fetchpriority=”high”>
fetchpriority=”high”>
( Image credit: JIM WATSON/AFP by means of Getty Images)
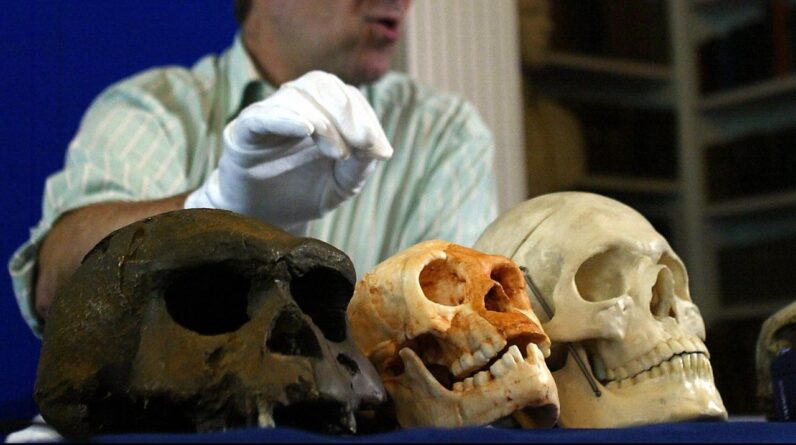
Up until Homo floresiensis was found, researchers presumed that the development of the human family tree was specified by larger and larger brains. Via a procedure called encephalizationhuman brains developed to be reasonably more huge than would be anticipated based upon matching body size.
This proportionally larger brain is what anthropologists argued allowed us and our family members to carry out more complicated jobs such as utilizing fire, creating and wielding tools, making art and domesticating animals.

Exhibition on brain size at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C. (Image credit: Tesla Monson)These theories had actually to be tossed out the window when archaeologists revealed our fossil cousins Homo floresiensis through clinical publication in 2004. Homo floresiensis lived from about 700,000 to 60,000 years earlier in the rain forests of Indonesia, partly synchronous with our own types.Appropriately nicknamed Hobbits, Homo floresiensis were short-statured, at simply over 3 feet (1 meter)high, and had a chimp-size brain. This discovery overthrew the presumption that brains have actually been increasing in size over the previous numerous million years and produced confusion about what separates current human family members in our genus Homo from our more ancient forefathers.Our brand-new research study on the skulls and teeth supplies an unique theory for how the Hobbits developed to be little
We are teachers of sociology at Western Washington University. After going to a 2023 workshop for biological anthropologists studying juveniles in the fossil recordwe started taking a look at brain size modifications throughout human development
Related: Antiquated human ‘hobbits’ were even much shorter than we believed, 700,000-year-old teeth and bone expose
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Our previous deal with the percentages of molar teeth created brand-new insights into the development of pregnancy by showing that fetal development rates are firmly connected to molar percentages in primates. Now, we wished to see whether we might reveal a relationship in between tooth percentages and brain size amongst our fossil family members.
Paleontologists have just minimal skeletal products, often just a couple of teeth, for lots of fossil types, consisting of Homo floresiensisIf tooth percentages can offer details about fossil brain size, it opens a world of possibilities for evaluating previous modifications in encephalization.
Rebuilding brain size utilizing teethWe looked at information on tooth and brain size for 15 fossil types on the human ancestral tree, covering about 5 million years of development. Rather oxymoronically, the 3rd molars– otherwise called knowledge teeth– have actually gotten proportionally smaller sized as brain size has actually gotten bigger throughout human development, for the majority of types.
In general, human loved ones with fairly bigger knowledge teeth are more ancient and had smaller sized brains. More current taxa, like Homo neanderthalensishad reasonably smaller sized 3rd molars, compared to their other teeth, and bigger brains.
This relationship permits scientists to find out something about brain size for fossils that are insufficient, possibly existing just as a couple of only teeth. Given that teeth are predominately made from inorganic matter, they make it through in the fossil record far more frequently than other parts of the body, comprising the large bulk of paleontological products recuperatedHaving the ability to understand more about brain size from simply a couple of teeth is a genuinely helpful tool.
