Visualization of the southern polar vortex over Antarctica this year.
(Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory)
Abrupt and uncommon warming occasions in Antarctica might have postponed the arrival of the ozone hole that appears above the frozen continent every year, researchers state.
These warming occasions most likely affected a swirl of winds referred to as the southern polar vortex, which in turn impacted the ozone hole’s development, the scientists state.
Ozone is a gas that forms a layer in the stratosphere– the middle area of the environment that extends in between 12 and 31 miles (20 to 50 kilometers) above Earth’s surface area– and guards life from damaging ultraviolet solar radiation. The Antarctic ozone hole opens in this protective layer every year throughout the Southern Hemisphere’s spring, which lasts from September to November. Records returning to 1979 show that the ozone layer above the South Pole generally begins to break down at the start of August, however this year’s occasion appears to have actually been postponed.
“Instead of the typical behavior, deepening progressively during August, the ozone hole didn’t develop until the end of the month,” scientists with the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service, a European Union body that supplies everyday analyses and projections concerning Earth’s environment, composed in a declaration
The hold-up is because of 2 warming episodes that warped the southern polar vortex previously this year, according to the declaration. On different celebrations in July and August, temperature levels in the stratosphere above Antarctica increased by 27 and 31 degrees Fahrenheit (15 and 17 degrees Celsius), respectively. Such warming occasions are uncommon over the South Pole, the scientists kept in mind, however they’re more typical over the North Pole
Related: ‘We remained in shock’: Antarctica is acting in a manner we’ve never ever seen before. Can it recuperate?
It’s uncertain what triggered the 2 warming occasions, however NASA researchers kept in mind extremely uncommon weather condition in the troposphere (the layer of the environment straight above Earth) over Antarctica in July, with temperature levels reaching record-high levels. Variations in sea surface area temperature levels and sea ice can propagate up into the stratosphere, “but the attribution of why these systems develop is really difficult to do,” Paul Newmana climatic researcher at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, stated in a different declaration
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Particular conditions are required for the ozone hole to form, consisting of a strong polar vortex, solar radiation and ozone-depleting compounds (ODS).
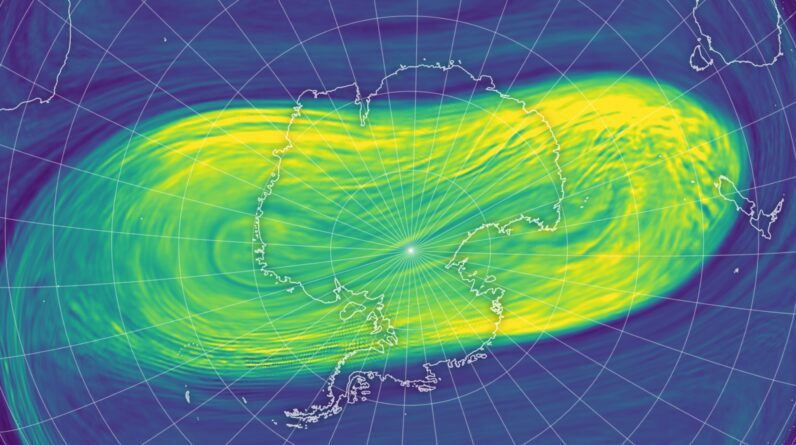
A strong polar vortex is identified by effective, circular winds and very cold temperature levels– conditions that triggered a hole larger than North America to open over Antarctica in 2015.
2 diagrams of air temperature level over Antarctica reveal the polar vortex in 2023( left )and 2024(right). (Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory)
Rather of being strong and circular, this year’s southern polar vortex was weak and lengthened, according to the declaration. This postponed ozone exhaustion in the stratosphere, even as sunshine returned in August after the South Pole’s polar night.
Ozone deficiency normally starts in a belt around the edge of the vortex, and after that works its method inward to form a hole through austral spring. The hole vanishes as temperature levels warm gradually throughout the Southern Hemisphere summer season, typically in December.
The Antarctic ozone hole initially formed due to people pumping ozone-depleting chemicals into the environment. International arrangements now prohibit these chemicals, consisting of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) that were utilized in a/c unit and fridges.
Proof recommends the ozone layer is recoveryhowever “a slow start of an ozone hole can’t automatically be attributed to a recovery of the ozone layer,” the scientists composed in the declaration. “The health of the stratospheric ozone layer depends on a complex combination of chemical and meteorological factors.”
If nations continue to appreciate the restriction on ODS, the hole ought to in theory recuperate within about 4 years, the scientists kept in mind. “In the meantime, the size and behavior of the ozone hole will be influenced by meteorological variability, anthropogenic and natural ODS sources and the impacts of climate change,” they included. Natural reasons for ozone deficiency consist of volcanic eruptions, such as Tonga’s 2022 record-shattering eruption
Sascha is a U.K.-based student personnel author at Live Science. She holds a bachelor’s degree in biology from the University of Southampton in England and a master’s degree in science interaction from Imperial College London. Her work has actually appeared in The Guardian and the health site Zoe. Composing, she takes pleasure in playing tennis, bread-making and searching pre-owned stores for covert gems.
A lot of Popular
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.