 >
>
(Image credit: Helen Farr and Erich Fisher)
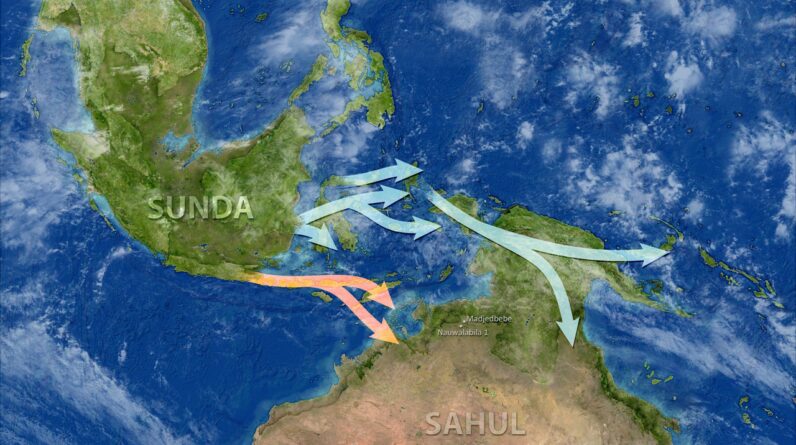
A brand-new research study of almost 2,500 genomes might have lastly settled the dispute about when contemporary human beings shown up in Australia. Utilizing a varied database of DNA from ancient and modern Aboriginal individuals throughout Oceania, scientists have actually identified that individuals started to settle northern Australia by 60,000 years back which they got here by means of 2 unique paths.
Professionals have actually long disputed the date that people very first gotten here in Australiaan accomplishment that needed the development of boat. While some scientists have actually utilized hereditary designs to support a “short chronology” of 47,000 to 51,000 years ago for the arrival, others have actually marshaled historical proof and Aboriginal understanding in assistance of the “long chronology,” in which the very first arrivals occurred 60,000 to 65,000 years back.
“This is the most comprehensive genetic study to date addressing this question, and it lends strong support to the long chronology rather than the short chronology,” research study co-author Martin Richardsan archaeogeneticist at the University of Huddersfield in the U.K., informed Live Science in an e-mail.
The group’s analysis likewise exposed 2 unique sets of individuals getting here through northern and southern paths. “This conclusion fits very well with the archaeological and oceanographic/paleoclimate evidence for an entry into Sahul at around 60,000 years ago,” Richards stated.
To reach their conclusions, the scientists utilized a molecular clock method, which presumes that anomalies in DNA series take place at a relatively continuous rate gradually. By taking a look at the distinctions in 2 DNA series, scientists can approximate when those series diverged from one another.
In the research study, the research study group utilized a number of analytical approaches to evaluate mitochondrial DNA (which is given through the mom’s line) and Y-chromosome information (which is given through the dad’s line). All of their analytical designs associated a date of about 60,000 years ago for the settlement of northern Australia.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
The hereditary information likewise exposed 2 unique settlements around the very same time. One group of individuals shown up in Australia by means of southern Sunda (the Indonesian islands), while another originated from northern Sunda (the Philippine island chain).
The 2 groups were at first part of the exact same population that vacated Africa around 70,000 to 80,000 years earlier, Richards stated, and “we think they split during the dispersal east, in South Asia or Southeast Asia,” potentially 10,000 to 20,000 years before they reached Australia.
“Our results indicate that Aboriginal Australians along with New Guineans have the most ancient unbroken ancestry of any group of people outside of Africa,” Richards stated.
Along the method, these early human leaders most likely interbred with antiquated human beings such as Homo longi H. luzonensis and even “the hobbit” H. floresiensisaccording to Richards, however it is presently uncertain to what level modern-day human beings communicated with antiquated individuals in the area.
Adam Brumman archaeologist at Griffith University in Australia who was not associated with the research study, informed Live Science in an e-mail that the research study supports the concept that early human motions had an important function in the preliminary peopling of Sahul. “I would put my money, if I had any, on the ‘long chronology’ model,” Brumm stated.
This hereditary research study has extensive ramifications for the antiquity of Aboriginal individuals in Australia. “Many Aboriginals believe they have always been in Country,” research study co-author Helen Farran archaeologist at the University of Southampton in the U.K., informed Live Science in an e-mail.
“This data supports a really deep heritage for these communities,” Farr stated, and “it tells of the close links people have had with Country and Sea Country for at least 60,000 years.” It likewise shows that seafaring understanding and abilities, which are not discovered in the historical record, were essential to early people’ survival.
Kristina Killgrove is a personnel author at Live Science with a concentrate on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her posts have actually likewise appeared in locations such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological sociology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, in addition to a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was previously a university teacher and scientist. She has actually gotten awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science composing.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