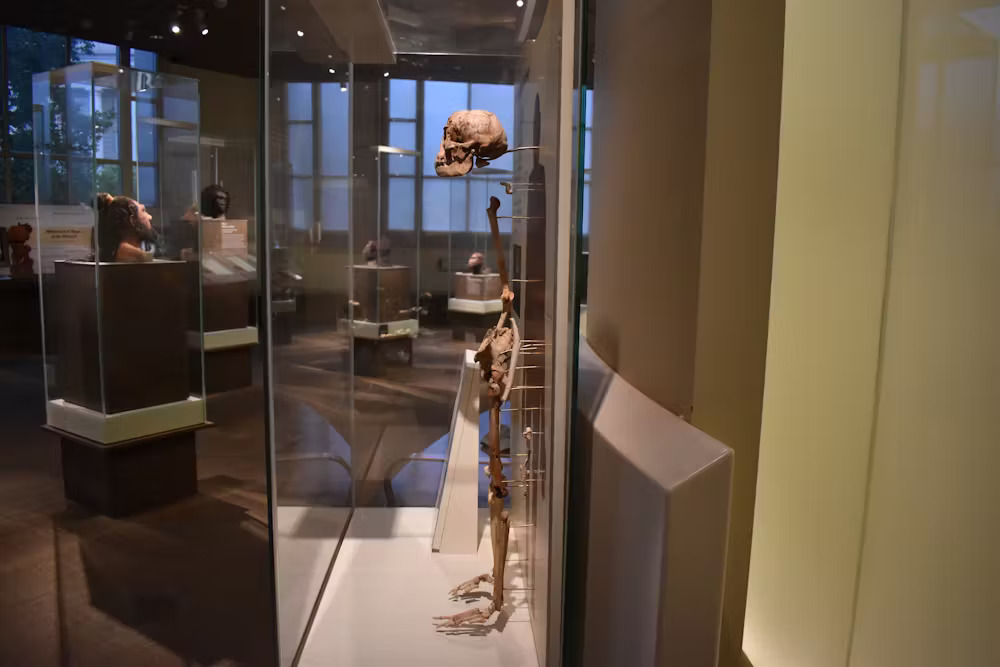

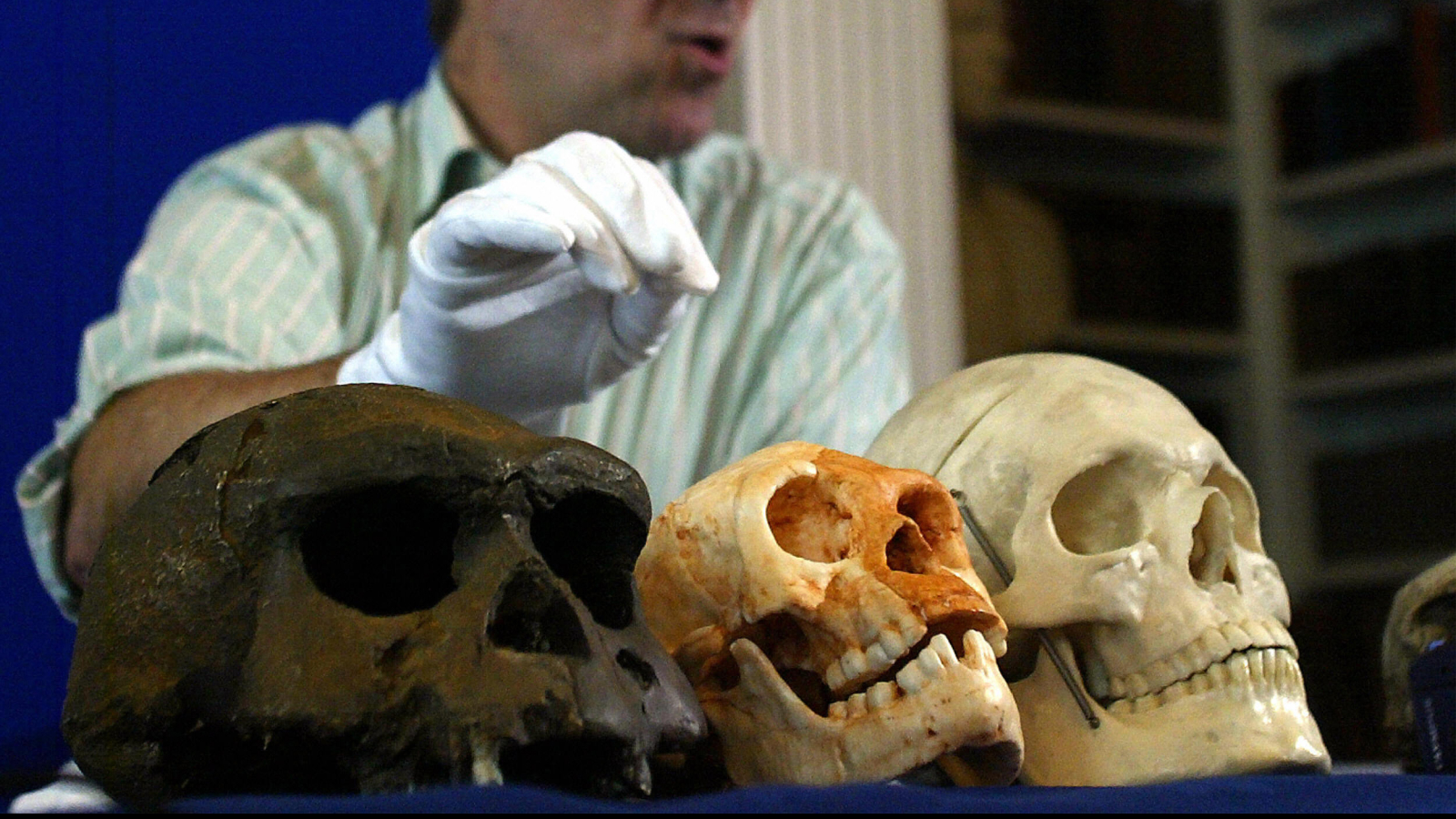
A reproduction of LB1, the most total skeleton ofHomo floresiensis,in profile in a display at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History. (Image credit: Tesla Monson )Researchers acknowledge now that the development of the brain and the teeth are inextricably linked throughout pregnancy. And for many types, bigger brains are associated with smaller sized knowledge teeth.
