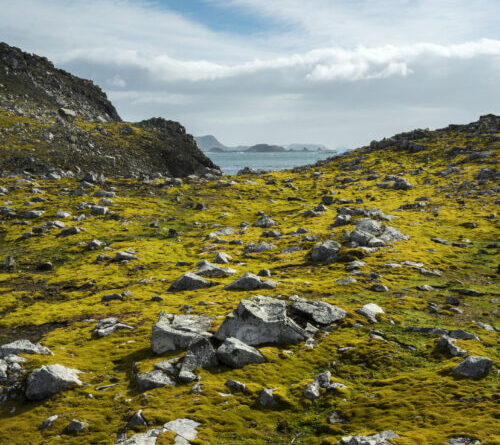
Plant development is speeding up on the Antarctic Peninsula and neighboring islands.
When satellites initially began peering down on the craggy, glaciated Antarctic Peninsula about 40 years back, they saw just a couple of small spots of plant life covering an overall of about 8,000 square feet– less than a football field.
Considering that then, the Antarctic Peninsula has actually warmed quickly, and a brand-new research study reveals that mosses, along with some lichen, liverworts and associated algae, have actually colonized more than 4.6 square miles, a location almost 4 times the size of New York’s Central Park.
The findings, released Friday in Nature Geoscience, based upon a precise analysis of Landsat images from 1986 to 2021, reveal that the greening pattern stands out from natural irregularity which it has actually sped up by 30 percent considering that 2016, quickly enough to cover almost 75 football fields annually.
Greening at the opposite end of the world, in the Arctic, has actually been extensively studied and reported, stated co-author Thomas Roland, a paleoecologist with the University of Exeter who gathers and evaluates mud samples to study ecological and environmental modification. “But the concept,” he stated, “that any part of Antarctica could, in any method, be green is something that still truly containers a great deal of individuals.”
Credit: Inside Climate News
Credit: Inside Climate News
As the world warms up,”even the coldest areas in the world that we anticipate and comprehend to be white and black with snow, ice, and rock are beginning to end up being greener as the world reacts to environment modification,”he stated.
The tenfold boost in plant life cover given that 1986″ is not substantial in the international plan of things,”Roland included, however the speeding up rate of modification and the possible environmental results are considerable.” That’s the genuine story here,” he stated.” The landscape is going to be changed partly due to the fact that the existing plants is broadening, however it might likewise be modified in the future with brand-new greenery can be found in.”
In the Arctic, plants is broadening on a scale that impacts the albedo, or the general reflectivity of the area, which identifies the percentage of the sun’s heat that is soaked up by the Earth’s surface area rather than being bounced far from the world. The spread of plant has not yet altered the albedo of Antarctica on a significant scale due to the fact that the vegetated locations are still too little to have a local effect, stated co-author Olly Bartlett, a University of Hertfordshire scientist who specializes in utilizing satellite information to map ecological modification.
“The genuine significance has to do with the environmental shift on the discovered land, the land that’s ice-free, developing a location ideal for advanced plant life or intrusive types to get a grip,” he stated.
Bartlett stated Google Earth Engine made it possible for the researchers to process a huge quantity of information from the Landsat images to fulfill a high requirement of confirmation of plant development. As an outcome, he included, the modifications they reported might really be conservative.
“It’s ending up being simpler for life to live there,” he stated. “These rates of modification we’re seeing made us believe that maybe we’ve caught the start of a more significant improvement.”
In the locations they studied, modifications to the albedo might have a little regional impact, Roland stated, as more land without reflective ice “can feed into a favorable feedback loop that produces conditions that are more beneficial for plant life growth also.”
Antarctic forests at comparable CO2 levels
Other research study, consisting of fossil research studies, recommends that beech trees grew on Antarctica as just recently as 2.5 million years back, when co2 levels in the environment resembled today, another sign of how untreated greenhouse gas emissions can quickly warm Earth’s environment.
Presently, there are just 2 types of blooming plants belonging to the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctic hair yard, and Antarctic pearlwort. “But with a couple of brand-new turf seeds occasionally, or a couple of spores, and all of an abrupt, you’ve got a really various environment,” he stated.
And it’s not simply plants, he included. “Increasingly, we’re seeing proof that non-native insect life is taking hold in Antarctica. Which can drastically alter things too.”
The research study demonstrates how environment warming will shock Antarctic environments, stated preservation researcher Jasmine Lee, a research study fellow with the British Antarctic Survey who was not associated with the brand-new research study.
“It is clear that bank-forming mosses are broadening their variety with warmer and wetter conditions, which is most likely assisting in comparable growths for a few of the invertebrate neighborhoods that count on them for environment,” she stated. “At the exact same time, some expert types, such as the more dry-loving mosses and invertebrates, may decrease.”
She stated the brand-new research study is important due to the fact that it supplies information throughout a broad area revealing that Antarctic environments are currently quickly modifying and will continue to do so as environment modification advances.
“We focus a lot on how environment modification is melting ice sheets and altering sea ice,” she stated. “It’s great to likewise highlight that the terrestrial communities are being affected.”
The research study reveals environment effects growing in “areas formerly believed almost unsusceptible to the sped up warming we’re seeing today,” stated environment policy specialist Pam Pearson, director of the International Cryosphere Climate Initiative.
“It’s as crucial a signal as the loss of Antarctic sea ice over the previous a number of years,” she stated.
The brand-new research study recognized vegetative modifications by comparing the Landsat images at a resolution of 300-square-feet per pixel, detailed enough to precisely map vegetative development, however it didn’t determine particular environment modification aspects that may be driving the growth of plant life.
Other current research studies have actually recorded Antarctic modifications that might stimulate plant development, consisting of how some areas are impacted by warm winds and by increasing quantities of rain from climatic rivers, as well as by decreasing sea ice that leads nearby land locations to warm, all indications of fast modification in Antarctica.
Roland stated their brand-new research study remained in part stimulated by previous research study demonstrating how quick spots of Antarctic moss were growing vertically and how microbial activity in small spots of soil was likewise speeding up.
“We ‘d taken these sediment cores, and done all sorts of analysis, consisting of radiocarbon dating … revealing the development in the plants we ‘d tested increasing drastically,” he stated.
Those measurements validated that the plants are delicate to environment modification, and as a next action, scientists needed to know “if the plants are growing sideways at the very same significant rate,” he stated. “It’s something for plants to be growing upwards extremely quick. If they’re growing outwards, then you understand you’re beginning to see huge modifications and enormous boosts in plant life cover throughout the peninsula.”
With the research study recording considerable horizontal growth of plants, the scientists are now studying how just recently deglaciated locations were very first colonized by plants. About 90 percent of the glaciers on the Antarctic Peninsula have actually been diminishing for the previous 75 years, Roland stated.
“That’s simply producing a growing number of land for this possibly fast plants action,” he stated. “So like Olly states, among the important things we can’t eliminate is that this actually does increase rather considerably over the next couple of years. Our findings raise severe issues about the ecological future of the Antarctic Peninsula and of the continent as a whole.”
This story initially appeared on Inside Climate News.
[
1.
Greening of Antarctica demonstrates how environment modification impacts the frozen continent
2.
Neo-Nazis head to encrypted SimpleX Chat app, bail on Telegram
3.
How London’s Crystal Palace was constructed so rapidly
4.
Helene wrecked the NC plant that makes 60 % of the nation’s IV fluid supply
5.
Halls of Torment is Diablo cranked as much as 50,000 kills/hour
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.