

Is that truly a drifting spoon on Mars or simply an odd rock?
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
As one of Earth’s closest next-door neighbors in area, Mars has actually long mesmerized people with the possibility of alien life situated simply a brief rocket journey away. No such life has actually been discovered. Now, as NASA and other area companies have actually started to check out the skies and surface area of the Red Planet utilizing robotic innovation, images of odd functions and developments continue to irritate skywatchers ‘hopes, worries and interests.
Here are a few of our preferred things on Mars that appear like they do not belong on a dead and dirty world.
Much of these are an outcome of[ pareidolia — the propensity for human beings to look for familiar patterns and shapes in inanimate things. Some of them might even lead researchers to the long-sought proof of previous Martian life.An open “travel book”

( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
Possibly tired from searching for proof of ancient water, NASA’s Curiosity rover took a time-out in April 2023 to scan the pages of an old Martian hardback depending on the dust of Gediz Vallis. While the odd things might appear like a book with a single page frozen mid-turn, it remains in truth simply a rock– and a little one at that. The captivating little book-rock procedures simply 1 inch (2.5 centimeters) broad, according to NASA. Hey, a minimum of it’s travel-size!
Related:’Spiders on Mars’ completely awakened in the world for 1st time– and researchers are squealing with
happiness
A[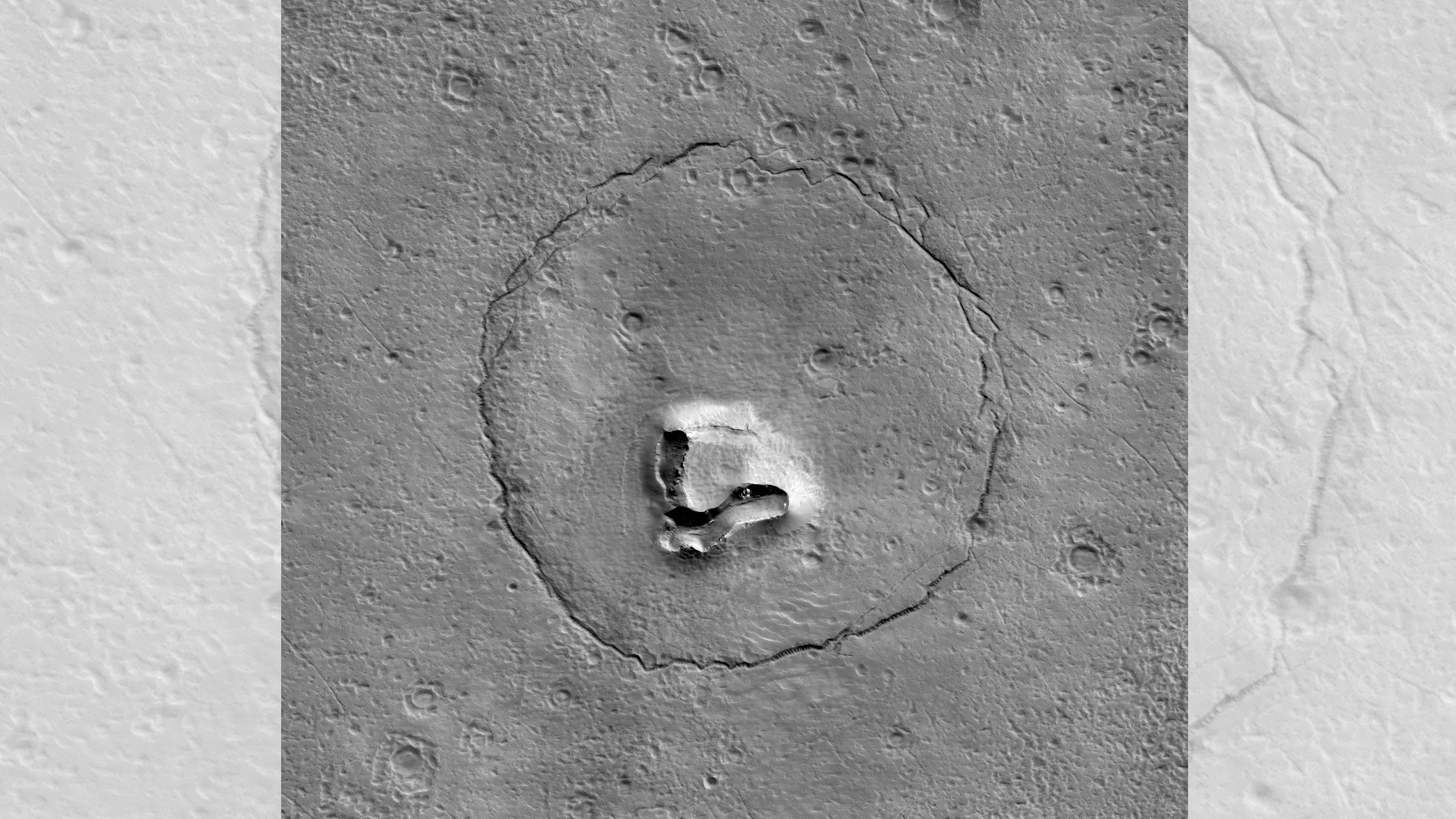
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona)
In an image shared in January 2023 by the University of Arizona( UA), what seems the face of a massive Martian teddy bear– total with 2 beady eyes, a button nose and an upturned mouth– smiles at the cam of NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. According to UA, the cuddly-wuddly development is most likely simply a broken-up hill in the center of an ancient crater. As far as we’re worried, it’s the prettiest stack of debris in the recognized universe.
