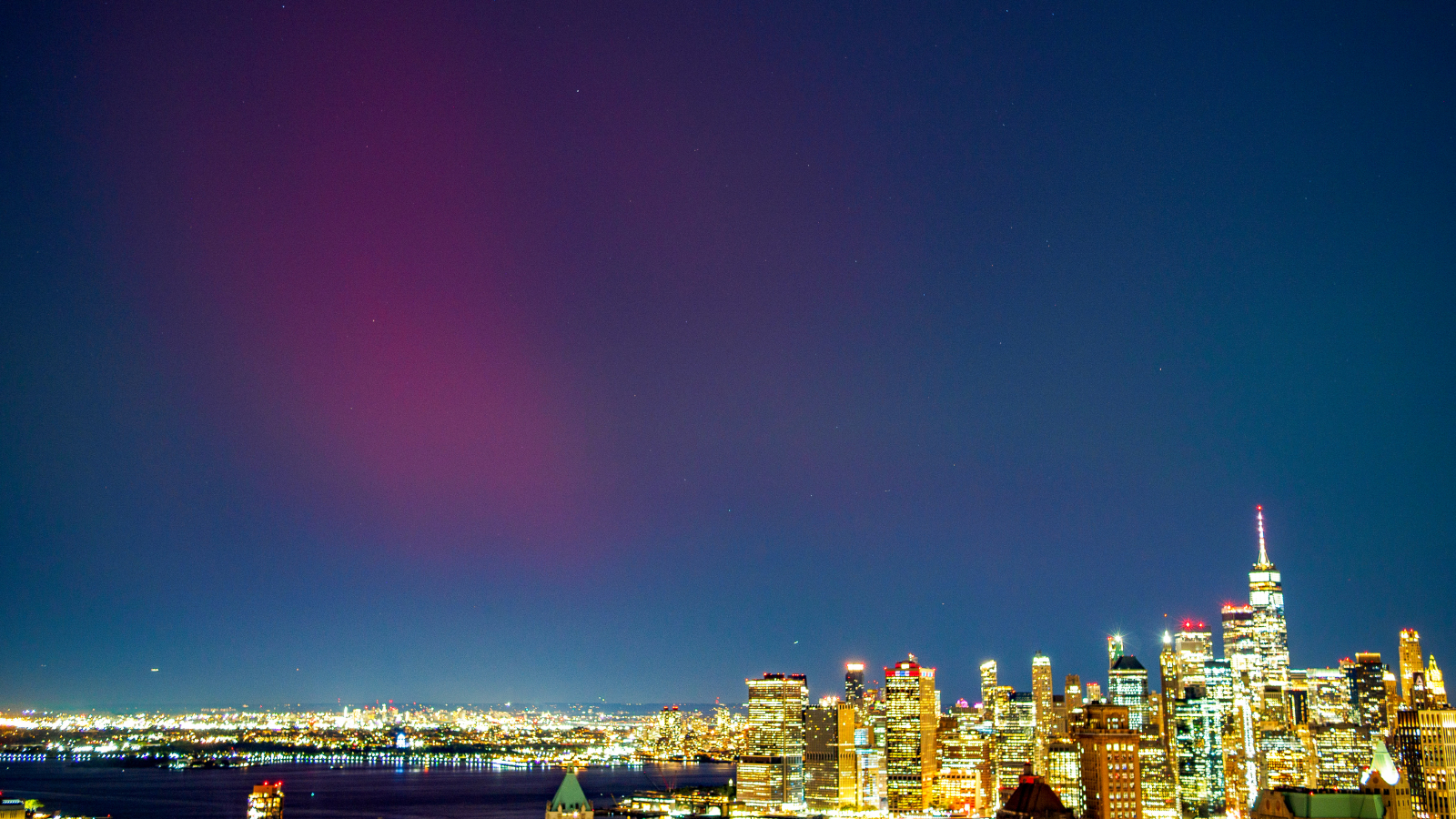
(Image credit: Brandon Rosenblum by means of Getty Images)
Skywatchers in as much as 18 U.S. states might witness auroras in the coming days as a “moderate” geomagnetic storm rocks Earth’s electromagnetic field, beginning on Friday(June 13 ).
On Wednesday(June 11 ), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center provided an preliminary alert for a G2(moderate)geomagnetic storm beginning on Saturday(June 14). On Friday, the center launched an upgraded caution that the storm might start later on the exact same day. The area weather condition occasion is anticipated to end on Sunday(June 15)or Monday (June 16).
The disruption has the prospective to increase to a G3( strong )geomagnetic storm over the weekend, according to Spaceweather.comhowever this is not ensured. Some other outlets have actually reported that the storm might reach G4 (serious) status. These reports have actually most likely developed from confusion surrounding a declaration from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory, which was describing what took place throughout a various G4 storm that took place previously this monthand the upcoming storm will not be anywhere near as extreme.
Geomagnetic storms are disruptions to Earth’s electromagnetic field, or magnetosphere, set off by variations in the solar wind. They are typically triggered by huge clouds of allured particles from appearing solar flares, referred to as coronal mass ejections (CMEs). In this case, the disruption is being triggered by a co-rotating interaction area– turbulence in the solar wind triggered by fast-moving streams clashing with slower wind ahead of them– that stemmed from a big “coronal hole” on the solar surface area.
These disruptions can squeeze Earth’s magnetosphere, possibly triggering extensive aurora display screens at uncommonly low latitudes. They can likewise trigger short-lived radio blackouts, damage power facilities on the ground and trigger satellites to fall from the sky as Earth’s environment takes in excess energy and broadens. (Geomagnetic storms are categorized utilizing a scale that ranks their strength from G1 (small) to G5 (extreme)– which is extremely uncommon.)
Related: The United States isn’t gotten ready for a huge solar storm, workout discovers
The geomagnetic storm is being set off by a co-rotating interaction area released by a coronal hole in the sun’s southern hemisphere. (Image credit: NASA/SDO)
The 18 states that might see auroras beginning tonight are Alaska, Montana, North Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, South Dakota, Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Idaho, Washington, Oregon, New York, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island and Wyoming, according to Live Science’s sis website Space.com
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
The aurora might likewise be seen in the U.K. and parts of Europe. There is no assurance that you will see auroras if you live in these locations, as your view might be obscured by cloudy weather condition, haze from wildfires or light contamination.
Solar activity has actually been high in the last few years thanks to solar optimum — the most active stage of the sun’s approximately 11-year cycle of activity, when our home star’s electromagnetic field entirely turnsThis stage started in early 2024much earlier than at first anticipatedand is most likely now endingSolar activity might stay high for numerous years to come.
In May 2024, Earth experienced a G5 geomagnetic storm– the most effective in 21 yearswith a few of the most prevalent auroras in the last 500 years — after a minimum of 5 various CMEs strike our world in fast successionThis storm was so effective that it triggered tractors and other GPS-controlled equipment to dance from side to side throughout numerous U.S. states.
Harry is a U.K.-based senior personnel author at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to end up being a reporter. He covers a vast array of subjects consisting of area expedition, planetary science, area weather condition, environment modification, animal habits and paleontology. His current deal with the solar optimum won “best space submission” at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the “top scoop” classification at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He likewise composes Live Science’s weekly Earth from area series.
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.