Labrys portucalensis F11, a pressure of aerobic germs from the Xanthobacteraceae household, can break down and change a minimum of 3 kinds of per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS), and a few of the harmful by-products, according to brand-new research study.
Labrys portucalensis F11 can be possibly utilized for PFAS biodegradation in polluted environments. Image credit: Wijayahena et aldoi: 10.1016/ j.scitotenv.2024.178348.
” The bond in between carbon and fluorine atoms in PFAS is extremely strong, so most microorganisms can not utilize it as an energy source,”stated Professor Diana Aga, a scientist at the University at Buffalo and SUNY.
“The Labrys portucalensis F11 bacterial pressure established the capability to slice away the fluorine and consume the carbon. “
Labrys portucalensis F11 was separated from the soil of an infected commercial website in Portugal and had actually formerly shown the capability to strip fluorine from pharmaceutical impurities. It had actually never ever been evaluated on PFAS.
In the brand-new research study, Professor Aga and her associates discovered that Labrys portucalensis F11 metabolized over 90% of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) following a direct exposure duration of 100 days.
PFOS is among the most regularly spotted and consistent kinds of PFAS and was designated dangerous by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency in 2015.
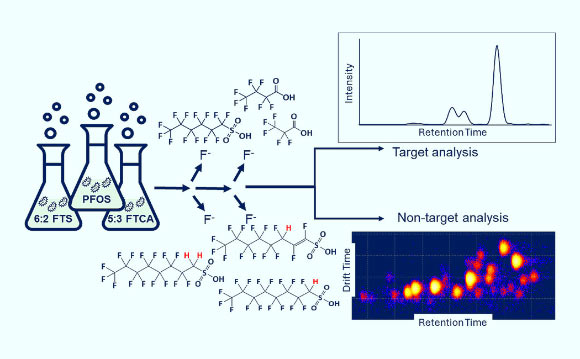
Labrys portucalensis F11 likewise broke down a significant part of 2 extra kinds of PFAS after 100 days: 58% of 5:3 fluorotelomer carboxylic acid and 21% of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate.
Unlike numerous previous research studies on PFAS-degrading germs, the brand-new research study represented shorter-chain breakdown items– or metabolites.
In many cases, Labrys portucalensis F11 even eliminated fluorine from these metabolites or broke them down to minute, undetected levels.
“Many previous research studies have actually just reported the deterioration of PFAS, however not the development of metabolites,” stated Mindula Wijayahena, a Ph.D. trainee at the University at Buffalo and SUNY.
“We not just represented PFAS by-products however discovered a few of them continued to be additional deteriorated by the germs.”
PFAS are a group of common chemicals extensively utilized given that the 1950s in whatever from nonstick pans to fire-fighting products.
They’re far from the meal of option for any germs, however some that reside in polluted soil have actually altered to break down natural impurities like PFAS so that they can utilize their carbon as an energy source.
“If germs make it through in an extreme, contaminated environment, it’s most likely due to the fact that they have actually adjusted to utilize surrounding chemical toxins as a food source so they do not starve,” Professor Aga stated.
“Through advancement, some germs can establish efficient systems to utilize chemical impurities to assist them grow.”
The findings were released in the journal Science of The Total Environment
_____
Mindula K. Wijayahena et al2025. PFAS biodegradation by Labrys portucalensis F11: Evidence of chain reducing and recognition of metabolites of PFOS, 6:2 FTS, and 5:3 FTCA. Science of The Total Environment 959: 178348; doi: 10.1016/ j.scitotenv.2024.178348
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.