Frozen “mineral flowers”
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS )
Branching outside like a small coral, this fragile mineral flower has to do with the closest thing to greenery one can discover on the Red Planet today. Mineral deposits like these prevail sights throughout Mars and arise from ancient water blending with ancient rock. Still, it’s unusual to see a deposit that’s so completely flower-like, NASA scientists stated. You’ll observe 2 somewhat less excellent, circular rocks of the very same type to the right of the coral. Interest identified this flower function in February 2022.
A mystical “doorway”
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
Is this completely hewn “doorway” into a Martian cliffside proof of smart alien life on the Red Planet– or maybe indications of a secret society of human astronauts in private Mars bunkers? Unfortunately (for conspiracy theorists), the fact is far easier: It’s simply a worn down rock development captured at the ideal angle. The image was caught by NASA’s Curiosity rover in 2022.
Fossilized “animal tracks”
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
Did alien animals when skitter throughout the surface area of Mars, leaving fossilized tracks embedded in the rocks? One scientist made this questionable claim in 2018, indicating pictures of stick-like structures, each about the size of a grain of rice, crisscrossing a Martian rock. NASA scientists rapidly unmasked the claims, keeping in mind that comparable functions abound in the world in locations where salts end up being focused in water, such as vaporizing lakes. Their existence on Mars is yet more proof of previous rivers and lakes on the Red Planet, however they use no evidence that living animals ever embellished its surface area.
A bushel of “blueberries”
( Image credit: NASA)
Blueberries are not a considerable source of iron when taken in the world– however these geological “blueberries” found by NASA’s Opportunity rover on Mars in 2004 are developed in a different way. The iron-rich spheres, polished smooth by numerous quantities of water billions of years earlier, are a few of the earliest proof researchers have of Mars when being an extremely damp world. Whether they likewise taste excellent on cheesecake is a concern for future generations to face.
Countless black “spiders on Mars”
(Image credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin( left) ESA/TGO/CaSSIS( right ))
Every spring, countless squiggly black “spiders” emerge from their hibernation near the Martian south pole. No, they are not genuine spiders– they are not alive at all, naturally. The seasonal phenomenon is an outcome of buried co2 ice sublimating, or turning to gas, as the weather condition warms. The recently launched gas bursts through layers of surface area ice, bring with it dark dust that splashes throughout the ground in craggy patterns. To be noticeable from area, as these developments are, the “spiders” should be relatively huge– every one determining 150 to 3,300 feet (45 meters to 1 kilometer) throughout, according to the European Space Agency (ESA). Please, no one inform Ziggy Stardust the problem.
Ruins of an “Inca City”
(Image credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin)
Near the Martian south pole wonder structures that appear like the ruins of a huge and ancient city. Called the “Inca City” for its similarity to real ruins found in South America, the strange rock development might be made from raised dune that turned to stone in time, according to ESA. Its specific origins stay a secret. The labyrinthine development appears to curve, forming part of a huge circle 53 miles (86 km) in size, leading researchers to presume it might belong to a much bigger effect crater from a meteor strike ages earlier.
