(Image credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, and STScI)
The world’s very first telescope, crafted in 1608 by the Dutch glasses maker Hans Lippersheyresulted in sensational innovations that would later on reinvent our understanding of deep space. While his telescope utilized easy lenses to amplify challenge about 3 times their size, later on researchers developed on this principle to peer into the depths of deep space.
Some telescopes are more effective than others, allowing us to identify remote stars and galaxies and enabling scientists to study severe phenomena like great voids and Einstein ringsWhat’s the most effective telescope, and how far can it see into area?
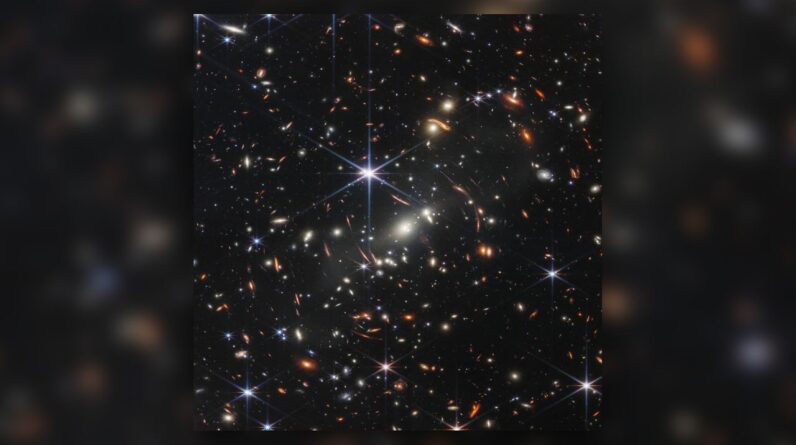
The response isn’t unexpected to anybody acquainted with today’s headings: The most effective telescope is currently the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which was introduced in December 2021 to identify infrared and near-infrared wavelengths, or wavelengths on the electro-magnetic spectrum that are undetectable to people however can be felt as heat. Its predecessor and cousin, the Hubble Space Telescopewas mostly created to discover visible-spectrum light and ultraviolet light, a wavelength that is typically produced by young stars
In area, lots of things do not produce or show adequate visible-spectrum light to see with the naked eye or to discover from far. Infrared light stretches so long that it is much easier to identify from large ranges. The long wavelengths even have the advantage of piercing through clouds of dustmaking them especially engaging for astronomers wishing to peer into the inmost depths of deep space.
Even the effective brand-new Vera C. Rubin Telescopejust recently triggered in Chile, can’t see this far into area due to the fact that it needs to compete with anomalous blockages such as dust.
When the universe started, it was condensed into a hot mash of particles (protons, neutrons and electrons). As deep space broadened and cooled, the very first stars and galaxies started to coalesce. The earliest of these we can see are around 13.7 billion years of ageswhich is simply a little over a hundred million years after the Big Bang.
Related: The number of galaxies orbit the Milky Way?
“The James Webb Space Telescope has proven itself capable of seeing 98% of the way back to the Big Bang,” Peter Jakobsenan affiliate teacher of astrophysics at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, informed Live Science in an e-mail. “This exceeds the hopes and expectations of most of us involved in the early planning of the James Webb Space Telescope.”
Pictures of 850 galaxies from the early universe, dating in between 11 and 13 billion years of ages, that were taken by James Webb Space Telescope. (Image credit: NASA/STScI/CEERS/ TACC/S. Finkelstein/M. Bagley/Z. Levay)
Much of the power behind the JWST originates from its big main mirror, Carol Christianan astrophysicist at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, informed Live Science by means of e-mail.
JWST’s main mirror procedures 21.3 feet (6.5 meters) in size, providing it an overall gathering location of more than 270 square feet (25 square m). On the other hand, Hubble’s main mirror is 8 feet (2.4 m) in size and has a gathering location of almost 50 square feet (4.5 square m). Both telescopes can see billions of light-years away since they remain in area, well beyond the obscuring haze of Earth’s environment.
JWST is likewise geared up with infrared light detectors positioned to soak up light rerouted from its big mirrors that aid it determine remote light that Hubble can not see.
