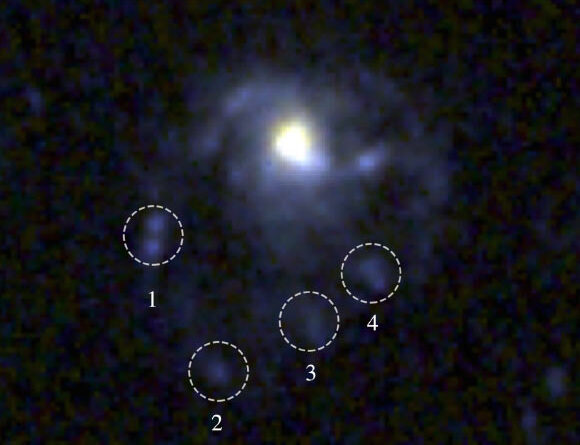
Astronomers utilizing the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have actually gotten a brand-new picture of the almost face-on spiral nebula NGC 3370.
This Hubble image reveals NGC 3370, a spiral nebula some 90 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ Hubble/ A. Riess/ K. Noll.
NGC 3370 lies around 90 million light-years far from Earth in the constellation of Leo.
Otherwise referred to as the Silverado Galaxy, IRAS 10444 +1732, LEDA 32207 or UGC 5887, this galaxy is almost equivalent to our Milky Way both in size and mass.
NGC 3370 was initially found by the German-British astronomer William Herschel on March 21, 1784.
It belongs to the NGC 3370 group of galaxies in addition to NGC 3447 and NGC 3455.
NGC 3370 is home to 2 type of items that astronomers reward for their effectiveness in figuring out ranges to far galaxies: Cepheid variable stars and Type Ia supernovae.
“Cepheid variable stars alter in both size and temperature level as they pulsate,” the Hubble astronomers stated in a declaration.
“As an outcome, the luminosity of these stars differs over a duration of days to months.”
“It does so in a manner that exposes something essential: the more luminescent a Cepheid variable star is, the more gradually it pulsates.”
“By determining the length of time a Cepheid variable’s brightness requires to finish one cycle, we can figure out how intense the star really is.”
“Paired with how intense the star appears from Earth, this info provides the range to the star and its home galaxy.”
“Type Ia supernovae supply a method to determine ranges in a single explosive burst instead of through routine brightness variations.”
“These surges take place when the dead core of a star sparks in an abrupt flare of nuclear combination.”
“They peak at extremely comparable luminosities, and just like for a Cepheid variable star, understanding the intrinsic brightness of a supernova surge enables its range to be determined.”
“Observations of Cepheid variable stars and Type Ia supernovae are both important for specifically determining how quick our Universe is broadening.”
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.