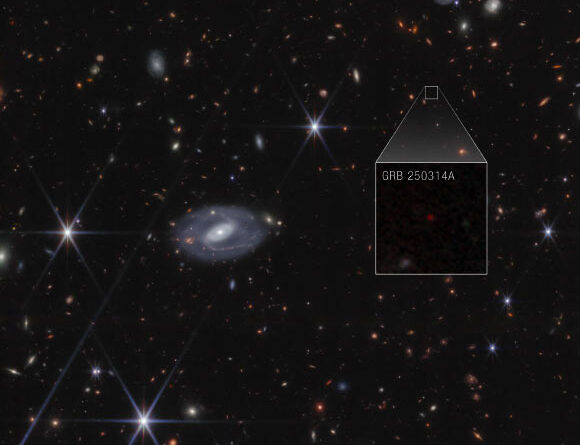
Astronomers utilizing the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have actually found a supernova surge accompanying the gamma-ray burst occasion GRB 250314A at a redshift of 7.3, when deep space was just 730 million years of ages. The previous chart-topping supernova occasion happened when deep space was 1.8 billion years of ages. The discovery is reported in 2 documents in the journal Astronomy & & Astrophysics
Webb recognized the source of an incredibly brilliant flash of light referred to as a gamma-ray burst: a supernova that blew up when deep space was just 730 million years of ages. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ CSA/ STScI/ A. Levan, IMAPP/ A. Pagan, STScI.
” Only Webb might straight reveal that this light is from a supernova– a collapsing enormous star,” stated Dr. Andrew Levan, an astronomer at Radboud University and the University of Warwick, and lead author of among the 2 documents.
“This observation likewise shows that we can utilize Webb to discover private stars when deep space was just 5% of its present age.”
While a gamma-ray burst generally lasts for seconds to minutes, a supernova quickly lightens up over a number of weeks before it gradually dims.
On the other hand, the supernova related to GRB 250314A lightened up over months.
Given that it took off so early in the history of deep space, its light was extended as the universes broadened over billions of years.
As light is extended, so is the time it considers occasions to unfold.
Webb’s observations were purposefully taken 3.5 months after the GRB 250314A occasion ended, considering that the underlying supernova was anticipated to be brightest at that time.
“Webb offered the fast and delicate follow-up we required,” stated Dr. Benjamin Schneider, an astronomer at the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille.
Gamma-ray bursts are extremely unusual. Those that last a couple of seconds might be brought on by 2 neutron stars, or a neutron star and a great void clashing.
Longer bursts like this one, which lasted around 10 seconds, are regularly connected to the surges of huge stars.
On March 14, 2025, the SVOM objective, a Franco-Chinese telescope that introduced in 2024 and was developed to find short lived occasions, identified a gamma-ray burst from an extremely far-off source.
Within an hour and a half, NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory identified the X-ray source’s area on the sky. That allowed subsequent observations that would determine the range for Webb.
Eleven hours later on, the Nordic Optical Telescope was marked time and exposed an infrared-light gamma-ray burst afterglow, a sign that the gamma ray may be related to an extremely remote item.
4 hours later on, ESO’s Very Large Telescope approximated the things existed 730 million years after the Big Bang.
“There are just a handful of gamma-ray bursts in the last 50 years that have actually been identified in the very first billion years of deep space,” Dr. Levan stated.
“This specific occasion is really unusual and extremely interesting.”
Given that this is the earliest, farthest supernova to be spotted to date, the scientists compared it to contemporary, close-by supernovae. The 2 ended up being extremely comparable, which shocked them.
Why? Little is still understood about the very first billion years of deep space.
Early stars most likely consisted of less heavy components, were more enormous, and led much shorter lives.
They likewise existed throughout the Era of Reionization, when gas in between galaxies was mostly nontransparent to high-energy light.
“Webb revealed that this supernova looks precisely like modern-day supernovae,” stated University of Leicester’s Professor Nial Tanvir.
“Webb’s observations show that this far-off galaxy resembles other galaxies that existed at the very same time,” stated Dr. Emeric Le Floc’h, an astronomer at the CEA Paris-Saclay.
_____
A.J. Levan et al2025. JWST exposes a supernova following a gamma-ray burst at z ≃ 7.3. A&A 704, L8; doi: 10.1051/ 0004-6361/2025 56581
B. Cordier et al2025. SVOM GRB 250314A at z ≃ 7.3: A blowing up star in the age of re-ionization. A&A 704, L7; doi: 10.1051/ 0004-6361/2025 56580
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.