The Hubble group has actually launched a spectacular brand-new image snapped by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope of the disallowed spiral nebula IC 1954.
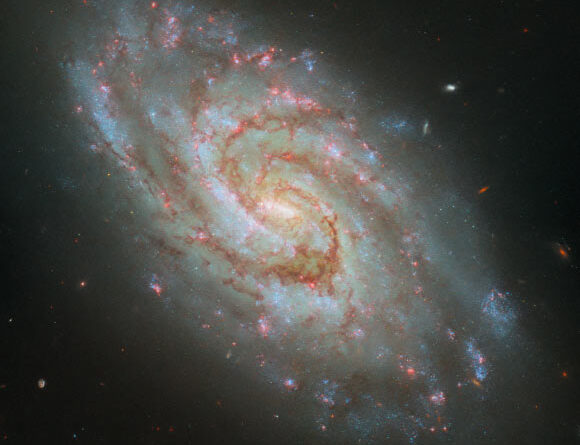
This Hubble image reveals IC 1954, a little disallowed spiral nebula situated 45 million light-years away in the constellation of Horologium. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ Hubble/ D. Thilker/ J. Lee/ PHANGS-HST Team.
IC 1954 lies some 45 million light-years far from Earth in the southern constellation of Horologium.
This little spiral nebula was found in 1898 by the Scottish astronomer Robert Innes.
Otherwise called ESO 200-36, IRAS 03300-5204 or LEDA 13090, it has a size of 20,000 light-years.
IC 1954 has a brilliant main bar and slackly winding spiral arms threaded with dark clouds of dust.
Together with 4 other galaxies, it forms the LGG 93 galaxy group, likewise called the IC 1954 group.
“IC 1954 sports a radiant bar in its core, 2 primary wonderfully winding spiral arms and clouds of dark dust throughout it,” the Hubble astronomers stated in a declaration.
A picture of IC 1954 was formerly launched by the Hubble group in 2021. The brand-new image now consists of H-alpha information.
“The enhanced protection of star-forming nebulae, which are popular emitters of the red H-alpha light, can be seen in the many radiant, pink areas throughout the disk of the galaxy,” the scientists stated.
“Interestingly, some astronomers presume that the galaxy’s ‘bar’ is really an energetic star-forming area that simply takes place to lie over the stellar center.”
The color picture of IC 1954 was made from different direct exposures taken in the noticeable, ultraviolet and near-infrared areas of the spectrum with Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
6 filters were utilized to sample numerous wavelengths. The color arises from designating various shades to each monochromatic image connected with a specific filter.
“By surveying IC 1954 and over fifty other neighboring galaxies in radio, infrared, optical, and ultraviolet light, astronomers intend to totally trace and rebuild the course matter takes through stars and the interstellar gas and dust in each galaxy,” the researchers stated.
“Hubble’s observing abilities form a fundamental part of this study: it can catch more youthful stars and star clusters when they are brightest at ultraviolet and optical wavelengths, and its H-alpha filter efficiently tracks emission from nebulae.”
“The resulting dataset will form a gold mine of research study on the development of stars in galaxies, which the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope will build on as it continues its science operations into the future.”
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.