An ancient smiley face
( Image credit: ESA/TGO/CaSSIS)
Did somebody spray-paint a smiling face onto the Martian surface area? Not rather, in spite of what it appears like in this infrared image snapped by ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter. Noticeable just under specific conditions, the face seen here is really the residues of an ancient lake, described by chloride salt deposits and dotted with 2 meteor crater eyes. While no Martian graffiti artists are going to appear from the lake to declare their work, the face-like structure might include proof of ancient life on the Red Planet. As Mars’ once-plentiful lakes dried up, the staying water sources most likely ended up being extremely salted, perhaps providing a sanctuary for microbial life.
An incredibly out-of-place rock
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/ MSSS)
Among these things is not like the other. Sticking out like an aching Martian thumb inside dirty Jezero Crater, this uncommonly white rock is the very first of its kind ever seen on the Red Planet. Called “Atoko Point” after a likewise light-colored function of the Grand Canyon, the speckled rock is most likely made from the minerals pyroxene and feldspar, according to an analysis by NASA’s Perseverance rover. How did such a white rock discover itself in such dark-hued business? It likely toppled below the crater rim or was transferred to the crater flooring from somewhere else on Mars back when rivers raved throughout the area.
A stony “Star Trek” sign
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Appears like somebody from Starfleet left their communicator badge on the Red Planet– or so it would appear from the familiar shape of this rock identified by the Curiosity rover. The rock’s delta shape is simply a coincidence, according to NASA. It is among thousands found on Mount Sharp, which Curiosity has actually been checking out for many years in its search to reveal ideas about Mars’ previous and whether it ever held the conditions for life.
A “tile floor”
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS/ IRAP)
While scaling the slopes of Mount Sharp in 2021, NASA’s Curiosity rover discovered residues of what appears like a tile flooring from a Martian restroom. Lots of interlocked polygons broken through the dirt; most include 5 or 6 sides and date to in between 3.8 billion and 3.6 billion years earlier. These rugged polygons are mud fractures, which have actually consistently dried and dampened once again throughout unknown years. They most likely date to a time when the water level in the surrounding Gale Crater fluctuated consistently, triggering the polygonal fractures in the ground to appear and vanish gradually before a last drought left them as they are today.
