(Image credit: Mattias Jakobsson(left)/ Lyla Jung( best))
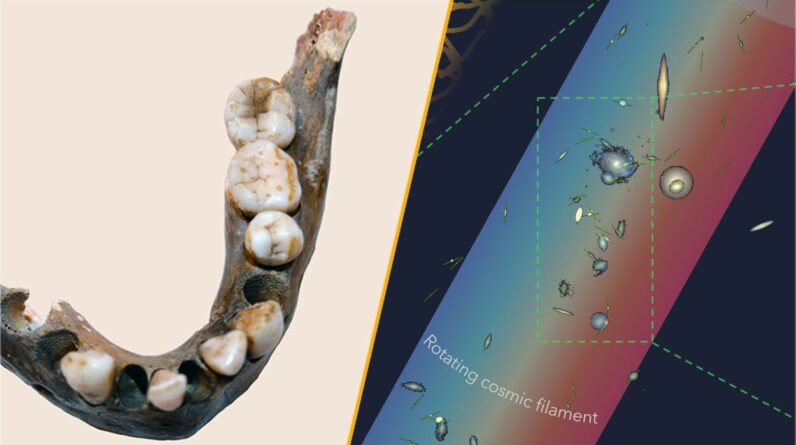
Today’s greatest science news took us to an area 140 million-light-years away, where researchers have actually found the biggest spinning item in the recognized universeThe massive turning filament is broader than the Milky Way and is connected to a daisy-chain of 14 galaxies, which is how astronomers discovered it. The filament is whirling at around 68 miles per 2nd(110 kilometers per second).
More detailed to home, scientists aimed to southern Africa, where a human population was genetically separated for 100,000 years
Our preferred interstellar visitor is emergingInterstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is emerging in ‘ice volcanoes’, brand-new images recommend
Comet 3I/ATLAS appears to have spiral jets shooting off its surface area, which might signify
“ice volcanoes.”
(Image credit: Josep M. Trigo-Rodríguez/ B06 Montseny Observatory)
The world has actually been interested by interstellar visitor comet 3I/ATLAS given that it zoomed into our awareness in July. Ever since, we’ve discovered lots about the cosmic trespasser, which is not an alien spacecraft.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Now scientists have actually trained their sights on the quick area rock utilizing the Joan Oró Telescope at the Montsec Observatory in northeastern Spain, and matched its observations with those made by other observatories in the area. The group observed that the comet warmed up and lightened up quickly as it approached the sun, which is a hint that ice is sublimating from its surface area. That would make 3I/ATLAS comparable to other things in our planetary system, such as the dwarf worlds that orbit beyond Neptune.
Discover more area news
— James Webb telescope areas odd ‘super-puff’ world anxiously chasing its own environment through area
— An additional planetary system world as soon as orbited beside Earth– and it might be the factor we have a moon
—Russia unintentionally damages its only working launch pad as astronauts take off to ISS
Life’s Little MysteriesDo your dreams alter as you age?
How do our dreams alter as we age? (Image credit: FreshSplash by means of Getty Images)
Dreaming is an almost universal human experience. There can be substantial variations in how brilliant, practical or remarkable various individuals’s dreams are. What about the dreams of the very same individual– do they alter as an individual ages
—If you enjoyed this, register for our Life’s Little Mysteries newsletter
Making water out of thin airMIT development utilizes ultrasound to shake drinking water out of the air, even in dry areas
Today, MIT engineers explained a method to extract water from air. (Image credit: Ikra Iftekhar(CC BY-NC-ND 3.0))
Scientists at MIT have actually discovered a method to draw the water out of the air and turn it into drinking water– and the procedure takes simply minutes. Previous evaporation water collecting systems cool damp air or utilize spongy products to soak up water vapor and condense it into beads. Previous variations generally depend on sunshine to power the evaporation, which can take hours or days and does not operate in dry areas.
The brand-new approach utilizes acoustic waves to shake the liquid from the sponges and is 45 times more effective than counting on evaporation alone, the scientists state. One difficulty of the brand-new gadget, nevertheless, is that it requires a source of power, however the scientists believe they can navigate this issue by matching their gadget with a solar battery.
Discover more innovation news
—When an AI algorithm is identified ‘female,’ individuals are most likely to exploit it
—New ‘physics faster way’ lets laptop computers take on quantum issues when scheduled for supercomputers and AI
In science news this week—Law of ‘optimum randomness’ describes how damaged things shatter in the most frustrating method possible
—Injecting anesthetic into a ‘lazy eye’ might fix it, early research study recommends
—Anacondas ended up being enormous 12 million years back– and it worked so well, they have not altered size given that
—Volcanic eruption set off ‘butterfly result’ that resulted in the Black Death, scientists discover
Beyond the headingsCould hunks of ancient rock prowling in Earth’s crust conceal huge, carbon-free helium tanks?
New discoveries of carbon-free helium tanks are transforming the market. (Image credit: Pulsar Helium)
Helium is utilized in MRI makers, superconductors and quantum computer systems– and there’s an enormous scarcity looming. Historically, helium was just discovered in small amounts together with gas, that made drawing out functional helium a substantial source of carbon emissions.
As Live Science personnel author Sascha Pare found, a handful of huge, extremely focused, carbon-free helium tanks have actually altered the geological photo.
Can that assist us discover other huge helium caches– and fix the helium scarcity?
Something for the weekendIf you’re searching for something a bit longer to check out over the weekend, here are a few of the very best interviews, viewpoint pieces and science histories released today.
—‘Intelligence comes at a rate, and for lots of types, the advantages simply aren’t worth it’: A neuroscientist’s take on how human intelligence progressed [Book extract]
—Your AI-generated picture of a feline riding a banana exists since of kids clawing through the dirt for harmful components. Is it truly worth it? [Opinion]
—Science history: Computer researcher sets out ‘Moore’s law,’ assisting chip style for a half century– Dec. 2, 1964 [Science history]
Science in movement18,000 dinosaur tracks found along ancient Bolivian shoreline– and they set a brand-new record
With the discovery, Carreras Pampa in Bolivia has actually turned into one of the premier dinosaur track websites worldwide.
(Image credit: Raúl Esperante)
While excavating in Bolivia’s Carreras Pampa tracksite, researchers discovered more than 18,000 fossilized dinosaur footprints and swim marks. The large path of ancient footprints covers a location of 80,570 square feet (7,485 square meters), and the large size of the location shows up in a video the scientists took of the website.Follow Live Science on social networksDesire more science news? Follow our Live Science WhatsApp Channel for the most recent discoveries as they take place. It’s the very best method to get our specialist reporting on the go, however if you do not utilize WhatsApp we’re likewise on Facebook X (previously Twitter) Flipboard Instagram TikTok Bluesky and LinkedIn
Tia is the editor-in-chief (premium) and was previously handling editor and senior author for Live Science. Her work has actually appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com, Science News and other outlets. She holds a master’s degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science composing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia belonged to a group at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that released the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won several awards, consisting of the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







