(Image credit: Mingzheng Wu/Rogers Research Group )
A brand-new brain-machine user interface(BMI) utilizes light to “speak” to the brain, mouse experiments reveal.
The minimally intrusive cordless gadget, which is put under the scalp, gets inputs in the type of light patterns, which are then communicated to genetically customized nerve cells in brain tissue.
In the brand-new research study, these nerve cells triggered as if they were reacting to sensory info from the mice’s eyes. The mice found out to match these various patterns of brain activity to carry out particular jobs– specifically, to discover the places of delicious treats in a series of laboratory experiments.The gadget marks an action towards a brand-new generation of BMIs that will can getting synthetic inputs– in this case, LED light– independent of normal sensory channels the brain counts on, such as the eyes. This would assist researchers construct gadgets that user interface with the brain, without needing tracking wires or large external parts.
“The technology is a very powerful tool for doing fundamental research,” and it might attend to human health obstacles in the longer term, stated John Rogersa bioelectronics scientist at Northwestern University and senior author of the research study, which was released Dec. 8 in the journal Nature Neuroscience
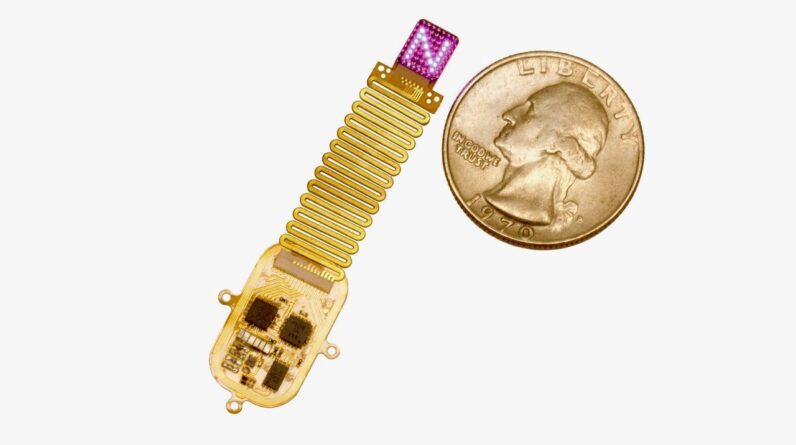
Bypassing the sensory systemThe gadget, which is smaller sized than a human forefinger, is soft and versatile, so it complies with the curvature of the skull. It consists of 64 small LEDs, an electronic circuit that powers the lights, and a receiver antenna. In addition, an external antenna manages the LEDs utilizing near-field-communications (NFC)– electro-magnetic fields for short-range interactions as is provided for contactless card payments.
The compact gadget is created to be put under the skin, instead of being implanted straight into the brain. “It projects light directly onto the brain [through the skull], and the response of the brain to that light is generated by a genetic modification in the neurons,” Rogers informed Live Science.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Brain cells do not typically react to light that is shone on them, so gene modifying is needed to make that take place.
“The genetic modification creates light-sensitive ion channels,” Rogers described. When triggered by light, these channels permit charged particles to stream into brain cells, tripping a signal that then gets sent out to other cells. “Through that mechanism, we create light sensitivity directly in the brain tissue itself,” he stated. The genetic engineering of the brain cells was done utilizing a viral vector, a safe infection made to provide the preferred hereditary tweak into particular cells in various areas of the brain.
Using light to manage the activity of genetically customized cells is called optogeneticsand it’s a reasonably brand-new science. In previous workthe scientists utilized a comparable method to trigger simply one group of brain cells, however the brand-new gadget allowed them to toggle the activity of numerous nerve cells throughout the brain.
“[The genetic modification] is not just stimulating the part of the brain that’s naturally responsible for visual perception, but across the entire surface of the cortex,” Rogers stated. Therefore, sending out various patterns of lighting develops a matching circulation of neural activity. “It’s like we can project a series of images — almost like play a movie — directly into the brain by controlling [the] sequence of patterns.”
The scientists evaluated the implant in the mice by wirelessly advising it to produce different patterned bursts of light. The mice were trained to react to each pattern with a particular habits, suggesting that they might compare the patterns transferred. With each kind of signal, they needed to go to a particular cavity in a wall, and for picking properly, they ‘d get sugar water as a benefit.
Bin Hea neuroengineering scientist at Carnegie Mellon University who wasn’t associated with the research study, called it an unique method for utilizing light to tune circuits throughout the brain. “It may have various applications in neuroscience research using animal models … and beyond,” he stated.
The scientists see possible for this gadget in future prosthetics. Applications might consist of adding feelings, like touch or pressure, to prosthetic limbs, or sending out visual or acoustic signals to vision or hearing prostheses.
“Optogenetic techniques are just beginning to be used with humans,” Rogers stated. “There are tremendous advantages [to using light] because you don’t need to disrupt the brain tissues. You can use different wavelengths of light to control different regions of the brain.”
Rogers stated that from an innovation perspective, the platform might scale to cover much bigger locations of the brain and include more micro-LEDs. They would have to reconsider the power-supply requirements to support a bigger gadget. It must technically operate in people as it carries out in mice, however even more research study will be required before any tests are tried in human beings.
“The biggest hurdle is around the regulatory approval for the genetic modification,” he stated.
Brain test: Test your understanding of the most complicated organ in the body
Payal Dhar (she/they) is a self-employed reporter, composing on science, innovation, and society. They cover AI, engineering, products science, cybersecurity, area, video games, online neighborhoods, and any glossy brand-new innovation that captures their eye. She has actually composed for Science News, Scientific American, Nature, Washington Post, Guardian, Chemical & & Engineering News, IEEE Spectrum, and others. They likewise compose science-fiction and fantasty. You can follow her @payaldhar. bluesky.social or read her work at payaldhar.contently.com.
You should validate your show and tell name before commenting
Please logout and after that login once again, you will then be triggered to enter your display screen name.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