Completely circular dune
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
Mars is covered in dunes of all sizes and shapes, however few of them are as completely circular as the group identified above by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2022. Snapped while flying over Mars ‘northern hemisphere, the image reveals a bubbling patchwork of dark and oddly round dunesinclining southward in the instructions where the Martian wind most likely blew them. Researchers are still not specific why these specific dunes are so circular or why they seem gradually moving far from Mars’ equator at a rate of approximately 3.3 feet (1 m) per Martian year (687 days in the world).
A “shark fin” and a “crab claw”
(Image credit: NASA)
While trawling through Jezero Crater, NASA’s Perseverance rover spotted a couple of fishy-looking rocksThe 2 odd stones– one sticking out up like a shark fin, and the other crimped like a crab claw– shocked scientists. There isn’t much secret to them. They are simply rocks, shaped by the wind over billions of years and left in the Martian dust for pattern-seeking human minds to discover.
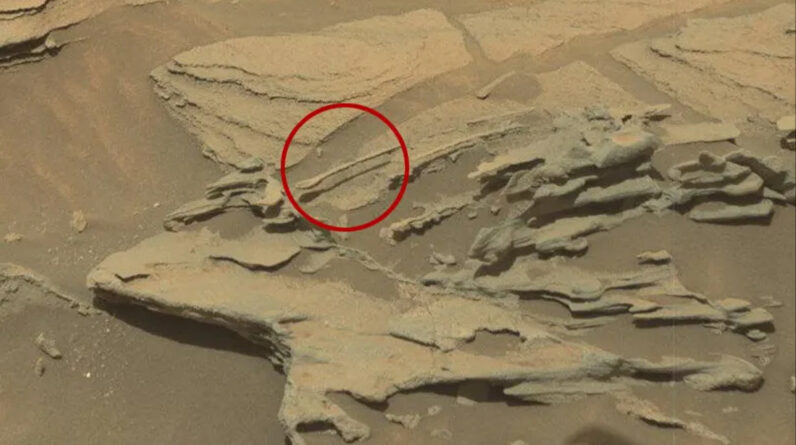
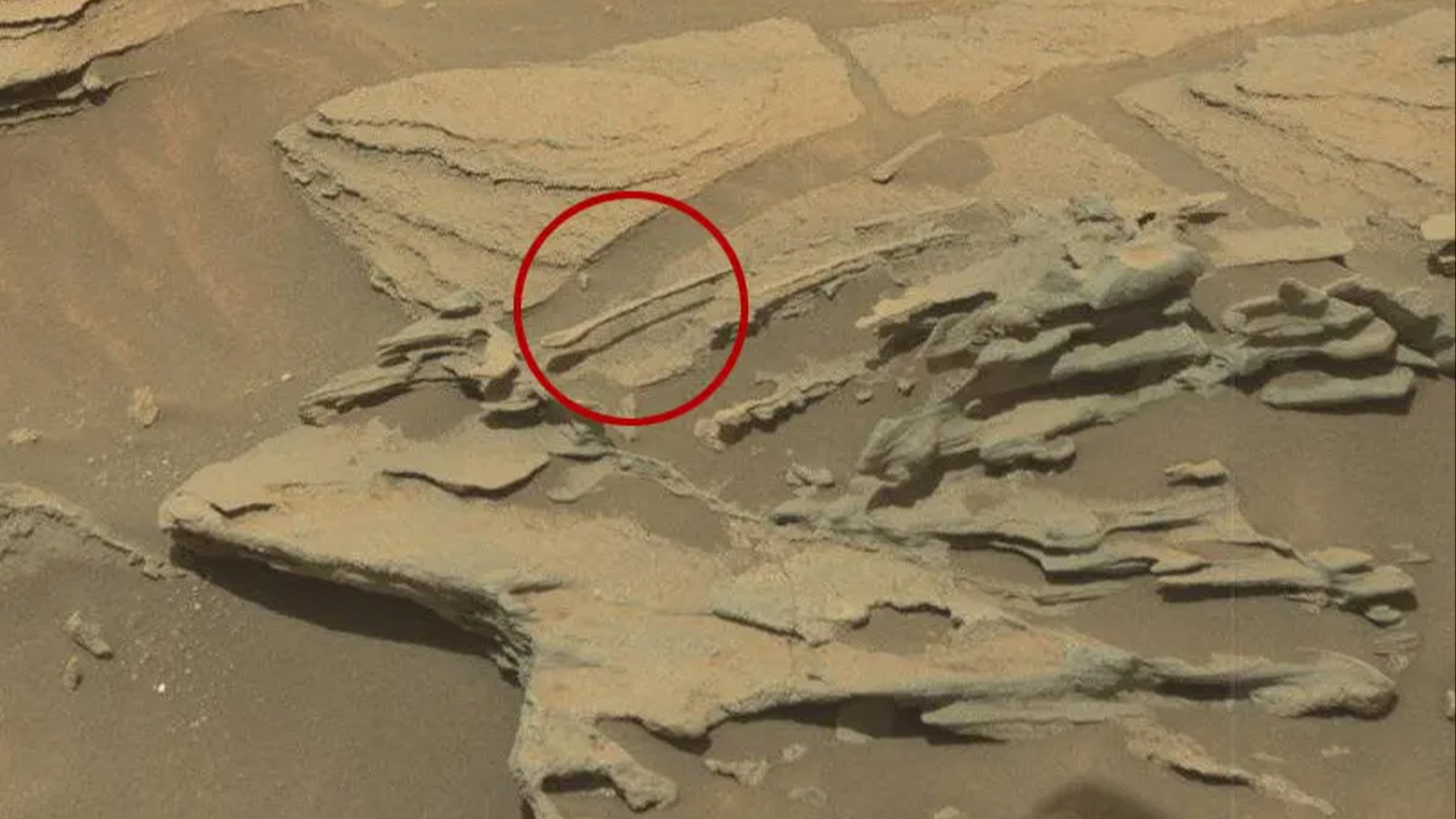
A “floating spoon”
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS )
In 2015, NASA’s Curiosity rover identified what seemed a wood spoondrifting in midair with a shadow on the ground below it. It was, obviously, a visual fallacy; the spoon is just a rock, formed by the wind over eons, likewise called a ventifact. The deal with of the spoony rock juts out from a bigger development, enabling the spoon’s rounded suggestion to hover over the ground listed below, casting an unique shadow below it.
A spooky “face”
(Image credit: NASA)
Among the earliest Martian rock developments to record the general public’s interest was this notorious “face” identified by NASA’s Viking 1 satellite in 1976. While circling around the world trying to find a landing website for its robotic buddy, Viking 2, the satellite identified a mound of rocks, partly obscured in shadow, clearly looking like a human face. Follow-up observations with later spacecraft revealed that the face showed up just from particular angles and under particular light conditions, showing that the Martian mound’s humanlike look was simply a technique of light and shadow.
