New research study by researchers from the University of Reading and the University of Durham reveals that encephalization (i.e., relative brain size boost) throughout 7 million years of hominin advancement developed from boosts within specific types.
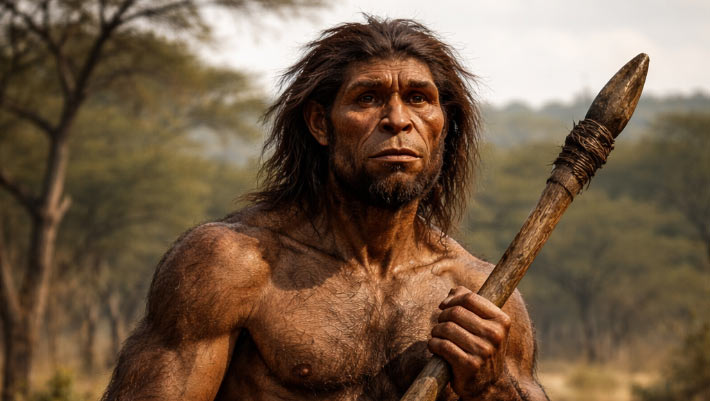
Modern human beings, Neanderthals, and other current family members on the human ancestral tree progressed larger brains far more quickly than earlier types. Image credit: SINC/ José Antonio Peñas.
“One of the most apparent evolutionary modifications throughout human development and one totally connected with our distinct cognitive and behavioral characteristics has actually been a boost in brain size,” stated lead author Dr. Thomas Puschel and his associates.
“Encephalization throughout human development has actually long been disputed, and numerous research studies have actually compared hominin cranial capabilities throughout types to propose possible adaptive systems acting on brain size variation amongst hominins.”
“Some have actually argued for steady development in time, while others propose stressed stability with quick boosts followed by tension.”
“Other research studies support a mix of both designs, while others declare they can not be differentiated.”
For their brand-new research study, the authors put together the largest-ever dataset of ancient human fossils covering 7 million years and utilized innovative computational and analytical approaches to represent spaces in the fossil record.
These ingenious methods offered the most extensive view yet of how brain size developed with time.
“This research study totally alters our understanding of how human brains progressed,” stated Professor Chris Venditti, co-author of the research study.
“It was formerly believed that brain size leaps drastically in between types, fresh upgrades in between the current computer system designs.”
“Our research study rather reveals a stable, incremental ‘software application upgrade’ occurring within each types over countless years.”
The research study challenges old concepts that some types, like Neanderthals, were imperishable and not able to adjust and rather highlights progressive and constant modification as the driving force behind brain size development.
“Big evolutionary modifications do not constantly require remarkable occasions,” Dr. Puschel stated.
“They can occur through little, progressive enhancements gradually, just like how we find out and adjust today.”
The scientists likewise revealed a striking pattern: while larger-bodied types usually had larger brains, the variation observed within a specific types did not regularly associate with body size.
Brain size advancement throughout long evolutionary timescales extending countless years is for that reason formed by various elements to those observed within specific types– highlighting the intricacy of evolutionary pressures on brain size.
“Why and how people progressed big brains is a main concern in human advancement,” stated Dr. Joanna Baker, co-author of the research study.
“By studying brain and body size in different types over countless years, we expose that our trademark big brains occurred mostly from steady modifications within private types.”
The research study was released November 26, 2024 in the Procedures of the National Academy of Sciences
_____
Thomas A. Püschel et al2024. Hominin brain size boost has actually emerged from within-species encephalization. PNAS 121 (49 ): e2409542121; doi: 10.1073/ pnas.2409542121
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.