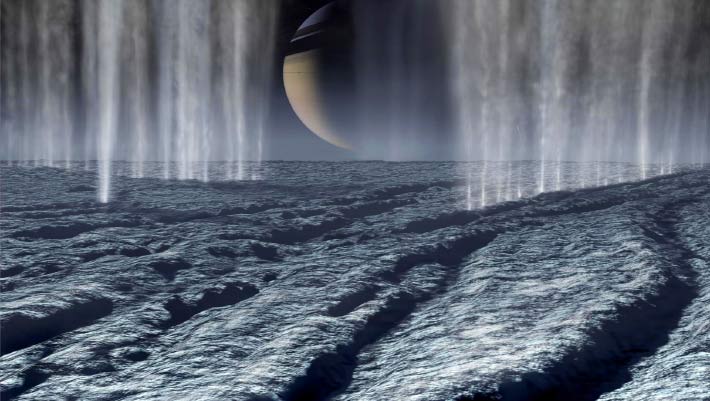
Saturn’s moon Enceladus continually ejects a plume of ice grains and gases stemming from its subsurface ocean through fractures near its south pole. Utilizing information from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, a group of planetary scientists at the University of Stuttgart and Freie Universität Berlin has actually now chemically examined newly given off particles coming from straight from Enceladus’ ocean. They had the ability to spot intermediates of possibly biologically pertinent natural particles– aliphatic, (hetero)cyclic ester/alkenes, ethers/ethyl and, tentatively, nitrogen- and oxygen-bearing substances– which were hence found for the very first time in ice particles from an ocean outside Earth.
An artist’s impression of NASA’s Cassini spacecraft flying through plumes appearing southern pole of Enceladus; these plumes are similar to geysers and expel a mix of water vapor, ice grains, salts, methane and other natural particles. Image credit: NASA/ JPL-Caltech.
Enceladus determines around 500 km in size; its surface area is covered by an ice shell with a typical density of around 25-30 km.
In 2005, Cassini discovered the very first proof that Enceladus has a concealed ocean underneath the surface area.
Jets of water burst from fractures near the moon’s south pole, shooting ice grains into area.
Smaller sized than grains of sand, a few of the small pieces of ice fall back onto the moon’s surface area, whilst others get away and form a ring around Saturn that traces Enceladus’ orbit.
“Cassini was spotting samples from Enceladus all the time as it flew through Saturn’s E ring,” stated Freie Universität Berlin scientist Nozair Khawaja, lead author of the research study.
“We had actually currently discovered lots of natural particles in these ice grains, consisting of precursors for amino acids.”
The ice grains in the ring can be centuries old. As they have actually aged, they might have been ‘weathered’ and for that reason changed by extreme area radiation.
The researchers wished to examine fresh grains ejected a lot more just recently to get a much better concept of exactly what is going on in Enceladus’ ocean.
They currently had the information. Back in 2008, Cassini flew directly through the icy spray. Beautiful grains ejected just minutes before struck the spacecraft’s Cosmic Dust Analyzer (CDA) instrument at about 18 km/s. These were not just the best ice grains Cassini had actually ever identified, however likewise the fastest.
“The ice grains consist of not simply frozen water, however likewise other particles, consisting of organics,” Dr. Khawaja stated.
“At lower effect speeds, the ice shatters, and the signal from clusters of water particles can conceal the signal from specific natural particles.”
“But when the ice grains struck CDA quickly, water particles do not cluster, and we have a possibility to see these formerly concealed signals.”
It took years to develop understanding from previous flybys and after that use it to understand this information.
Now, the authors have actually exposed what kind of particles were present inside the fresh ice grains.
They saw that particular natural particles that had actually currently been discovered dispersed in the E ring were likewise present in the fresh ice grains. This validates that they are developed within Enceladus’ ocean.
They likewise discovered completely brand-new particles that had actually never ever been seen before in ice grains from Enceladus.
For the chemists reading, the newly-detected molecular pieces consisted of aliphatic, (hetero)cyclic ester/alkenes, ethers/ethyl and, tentatively, nitrogen- and oxygen-bearing substances.
In the world, these exact same particles are associated with the chains of chain reactions that eventually result in the more complicated particles that are vital for life.
“There are numerous possible paths from the natural particles we discovered in the Cassini information to possibly biologically appropriate substances, which boosts the possibility that the moon is habitable,” Dr. Nozair stated.
“There is far more in the information that we are presently checking out, so we are anticipating discovering more in the future.”
“These particles we discovered in the newly ejected product show that the complex natural particles Cassini spotted in Saturn’s E ring are not simply an item of long direct exposure to area, however are easily offered in Enceladus’ ocean,” stated co-author Dr. Frank Postberg, likewise from Freie Universität Berlin.
The outcomes were released this month in the journal Nature Astronomy
_____
N. Khawaja et alDetection of natural substances in newly ejected ice grains from Enceladus’s ocean. Nat Astronreleased online October 1, 2025; doi: 10.1038/ s41550-025-02655-y
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.