Modern structures tend to take electrical energy and a/c for given. They typically have glass exteriors and windows that can’t be opened. And when the power goes out for days in the middle of a heat wave, as the Houston location experienced in July 2024 after Hurricane Beryl, these structures can end up being excruciating.
For centuries, civilizations understood how to shelter human beings in hot and dry environments.
As an architectural designer and scientist studying metropolitan strength, I have actually taken a look at a number of the methods and the lessons these ancient civilizations can provide for residing in hotter and drier conditions.
With international temperature levels increasing, research studies reveal that alarmingly hot summer seasons like those in 2023 and 2024 will end up being significantly typicaland extreme storms may lead to more power blackouts. To get ready for an even hotter future, designers today might gain from the past.
Related: Individuals are getting 2nd-degree burns from walkways
Sumerians: Keeping cool together
The Sumerians lived about 6,000 years earlier in a hot and dry environment that is now southern Iraq. Even then, they had methods for handling the heat.
Archaeologists studying residues of Mesopotamian cities explain how Sumerian structures utilized thick walls and little windows that might reduce heat direct exposure and keep indoor temperature levels cool.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Ur 2.0 ricostruzione 3d Immagini Ur 3d restoration of the ancient town – YouTube
Enjoy On
The Sumerians developed their walls and roofings with products such as adobe or mud that can soak up heat throughout the day and launch it throughout the nighttime.
They likewise built structures best beside each other, which minimized the variety of walls exposed to the extreme solar radiation. Little yards offered lighting and ventilation. Narrow streets made sure shade throughout the day and enabled pedestrians to move easily through the city
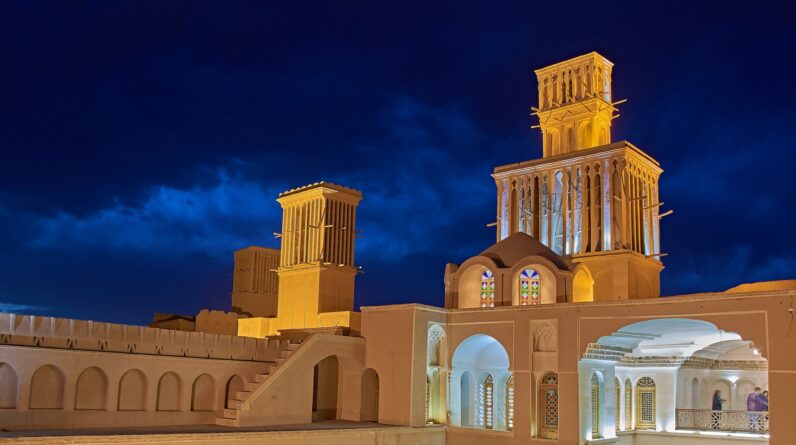
Ancient Egyptians: Harnessing the wind
The ancient Egyptians likewise utilized products that might assist keep the heat outPalaces were made from stone and had yards. Residential structures were made from mud brick.
Lots of people likewise embraced a nomadic habits within their structures to get away the heat: They utilized roof balconies, which were cooler in the evening, as sleeping quarters.
To cool structures, the Egyptians established a special innovation called the mulqafwhich includes high wall openings dealing with the dominating winds. These openings function as scoops to record wind and funnel it down to assist cool the structure. The getting in wind develops air blood circulation that assists vent heat out through other openings.
How this ANCIENT wind catcher make structure cool – YouTube
View On
The mulqaf concept might likewise be scaled approximately cool bigger areasCalled a wind catcher, it is presently utilized in structures in the Middle East and Central Asia, making them comfy without cooling, even throughout really hot durations.
Ancient Puebloans: Working with the sun
Civilizations on other continents and at other times established comparable methods for residing in hot and dry environments, and they established their own distinct services, too.
The Puebloans in what today is the U.S. Southwest utilized little windows, products such as mud brick and rockand created structures with shared walls to lessen the heat getting in.
Puebloan cliff houses at Mesa Verde provided security from the aspects and, since of their orientation, security from direct sun in summertime. (Image credit: Andreas F. Borchert, CC BY-SA)
They likewise comprehended the value of solar orientation. The ancient Puebloans developed whole neighborhoods under the overhang of south-facing cliffsThis orientation guaranteed their structures were shaded and remained cooler throughout the summer season however got sunshine and radiated heat to remain warmer throughout the winter.
Their descendants embraced comparable orientation and other urban-planning methodsand adobe homes are still typical in the U.S. Southwest.
Muslim caliphates: Using every drop of rain where it falls
Modern water management is likewise hardly ever created for dry environments. Stormwater facilities is developed to funnel overflow from rainstorms far from the city as quickly as possible. The very same cities should bring in water for individuals and gardens, often from far sources.
Throughout the 8th century, the Muslim caliphates in dry lands of northern Africa and the south of Spain developed their structures with rainwater harvesting strategies to record waterOverflow from rains was gathered throughout the roofing system and directed to tanks. The slope of the roofing system and the yard flooring directed the water so it might be utilized to water the vegetated landscapes of their yards.
Modern-day Mendoza, Argentina, utilizes this technique to water the plants and trees lining its splendid city streets
Landscaping in the Mosque of Cordoba, Spain, was created to funnel rainwater where required for watering. (Image credit: Adriana Zuniga )
Mayans and Teotihuacans: Capturing rainwater for later
At the city scale, individuals likewise gathered and saved stormwater to stand up to the dry season.
The ancient Teotihuacan city of Xochicalco and lots of Mayan cities in what today is Mexico and Central America utilized their pyramids, plazas and aqueducts to direct stormwater to big tanks for future usage. Plants were frequently utilized to assist clean up the water.
Big tanks like this one in Xochicalco, a Teotihuacan neighborhood in what is now Mexico, were utilized to record and save rainwater (Image credit: Adriana Zuniga)
Researchers today are checking out methods to save rainwater with great quality in India and other nationsRainwater harvesting and green facilities are now acknowledged as reliable techniques to increase city durability
Putting these lessons to work
Each of these ancient cultures provides lessons for remaining cool in hot, dry environments that contemporary designers can gain from today.
Some designers are currently utilizing them to enhance styles. Structures in the northern hemisphere can be oriented to make the most of southern direct exposure. South-facing windows integrated with shading gadgets can assist decrease solar radiation in the summer season Enable solar heating in winter season. Gathering rainwater and utilizing it to water gardens and landscapes can help in reducing water usage, adjust to drier conditions and increase city durability.
Retrofitting modern-day cities and their glass towers for much better heat control isn’t basic, however there are strategies that can be adjusted to brand-new styles for living much better in hotter and drier environments and for relying less on continuous summer season cooling. These ancient civilizations can teach us how.
This edited post is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Check out the initial short article
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.