A “giant’s fingerprint”
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona)
A long period of time earlier, something knocked into the surface area of Mars and left this huge, ridged, thumbprint-like anxiety behind. A huge finger was not the offender, naturally. Found inside a much bigger crater called Airy-0, this Martian hole is the outcome of an ancient meteor effect. The intense striations forming the “lines” of the finger print are a typical sight throughout Mars. Referred to as transverse aeolian ridges, they are produced when dune get covered in a thin layer of dust. The dust most likely consists of reflective minerals, offering the anxiety its radiant look in this image.
A rock with an, er … fracture
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU)
Attempt not to make fun of this rock snapped by NASA’s Perseverance rover in 2021. The split stone ended up being the butt of more than a couple of jokes after its close-up was very first launched to the general public. There’s truly very little to see, however– the Red Planet has lots of broken rocks, albeit not rather as plump as this one. Determination found this rock in dirty Jezero Crater, on its 102nd day on Mars.
An “angel” and a heart
(Image credit: ESA)
When it’s summer season on Mars, the angels come out to playThe Martian south pole is generally covered in a massive ice cap, however when the ice melts in warmer weather condition, patterns in the ancient, red-hued sediment listed below emerged. This image, snapped by ESA’s Mars Express spacecraft, reveals an angel-like pattern beside a heart-shaped one. Both of these familiar-looking structures are the outcome of meteor effect craters that scraped away Mars’ dirty topsoil to expose the darker sediment listed below.
A strangely green rock with “drill holes”
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Did a tired Martian teen obtain his moms and dads ‘power tools once again? That is one(not likely)description for an odd, green rock apparently pumped loaded with drill holes that was found by NASA’s Perseverance rover early in its objective. The approximately 6-inch( 15 cm) rock keeps an eye out of location in its environment, and researchers aren’t absolutely sure how to discuss it. Maybe it is the residue of a meteor that hit the Red Planet, or possibly it is a piece of Martian bedrock that was flung far throughout the world throughout an effect occasion. The majority of the holes are likewise a secret– however, if you look ideal of center, you might see a little train of small, consistent pockmarks left by Perseverance’s laser, which it fired at the rock while attempting to evaluate its structure.
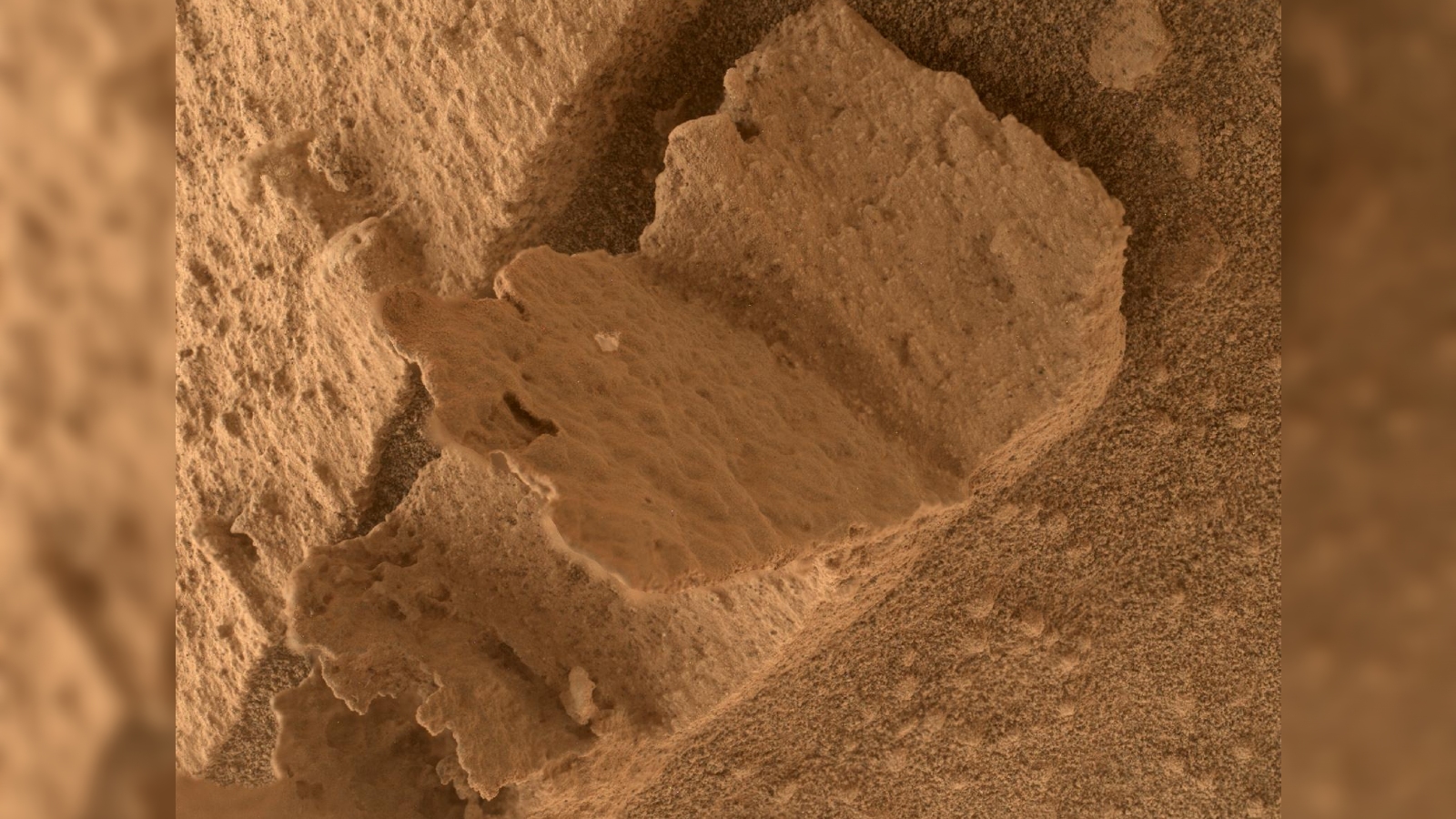
A little “foreign object”
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
