(Image credit: Regione Siciliana)
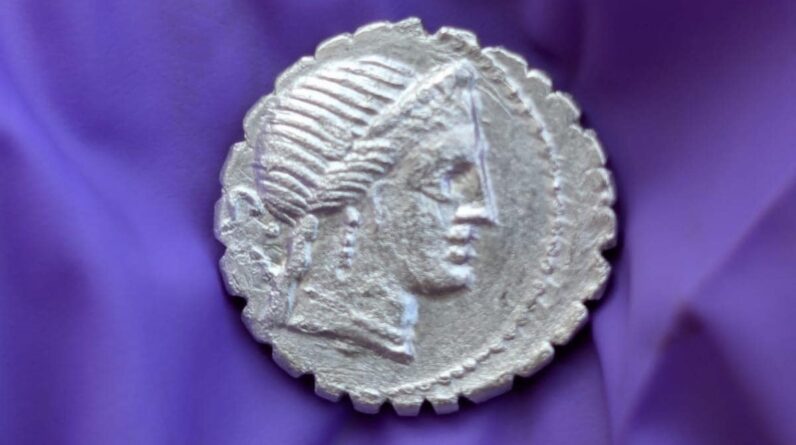
Archaeologists have actually found a chest of ancient silver coins “concealed in a hole in the wall” on a Mediterranean island near Sicily, perhaps throughout a pirate attack more than 2,000 years back.
The coins were minted in between 94 and 74 B.C. when the area was ruled by Rome, a republic at that time, according to a Sept. 2 Facebook post by Sicily’s local federal government. A few of the coins depict the profile of a human head, which has actually not yet been determined.
Archaeologists discovered the ancient chest of 27 coins while excavating the Acropolis of Santa Teresa and San Marco on the island of Pantelleria, about 70 miles (110 kilometers) southwest of Sicily, in the Sicilian Strait bounded by Sicily and Tunisia.
Parts of the ruins are even older than the coins and date from the Punic or Carthaginian duration, before the Punic Wars in between Carthage and Rome in the 3rd and 2nd centuries B.C.
Related: 1,600-year-old coin found in Channel Islands includes Roman emperor eliminated by getting into Goths
Ancient silver
The stash was found by a historical group led by Germany’s University of Tübingen, which has actually operated at the website for 25 years, according to an equated federal government declaration
The coins had actually been minted in Rome and were silver “denarii” the basic Roman coin for centuries, the declaration stated. At this time, a single denarius was comparable to about $20 — approximately a day’s spend for a soldier in the Roman legions.
A few of the coins were found after earth from the wall had actually escaped following rainy weather condition, and the rest were discovered under a stone. The stockpile was most likely concealed throughout among the regular pirate attacks at this time, University of Tübingen archaeologist Thomas Schäfer stated in the declaration.
Pirates plagued the eastern Mediterranean Sea and frequently robbed seaside settlements till their defeat in 67 B.C. in a project waged by the Roman basic Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus– Pompey the Great– who had actually increased to prominence as a henchman of the totalitarian Sulla.
Roman ruins
The chest of Roman coins was discovered near the place of the heads of 3 Roman statues that had actually been found at the website a couple of years previously, the declaration reported.
The marble heads depicted Julius Caesar; the Roman emperor Titus, who ruled from A.D. 79 to 81; and a lady who might have been either Agrippina the Elder (lived from 14 B.C. to A.D. 33), a granddaughter of Augustusthe very first emperor of the Roman Empire, or Antonia the Younger (lived from 36 B.C. to A.D. 37), a child of Mark Antony
Schäfer stated the Acropolis website on the island– called Cossyra or Cossura by the Romans– was unblemished by looters. It consisted of a “comitium or location of assembly, for the area’s “decurions” — a name provided to the chosen agents of an area, and likewise to Roman cavalry officers.
Just 5 such comitia had actually been found in all of Italy, and this one remained in the very best condition, he stated.
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.