White overshadows might provide open environments for life on worlds formed within or moved to their habitable zones, producing warmer surface area environments than those of worlds with main-sequence host stars, according to brand-new research study from the University of California, Irvine.
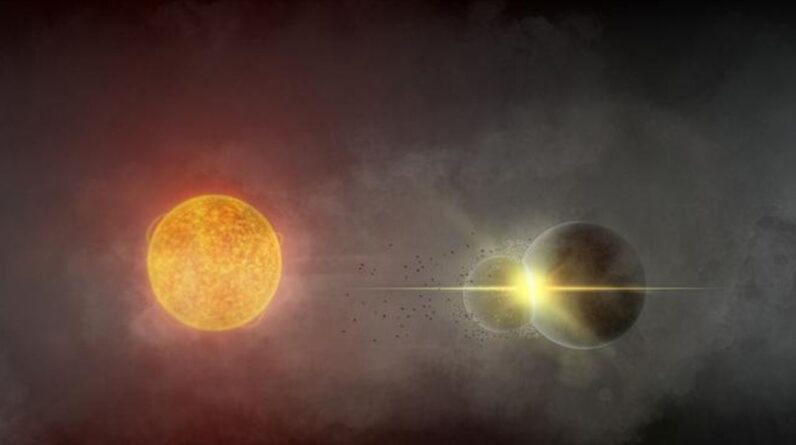
Exoplanets orbiting in the habitable zones of white overshadows might harbor more clement conditions for life to make up for the cooling and dimming of their host stars gradually. Image credit: David A. Aguilar/ CfA.
In the research study, University of California, Irvine astronomer Aomawa Shields and associates compared the environments of water worlds with an Earth-like climatic structure orbiting in the habitable zone of 2 various kinds of stars: a white dwarf and the main-sequence K-dwarf star Kepler-62.
Utilizing a 3D international environment computer system design usually utilized to study Earth’s environment, they discovered that the white dwarf exoplanet was much warmer than the Kepler-62 exoplanet regardless of comparable excellent energy circulation.
“While white dwarf stars might still emit some heat from recurring nuclear activity in their external layers, they no longer display nuclear combination at their cores,” Dr. Shields stated.
“For this factor, very little factor to consider has actually been offered to these stars’ capability to host habitable exoplanets.”
“Our computer system simulations recommend that if rocky worlds exist in their orbits, these worlds might have more habitable property on their surface areas than formerly believed.”
The white dwarf’s habitable zone is much closer to the star compared to that of other stars such as Kepler-62.
The authors worried that this leads to a much faster rotation duration– 10 hours– for the white dwarf exoplanet, while Kepler-62’s exoplanet has a 155-day rotation duration.
While both worlds would likely be locked into a concurrent orbit– with an irreversible dayside and a continuous nightside– the ultrafast white dwarf world’s rotation extends the cloud blood circulation around the world.
The much slower, 155-day orbital duration of the Kepler-62 world adds to a big, dayside, liquid water cloud mass.
“We anticipate concurrent rotation of an exoplanet in the habitable zone of a regular star like Kepler-62 to develop more cloud cover in the world’s dayside, showing inbound radiation far from the world’s surface area,” Dr. Shields stated.
“That’s generally an advantage for worlds orbiting near the inner edge of their stars’ habitable zones, where they might stand to cool down a bit instead of lose their oceans to area in a runaway greenhouse.”
“But for a world orbiting directly in the middle of the habitable zone, it’s not such an excellent concept.”
“The world orbiting Kepler-62 has a lot cloud cover that it cools down excessive, compromising valuable habitable area while doing so.”
“On the other hand, the world orbiting the white dwarf is turning so quickly that it never ever has time to develop almost as much cloud cover on its dayside, so it keeps more heat, which operates in its favor.”
Less dayside liquid clouds and a more powerful greenhouse impact on the nightside develop warmer conditions on the white dwarf world relative to the Kepler-62 world.
“These outcomes recommend that the white dwarf outstanding environment, as soon as considered unwelcoming to life, might provide brand-new opportunities for exoplanet and astrobiology scientists to pursue,” Dr. Shields stated.
“As effective observational abilities to examine exoplanet environments and astrobiology have actually begun line, such as those related to the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, we might be going into a brand-new stage in which we’re studying a completely brand-new class of worlds around formerly unconsidered stars.”
The research study was released in the Astrophysical Journal
_____
Aomawa L. Shields et al2025. Increased Surface Temperatures of Habitable White Dwarf Worlds Relative to Main-sequence Exoplanets. ApJ 979, 45; doi: 10.3847/ 1538-4357/ ad9827
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.