A little, rectangle-shaped item identified in Mars ‘Gale Crater in 2018 briefly provided NASA researchers a scare. Looking slightly like a dirty sheet of metal, the things was possibly believed to be a piece of the Curiosity rover that had actually inexplicably fallen off. Fortunately, a fast analysis revealed that the “foreign object,” as NASA at first called it, was simply a flake of rock that had actually divided off of a bigger development and wasn’t foreign to Gale Crater
at all.A weird, white tower
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Overlooking the Martian horizon in an image recorded by NASA’s Perseverance rover in 2023, a high, white column stands versus the dark, rocky background. It is, in truth, a Martian dust devil. And it’s a huge one: The dirty vortex caught here is taller than a typical twister in the world and 5 times taller than the Empire State Building, according to NASA. Formed when increasing cells of warm air fulfill falling columns of cool air, dust devils are extremely typical on Mars– maybe numbering as lots of as 145 million daily, one 2018 research study approximated.
A “scar” longer than the Grand Canyon
(Image credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin)
Open like a fresh injury in this image caught by ESA’s Mars Express orbiter in 2024, the Martian function referred to as Aganippe Fossa is a sight to see. The deep, dark gorge stretches around 375 miles(600 km )long– longer than the Grand Canyon, which determines about 277 miles (446 km) long. Found near the base of an extinct volcano, the Martian canyon most likely formed as the outcome of ancient volcanic activity– potentially when a big swimming pool of lava below the volcano pressed strongly up, tearing the ground asunder, according to ESA.
“Rock candy,” or ultra-rare crystals?
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
These oddly colored crystals on Mars were found by pure mishap. In May 2024, NASA’s Curiosity rover drove over a little rock in its course, accidentally squashing it. Buried within the stone burial place was a cache of uncommon minerals, consisting of some never ever seen before on the Red Planet. The yellow-colored crystals are made from pure essential sulfur. Researchers had actually long anticipated that this product existed on Mars however had no evidence up until Curiosity’s bout of damaging driving.
A “bullet” hole
(Image credit: NASA/JPL– Caltech/UArizona)
What appears like a hole blasted into the Martian landscape by a roaming bullet might be something far more interesting– a possible haven for future astronauts. The hole, which determines a couple of meters throughout, was imaged by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2022 on the flank of an enormous volcano called Arsia Mons. The pit lies along a lava circulation and seems a vertical shaft that might possibly link to a deep system of caverns listed below the volcano. The hole’s depth is unidentified, it might be an appealing haven for future astronauts who require a location to protect themselves from the extreme radiation that beams down on the Red Planet.
