New research study led by University of Hawai’i astronomers recommends our Universe might turn– simply very gradually.
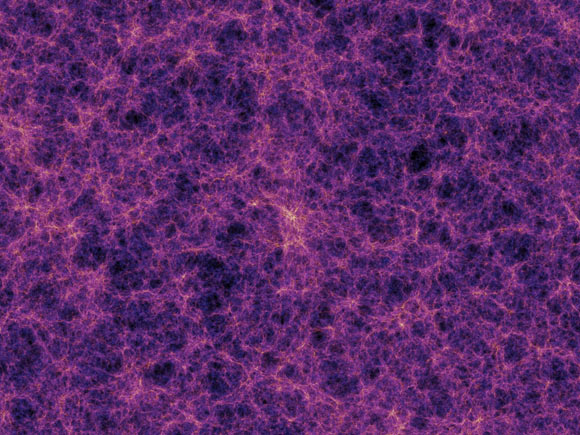
In forming deep space, gravity constructs a huge cobweb-like structure of filaments connecting galaxies and clusters of galaxies together along unnoticeable bridges numerous countless light-years long. This is referred to as the cosmic web. Image credit: Springel et al/ Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics.
“To paraphrase the Greek theorist Heraclitus of Ephesus, who notoriously stated Panta Rhei– whatever relocations, we believed that possibly Panta Kykloutai– whatever turns,” stated Dr. István Szapudi, an astronomer with the Institute for Astronomy at the University of Hawai’i.
Existing designs state deep space broadens equally in all instructions, without any indication of rotation. This concept fits the majority of what astronomers observe.
It does not describe the so-called Hubble stress– an enduring difference in between 2 methods of determining how quick the Universe is broadening.
One approach takes a look at remote taking off stars or supernovae, to determine the ranges to galaxies, and provides a growth rate for deep space throughout the previous couple of billion years.
The other approach utilizes the relic radiation from the Big Bang and provides the growth rate of the really early Universe, about 13 billion years earlier. Each provides a various worth for the growth rate.
Dr. Szapudi and his coworkers established a mathematical design of deep space.
The design followed basic guidelines. They included a small quantity of rotation. That little modification made a huge distinction.
“Much to our surprise, we discovered that our design with rotation deals with the paradox without opposing existing huge measurements,” Dr. Szapudi stated.
“Even much better, it works with other designs that presume rotation.”
“Therefore, maybe, whatever actually does turn. Or, Panta Kykloutai!”
The group’s design recommends deep space might turn when every 500 billion years– too sluggish to discover quickly, however enough to impact how area broadens in time.
“The concept does not break any recognized laws of physics,” the astronomers stated.
“And it may describe why measurements of deep space’s development do not rather concur.”
“The next action is turning the theory into a complete computer system design– and discovering methods to identify indications of this sluggish cosmic spin.”
The findings appear in the Regular monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
_____
Balázs Endre Szigeti et al2025. Can rotation fix the Hubble Puzzle? MNRAS 538 (4 ): 3038-3041; doi: 10.1093/ mnras/staf446
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.