Researchers at the University of Waterloo and Kyushu University have actually established the very first technique to develop redundant, encrypted copies of qubits– a turning point towards useful quantum cloud services and safe and secure quantum facilities.
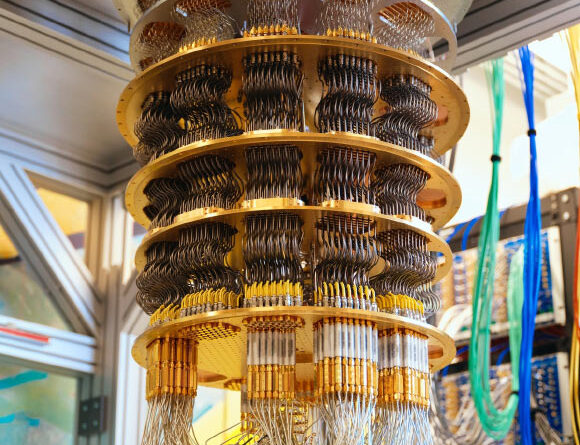
Google’s quantum computer system. Image credit: Google.
In quantum mechanics, the no-cloning theorem states it is difficult to make a similar copy of an unidentified quantum state.
University of Waterloo’s Dr. Achim Kempf and Kyushu University’s Dr. Koji Yamaguchi tension that this fundamental guideline still holds.
What they reveal rather is an approach that produces lots of encrypted variations of a single quantum bit, or qubit.
“This development will allow quantum cloud storage, like a quantum Dropbox, a quantum Google Drive or a quantum STACKIT, that securely and firmly shops the exact same quantum details on numerous servers, as a redundant and encrypted backup,” Dr. Kempf stated.
“It’s an essential action in making it possible for the accumulation of quantum computing facilities.”
“Quantum computing has significant capacity, especially for fixing really difficult issues, however it likewise positions special obstacles.”
“One of the most tough problems dealing with quantum computing is called the no-cloning theorem, which mentions that quantum info can not be copied, a minimum of not straight.”
“This is due to the fact that of the fragile method which quantum details is saved.”
According to the scientist, quantum details works a bit like splitting a password.
“If you have the very first half of the password and a buddy has the 2nd half, neither of you can utilize it alone– however if you put your 2 halves together, you obtain the important password,” Dr. Kempf stated.
“In a comparable sense, qubits are unique due to the fact that they can share details in a manner that grows as you integrate them.”
“A single qubit does not hold much by itself, however when qubits are connected together, they can keep a substantial quantity of info that just appears when they’re linked.”
“This distinct capability to hold shared info throughout numerous qubits is called quantum entanglement.”
“100 qubits can share info in 2 * 100 methods at the same time. This permits them to share a lot knotted details that all of today’s classical computer systems might not save it.”
“For all the capacity of quantum computing, nevertheless, the no-cloning theorem limitations how it can be used.”
“This is because, unlike in classical computing, where the copying of details– for sharing and for backups– is an extremely frequently utilized tool, there is no easy copy and paste in quantum computing.”
“We have actually discovered a workaround for the no-cloning theorem of quantum details,” Dr. Yamaguchi stated.
“It ends up that if we secure the quantum details as we copy it, we can make as numerous copies as we like.”
“This technique has the ability to bypass the no-cloning theorem due to the fact that after one choices and decrypts among the encrypted copies, the decryption crucial instantly ends, that is the decryption secret is a one-time-use secret.”
“But even a one-time essential makes it possible for crucial applications, such as redundant and encrypted quantum cloud services.”
The group’s work will appear in the journal Physical Review Letters
_____
Koji Yamaguchi & & Achim Kempf. 2026. Encrypted Qubits can be Cloned. Physical Review Lettersin press; arXiv: 2501.02757
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.