An underground “dog”
(Image credit: Root et al.)
Unusual structures do not appear just on Mars’surface area however underground. In September 2024, scientists integrated information from a number of Mars-orbiting spacecraft to produce a planet-wide map of gravitational abnormalities– locations where the pull of gravity is more powerful than average, recommending the existence of huge, thick structures found under the world’s surface area. The majority of these thick blobs are amorphous, however one captured the scientists’ attention: an odd, dog-shaped structurewith a dark tail and ears, situated near the Martian north pole. It’s uncertain how the thick, doggy structure formed, however it might be connected to a previous meteor effect or a pile-up of volcanic product.
Particles from deep space?
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
Nestled amongst the dirty, red rocks of Gale Crater, a rugged, gray things immediately captured the attention of researchers running NASA’s Curiosity rover. The shrapnel-like rock watches out of location due to the fact that it likely is– according to scientists, the pointy stone is most likely the residue of a meteorite that crash-landed on Mars’ surface area ages earlier. Called Ames Knob and determining about 4 inches large by 5.5 inches long (10 by 14 cm), this meteorite isn’t simply area garbage; according to NASA scientists, studying the rock might assist expose the previous conditions in the world when the meteorite fell, consisting of whether it arrived at land or in now-vanished water.
Particles … from Earth?
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
In 2022, NASA found what appeared like the wreck of an “alien” spacecraft on Mars. In this case, the “aliens” were, in truth, Earthlings; the wreckage seen by NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter was a piece of the helicopter’s own parachute and backshell, a saucer-like cover that assisted slow the robotic craft’s descent as it dropped onto the Red Planet together with the bigger Perseverance rover. This piece of damaged human innovation, photographed by Ingenuity while it was flying 26 feet (8 m) above the Martian surface area, looks especially alien amidst the desolate rocks and dust of the surrounding landscape.
An alien “egg”
( Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/LANL/ CNES/IRAP/LPGNantes/ CNRS/IAS/MSSS)
From specific angles, this pockmarked rock appears like an exuding, green egg coming from some unidentified alien beast. A fast analysis from NASA’s Curiosity rover exposed that the odd stone– called Egg Rock– is really a piece of a meteorite that landed on the Red Planet at some unidentified time in the past. Studying Martian meteorites like this one can expose important hints about the world’s past however is not likely to lead back to any extraterrestrial beast nests.
Swirling patterns
( Image credit: NASA/Christopher Kremer/Brown University)
Weird patterns sculpted into the surface area of Mars’Nili Fossae area aren’t alien sand art or the Martian variation of Peru’s Nazca LinesThey are, in truth, mineral deposits including big amounts of olivine, a mineral generally just discovered deep listed below the surface area of Mars. How did so much olivine-rich rock reach the world’s surface area? That concern provides an appealing secret for researchers. It might be that a substantial asteroid effect excavated the Martian interior, bringing olivine to the surface area in swirling splatters– or maybe the subsurface mineral saw daytime following an enormous volcanic eruption. Its exact origin stays a secret to this day.
An alien monolith?
(Image credit: Image: NASA HiRISE; Arrow: thesun.co.uk)
When amateur stargazers were browsing images from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, they identified something odd in the satellite’s information: a bizarrely rectangle-shaped item similar to the alien monolith from the opening scene of “2001: A Space Odyssey.” The bewildering function is certainly monolithic fit and size, according to objective researchers. It is most likely absolutely nothing more than a huge, completely rectangle-shaped rock.
A crawling robotic
(Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona)
Found from miles above by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, a crawling metal robotic sparkles on the Martian surface area far below. This is an uncommon case where the secret things is precisely what it appears like; that robotic is NASA’s Curiosity rover, making its method up Mount Sharp numerous years into its objective to check out the Red Planet. Concrete proof that Mars ever held life is still doing not have– however a minimum of we can state Mars is the just recognized world in deep space occupied specifically by robotics.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Brandon is the space/physics editor at Live Science. His writing has actually appeared in The Washington Post, Reader’s Digest, CBS.com, the Richard Dawkins Foundation site and other outlets. He holds a bachelor’s degree in innovative composing from the University of Arizona, with minors in journalism and media arts. He delights in composing most about area, geoscience and the secrets of deep space.
The majority of Popular
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.







