FAST FACTS
Call: Indian Ocean geoid low
Area: Laccadive Sea, southwest of India
Why it’s amazing: The substantial gravity hole formed on the website of an ancient ocean.
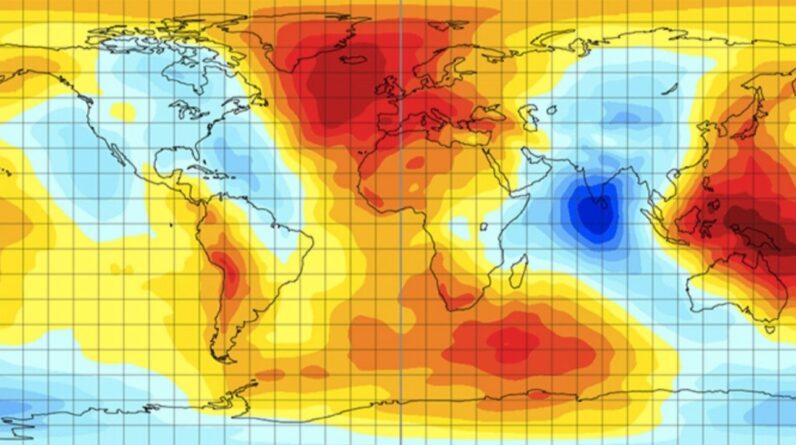
The Indian Ocean “gravity hole” is the website of the inmost damage in Earth’s gravitational field. It’s a circular ocean area with a gravitational pull that’s so weak, water level are 348 feet (106 meters) lower there than in other places in the world. Found in 1948, the origins of this huge gravity hole– or geoid low, as it is technically called– stayed a secret till just recently.
Related: A force more effective than gravity within the Earth’: How magnetism locked itself inside our world
The hole covers 1.2 million square miles (3.1 million square kilometers) and sits 746 miles (1,200 km) southwest of India. Numerous theories have actually attempted to describe its presence because geophysicists initially identified its trace, however the response just can be found in 2023 with a research study released in the journal Geophysical Research LettersScientists utilized 19 computer system designs to imitate the movement of Earth’s mantle and tectonic plates over the previous 140 million years, and after that teased out the situations generating a geoid low comparable to the real-life one.
The research study suggested that the Indian Ocean gravity hole formed after the death of an ancient ocean called Tethys, which existed in between the supercontinents Laurasia and Gondwana. Tethys rested on a portion of Earth’s crust that slipped below the Eurasian plate throughout the separation of Gondwana 180 million years back. As this taken place, shattered pieces of the crust sank deep into the mantle.
Around 20 million years back, as these pieces landed in the lowermost areas of the mantle, they displaced high-density product stemming from the “African blob” — a compact bubble of taken shape lava, 100 times taller than Mount Everestthat is caught below Africa. Plumes of low-density lava increased to change the thick product, reducing the general mass of the area and compromising its gravity.
Researchers are yet to validate these design forecasts with earthquake information, which might assist to confirm the presence of low-density plumes underneath the hole. