New orbital information expose that the most just recently active volcanic systems on Mars weren’t easy one-off blasts into area; rather, long-lived magmatic pipes underneath Pavonis Mons, among the Red Planet’s biggest volcanoes, improved lava circulations in time, with unique eruptive stages and progressing chemical signatures, providing fresh insights into the world’s inner characteristics and how rocky worlds develop and change their surface areas.
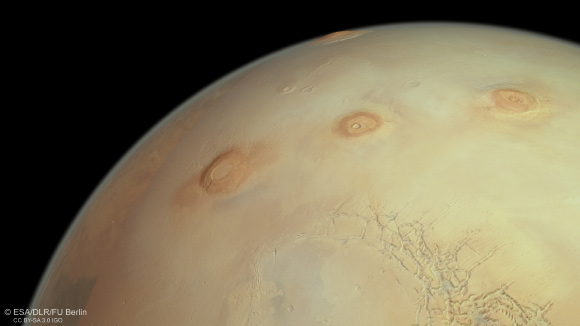
This viewpoint view from ESA’s Mars Express reveals 3 of Mars’notoriously gigantic volcanoes (from delegated right): Arsia, Pavonis and Ascraeus Mons. Image credit: ESA/ DLR/ FU Berlin.
What seems a single volcanic eruption is frequently the outcome of intricate procedures running deep underneath the surface area, where lava relocations, progresses, and modifications over extended periods of time.
To totally comprehend how volcanoes work, geoscientists study the volcanic items that appear at the surface area, which can expose the covert magmatic systems feeding volcanic activity.
Led by Adam Mickiewicz University scientist Bartosz Pieterek, the brand-new research study reveals that this intricacy likewise uses to Mars.
By integrating in-depth surface area mapping with orbital mineral information, the authors rebuilded the volcanic and magmatic development of the volcanic system south of Pavonis Mons in extraordinary information.
“Our outcomes reveal that even throughout Mars’ latest volcanic duration, lava systems below the surface area stayed active and complicated,” Dr. Pieterek stated.
“The volcano did not emerge simply when– it progressed gradually as conditions in the subsurface altered.”
The research study reveals that this volcanic system established through several eruptive stages, transitioning from early fissure-fed lava emplacement to later on point-source activity that produced cone-forming vent.
These lava streams appear various on the surface area, they were provided by the exact same underlying lava system.
Each eruptive stage protected an unique mineral signature, enabling the researchers to trace how the lava altered through time.
“These mineral distinctions inform us that the lava itself was progressing,” Dr. Pieterek stated.
“This most likely shows modifications in how deep the lava stemmed and the length of time it was kept underneath the surface area before emerging.”
“Because direct tasting of Martian volcanoes is presently not possible, research studies like this supply uncommon insight into the structure and advancement of the world’s interior.”
“The findings highlight how effective orbital observations can be in exposing the covert intricacy of volcanic systems– on Mars and on other rocky worlds.”
The outcomes were released on January 29, 2026 in the journal Geology
_____
Bartosz Pieterek et alSpectral proof for magmatic distinction within a Martian pipes system. Geologyreleased online January 29, 2026; doi: 10.1130/ G53969.1
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.