Earth’s environment develops special issues for terrestrial telescopes. These issues vary from light contamination to “atmospheric turbulence,” which is the random motion of air. Such elements can blur and misshape images and restrict a telescope’s capability to see deeply into area. Area, on the other hand, is darker and without these issues, a lot of our greatest telescopes are put well beyond Earth’s environment.
When it comes to James Webb, the telescope sits at a viewpoint almost 1 million miles (1.5 million kilometers) from Earth at a Lagrange point, or a point that has simply the ideal gravitational balance for satellites to remain steady in orbit.
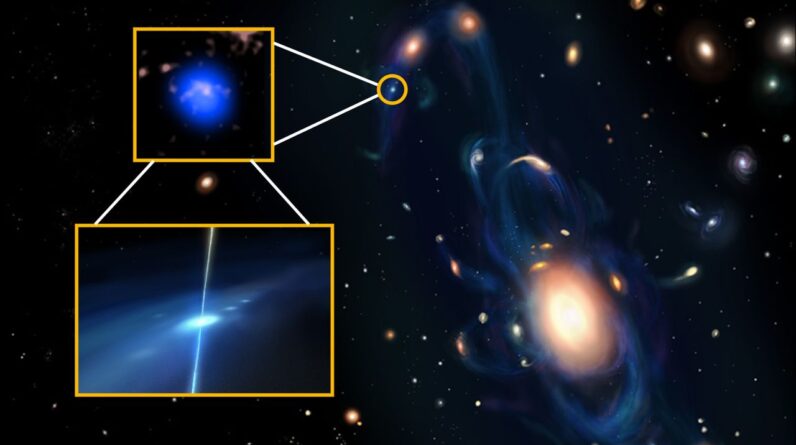
The galaxy JADES-GS-z14-0, the existing competitor for the most far-off in deep space, is displayed in the pullout taken by the James Webb Space Telescope. (Image credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, B. Robertson (UC Santa Cruz), B. Johnson (CfA), S. Tacchella (Cambridge), P. Cargile (CfA).)
How far can the James Webb Space Telescope see?
When we take a look at the night sky, we’re basically recalling in time Light journeys 299,792,458 meters per 2nd (186,282 miles per second), which indicates the light that reaches us from remote things in area is older than when it was dischargedIt takes light from our sun 43.2 minutes to reach Jupiter, however just 8 minutes to reach Earth. The range to the outer depths of the universes is greatly further, which makes complex the estimations. Determining how far a telescope can see into area is not a simple procedure, Jakobsen stated.
2 difficulties astronomers routinely require to represent are the growth of deep space and the limited speed of lighthe stated. Astronomers bypass these issues by determining the redshift of remote heavenly bodies.
Redshift is what we view as heavenly bodies speed up further and further away from us. As deep space broadens, the light given off by distant items extends to longer and “redder” wavelengths. The further and longer the light takes a trip, the higher its redshift ends up being.
Presently, among the farthest recognized redshift competitors is the galaxy JADES-GS-z14-0Jakobsen stated. Its redshift puts it at about 290 million years after the Big Bang.
Another competitor, which has actually not yet been released in a peer-reviewed journal, is the galaxy MoM-z14which has actually been dated to a simple 280 million years after the Big Bang. Its redshift was 14.44– bigger than the redshift of JADES-GS-z14-0, which is 14.18.
One research study examined a set of especially big and far-off galaxies discovered by the JWST and discovered they may be older than the present designs of our universe recommend.
The JWST has actually shown that it can peer much deeper into area than Hubble, which has actually just viewed as far back as 13.4 billion years
While the JWST is currently the champ in peering deep into our cosmic past, competitors are on the horizon. China is developing an area telescopecalled the China Space Station Telescope, that utilizes innovation that will allow it to catch more light frequencies than JWST, enabling it to withdraw higher details from the universes.
James Webb Space Telescope test: How well do you understand the world’s most effective telescope?
Taylor Mitchell Brown is a California-based independent science reporter who discusses archaeology, paleontology and Earth science. His work has actually appeared in Science, New Scientist, Live Science and somewhere else. He has a Bachelor of Science degree from UC San Diego.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.