( Image credit: Photo thanks to the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities )
A rock shelter found in the southern Sinai Desert consists of styles and engravings covering a duration of 10,000 years, the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities has actually revealed in 2 declarations
Found on the Umm Arak Plateau, the rock shelter was found throughout a historical study performed by a group of Egyptologists. They were helped by a regional homeowner called Sheikh Rabie Barakat, who assisted direct them to the website, the declarations stated.
The shelter has to do with 330 feet (100 meters) long and 10 feet (3 m) deep, with a ceiling as much as 5 feet (1.5 m) high. The earliest rock art, which was dated based upon its design, was discovered near the entryway and dates to in between approximately 10000 and 5500 B.C., the declarations stated. It illustrates a range of scenes, consisting of a hunter who’s holding a bow and is accompanied by a minimum of 2 searching pets.
Scenes from later period consist of individuals riding horses and bring weapons, and there are engravings that date to ancient and middle ages times. The rock art likewise consists of geometric images made from X’s, squares, ovals, crescents and more intricate shapes. The historical group remains in the middle of examining the styles.
The shelter is near ancient copper and blue-green mines and was most likely “used across the ages as a lookout point and a place for gathering and rest,” among the declarations stated.
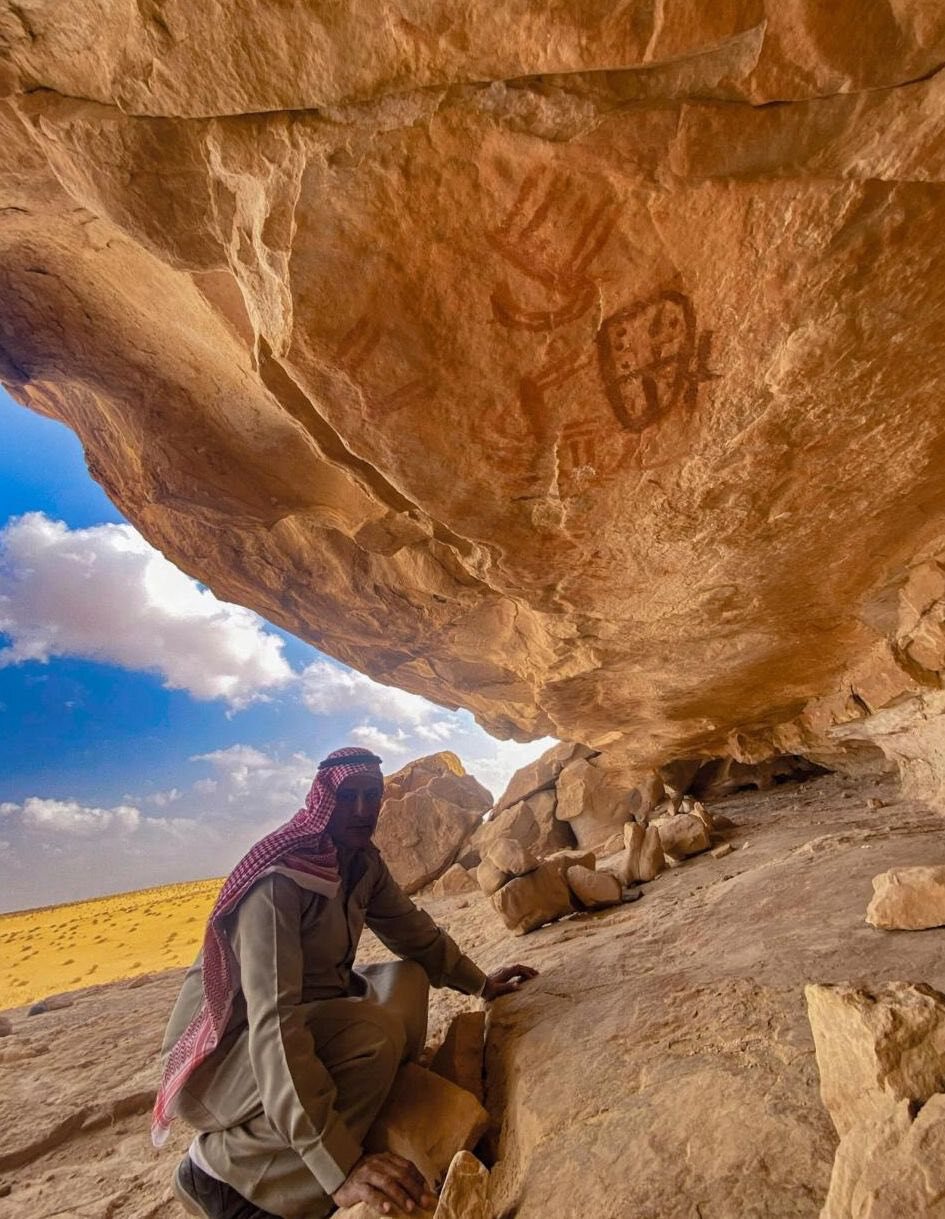

The recently discovered rock shelter lies in the south Sinai Desert.
Ancient individuals in Egypt might have left their mark on the rock shelter while mining the Sinai for resources, kept in mind John Darnellan Egyptology teacher at Yale University who has actually performed substantial research study in the Sinai however was not included with the brand-new discovery.
The “Sinai was an important region for ancient Egypt, a source of mineral wealth and a symbolically important region, the home of the goddess Hathor, ‘Mistress of Turquoise,'” Darnell stated. This discovery “will certainly help us better understand the interactions of the ancient [Egyptians] with the desert environment, and with those people living in and moving through the region.”
The images launched up until now “appear to show material of late antique through perhaps medieval date,” or approximately A.D 500 to 1500, Darnell stated, keeping in mind that the rock art consists of camels, people and Nabataean engravings.
The Nabataeans were an individuals who grew in the area in between approximately 400 B.C. and A.D. 200, and are most popular for constructing the city of Petra in JordanDarnell kept in mind that he anticipates seeing pictures of the earlier rock art found at the website.
Live Science got in touch with the historical group however did not hear back by the time of publication.
Ancient Egypt test: Test your smarts about pyramids, hieroglyphs and King Tut
Owen Jarus is a routine factor to Live Science who discusses archaeology and human beings’ past. He has actually likewise composed for The Independent (UK), The Canadian Press (CP) and The Associated Press (AP), to name a few. Owen has a bachelor of arts degree from the University of Toronto and a journalism degree from Ryerson University.
You need to verify your show and tell name before commenting
Please logout and after that login once again, you will then be triggered to enter your screen name.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.