Planetary scientists at Southwest Research Institute has actually finished a research study detailing how a proposed spacecraft might zip an interstellar comet, supplying impressive insights into the residential or commercial properties of bodies coming from beyond our Solar System. Utilizing the current discovery of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, they confirmed the objective principle, figuring out that 3I/ATLAS might have been obstructed and observed by the proposed spacecraft.
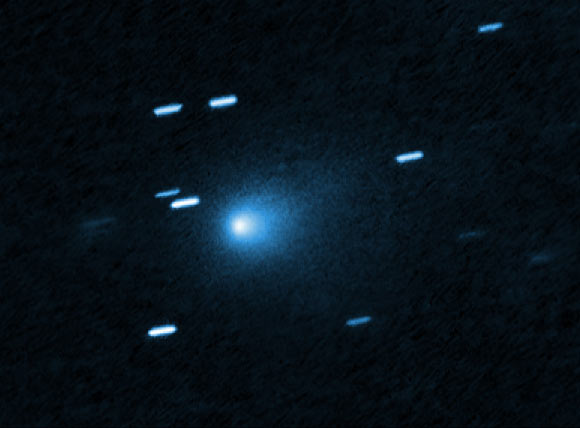
Hubble caught this picture of 3I/ATLAS on July 21, 2025, when the comet was 446 million km (277 million miles) from Earth. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ David Jewitt, UCLA/ Joseph DePasquale, STScI.
In 2017, the interstellar things 1I/’Oumuamua ended up being the very first interstellar comet found in the Solar System.
Its discovery was quickly followed by the discovery of the 2nd interstellar comet, 2I/Borisov in 2019, and now this year, 3I/ATLAS, that made around the world headings as it ended up being the 3rd formally acknowledged interstellar challenge cross into our Solar System.
“These brand-new type of things use mankind the very first possible chance to carefully check out bodies formed in other galaxy,” stated lead author Dr. Alan Stern, a planetary researcher at Southwest Research Institute.
“An interstellar comet flyby might provide extraordinary insights into the structure, structure and residential or commercial properties of these items, and it would substantially broaden our understanding of strong body development procedures in other galaxy.”
Researchers approximate that many interstellar items of extrasolar origin pass inside Earth’s orbit each year, which as lots of as 10,000 pass inside Neptune’s orbit in any given year.
Dr. Stern and associates dealt with the special style obstacles and specified the expenses and payload requirements related to an interstellar comet objective.
The hyperbolic trajectories and high speeds of these things prevent orbiting them with present innovation, however the research study revealed that flyby reconnaissance is possible and economical.
“The trajectory of 3I/ATLAS is within the interceptable series of the objective we developed, and the clinical observations made throughout such a flyby would be groundbreaking,” stated Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Matthew Freeman.
“The proposed objective would be a high-speed, head-on flyby that would gather a big quantity of important information and might likewise function as a design for future objectives to other interstellar comets.”
The authors developed the significant, extensive clinical goals for an objective to an interstellar comet.
Identifying the physical residential or commercial properties of the body would use insights to its development and development.
Taking a look at the interstellar comet structure might assist describe its origins and analyze how evolutionary forces have actually impacted the comet considering that its development.
Another goal is to completely examine the nature of the things’s coma, the getting away environment originating from its main body.
To establish objective trajectory alternatives, the scientists established software application that produced an agent, artificial population of interstellar comets then computed a minimum energy trajectory from Earth to the course of each comet.
The software application’s estimations revealed that a low-energy rendezvous trajectory is possible, and in a lot of cases, would need less launch and in-flight speed modification resources than numerous other planetary system objectives.
The researchers utilized this software application to compute the trajectory that the proposed spacecraft might have drawn from Earth to obstruct 3I/ATLAS.
They discovered that the objective might have reached 3I/ATLAS.
“The really motivating aspect of the look of 3I/ATLAS is that it even more reinforces the case that our research study for an interstellar comet objective made,” stated Dr. Mark Tapley, an orbital mechanics specialist at Southwest Research Institute.
“We showed that it does not take anything more difficult than the innovations and launch efficiency like objectives that NASA has actually currently flown to experience these interstellar comets.”
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.