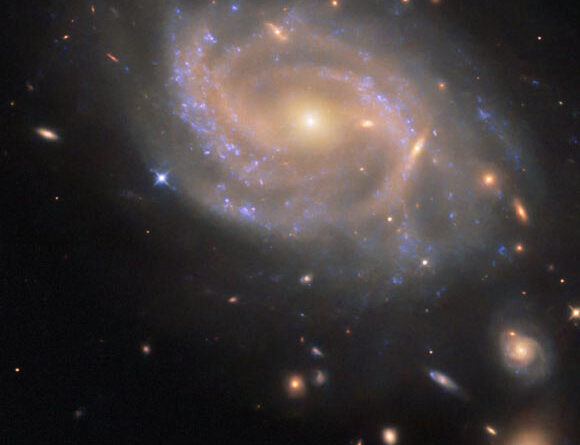
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has actually produced an impressive picture of the disallowed spiral nebula NGC 3285B.
This Hubble image reveals NGC 3285B, a disallowed spiral nebula some 137 million light-years away in the constellation of Hydra. The color image was made from different direct exposures taken in the ultraviolet and infrared areas of the spectrum with Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3(WFC3). It is based upon information acquired through 7 filters. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ Hubble/ R.J. Foley, UC Santa Cruz.
NGC 3285B lies roughly 137 million light-years away in the constellation of Hydra.
Understood as LEDA 31293, ESO 501-18 or IRAS 10322-2723, the galaxy has a size of 100,000 light-years.
NGC 3285B has a disk and a number of swirling arms. The galaxy’s core is big and shines vibrantly gold, while the spiral arms are a paler and faint reddish color.
It belongs to the NGC 3312 galaxy group (LGG 210) and the Hydra I galaxy cluster.
“NGC 3285B belongs to the Hydra I cluster, among the biggest galaxy clusters in the close-by Universe,” the Hubble astronomers stated in a declaration.
“Galaxy clusters are collections of hundreds to countless galaxies that are bound to one another by gravity.”
“The Hydra I cluster is anchored by 2 huge elliptical galaxies at its center.”
“Each of these galaxies has to do with 150,000 light-years throughout, making them about 50% bigger than our home galaxy, the Milky Way.”
NGC 3285B sits on the borders of the Hydra I cluster, far from the enormous galaxies at the.
“This galaxy drew Hubble’s attention since it hosted a Type Ia supernova in 2023,” the astronomers stated.
“Type Ia supernovae take place when a kind of condensed excellent core called a white dwarf detonates, sparking an abrupt burst of nuclear blend that quickly shines about 5 billion times brighter than the Sun.”
“The supernova, called SN 2023xqm, shows up here as a blue-ish dot on the left edge of the galaxy’s disk.”
“Hubble observed NGC 3285B as part of an observing program that targeted 100 Type Ia supernovae.”
“By seeing each of these supernovae in ultraviolet, optical, and near-infrared light, we intend to disentangle the impacts of range and dust, both of which can make a supernova appear redder than it really is.”
“This program will assist fine-tune cosmic range measurements that count on observations of Type Ia supernovae.”
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.