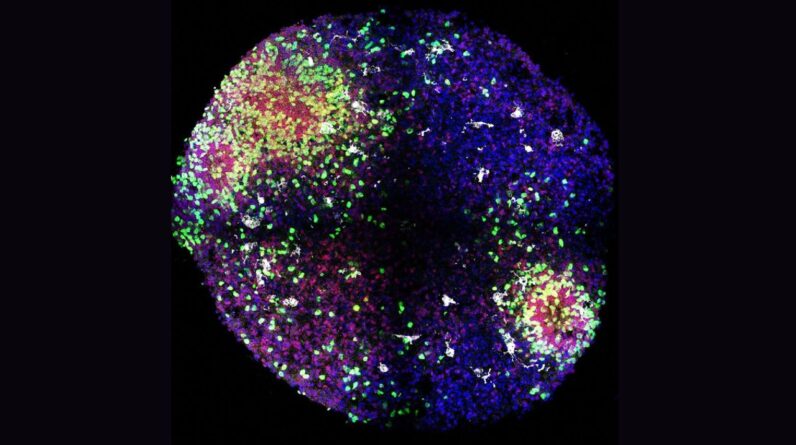
This figure reveals examples of organoids grown by the scientists, where in the center column you can see that IGF1 drives cells to multiply. (Image credit: Yu, D., Jain, S., Wangzhou, A. et al. Nature (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09362-8)
Aug. 6 in the journal Naturescientists have actually discovered a force that drives interneurons to increase in the establishing human brain– and they state it might be distinct to our types.
“That’s why we cannot use traditional animal models,” research study co-author Diankun Yuan assistant scientist in pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco( UCSF), informed Live Science. To reveal this system that might unfold just in the human brain, the scientists established an organoid — a mini 3D structure, grown from stem cells, that simulates a full-size structure discovered in the body.
Prior to the organoid research study, research study in laboratory animals recommended a link in between the activation of the maternal body immune system throughout pregnancy and a lower variety of interneurons in the cortices of their offspring, compared to offspring that didn’t experience an immune upset. That kind of activation may take place in reaction to a viral or bacterial infection. The research study authors explored this in previous research study with laboratory micein which they determined a crucial gamer behind the link: microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells.
Related: In a 1st, researchers integrate AI with a ‘minibrain’to make hybrid computer system
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
In the previous 5 years, researchers have actually started to acknowledge how the body immune system and nerve system establish in parallel, research study co-author Dr. Xianhua Piaoa physician-scientist who concentrates on neonatology and developmental neuroscience at UCSF, informed Live Science.
“The microglia really fine-tune and regulate nervous development,” she stated of the brand-new research study’s findings. “It really adds a new dimension as to how microglia exert their function.”
The group developed on previous work from other research study groups to establish their organoids, which looked like an essential structure in the fetal brain from which numerous cortical interneurons occurThis structure is short-lived, appearing around the 8th week of pregnancy in people and vanishing about 8 months after birth, Piao stated. The scientists discovered a method to include microglia into this design, which had not been done previously, she included.
The group discovered that the microglia in their organoids were a crucial source of insulin-like development element 1 (IGF1) in the establishing minibrains which the compound assisted to drive the remarkable boost in interneurons seen in early advancement.
When the group checked what would occur when they shut off IGF1 signaling in different methods, they discovered that it obstructed the fast boost in interneurons. “when we deleted this gene in microglia in the mouse model, we did not see any change,” Piao stated. That recommends that this chain of occasions began by microglia-made IGF1 might be distinct to human beings.
“These findings indicate an evolutionary adaptation of microglial function to support the increased demand for interneurons in the human cortex,” the scientists composed in their report. In other words, this finding mean a function of human development that may assist to discuss our distinct cognitive capabilities.
That stated, organoids aren’t precise reproductions of the human brain, so there’s a limitation to what the 3D designs can inform us. “So far the model is good enough for especially the proliferation stage, very early stage” of advancement, Yu stated. Presently, these organoids do not do as well with later phases of brain advancement, he kept in mind. They likewise do not record circuit-level activity in the brain, Piao stated, revealing only activity within smaller sized, separated structures.
Future work might assist to more clarify this formerly unidentified function of immune cells in the brain, she stated.
Nicoletta Lanese is the health channel editor at Live Science and was formerly a news editor and personnel author at the website. She holds a graduate certificate in science interaction from UC Santa Cruz and degrees in neuroscience and dance from the University of Florida. Her work has actually appeared in The Scientist, Science News, the Mercury News, Mongabay and Stanford Medicine Magazine, to name a few outlets. Based in NYC, she likewise stays greatly associated with dance and carries out in regional choreographers’ work.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.