The one exception in genus Homo is Homo floresiensisthe Hobbit. The knowledge teeth of the Hobbits are little proportional to the other molars– the normal pattern for members of genus HomoTheir brains are likewise little, which is rather uncommon.
There are 2 main methods for brain size to reduce: by decreasing development throughout pregnancy before birth or by decreasing development after birth, throughout youth. Due to the fact that teeth establish early in pregnancy, decreasing development rates throughout pregnancy tends to impact tooth sizes and shape, and even whether the teeth establish at allSlowing development later on, throughout youth, affects skeletal sizes and shape in other methods, due to the fact that various parts of the body establish at various times.
Our brand-new research study supplies proof that the body size of Homo floresiensis most likely avoided a larger-bodied Homo forefather by decreasing development throughout youth. The Hobbits’ little knowledge teeth recommend that, a minimum of in utero, they were on track for the proportionally larger brains that are the hallmark of people and their loved ones. Any brake that decreased brain development most likely happened after birth.
This is the exact same system through which some short-statured contemporary human populations have actually adjusted to their regional environmental conditions.
Getting little on islandsThe little body size of Homo floresiensis was likely an adjustment to the distinct conditions of their island environment on Flores.
Progressing little body size as an adjustment to surviving on a separated island is referred to as insular nanismThere are numerous examples of other mammals ending up being little on islands over the previous 60 million years. One of the most appropriate examples is the dwarf elephant, Stegodon sondaariithat survived on Flores and was hunted by H. floresiensis for food.
Both Homo floresiensis and Homo luzonensisanother brief, island hominin from Southeast Asia, most likely progressed really brief stature due to the fact that of the eco-friendly results of restricted food schedule and absence of big predatorswhich tends to identify island environments.
Since brain size and body size are securely connected, body size advancement naturally impacts brain developmentAmongst contemporary people, bigger individuals have bigger brains, and smaller sized individuals have smaller sized brains.
Individuals with smaller sized brains are definitely no less smart than individuals with bigger brains. Variation in body size determines brain size; it is not a procedure of cognitive capability. The island Hobbits crafted toolshunted large-for-them video game in the kind of pygmy elephants, and most likely made and utilized fire.
Our research study supports that their little body size stemmed from a downturn in development throughout youth. This procedure would likely have actually had little effect on brain function or cognitive capability. We assume that the Hobbits were little however extremely capable.
Exhibition of cranial variation in fossil hominids, withHomo floresiensis. in the foreground, at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History. (Image credit: Tesla Monson)Comprehending the advancement peopleNew research study, including our research study, continues to strengthen the significance of comprehending how pregnancy and kid development and advancement developed. If we need to know what identifies people from our evolutionary forefathers, and how we developed, we should comprehend how the earliest minutes of life have actually altered and why.
Our work likewise motivates the reevaluation of unlimited attention on increasing brain size as the primary force in human advancement. Other types in genus Homo had little brains however were most likely very little various from us.
This edited post is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Check out the initial post
Tesla Monson is an Associate Professor of Anthropology at Western Washington University in Bellingham, WA where she runs the Primate Evolution Lab. Her laboratory investigates primate advancement, biography, reproductive ecology and the development and advancement of the skeletal system.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.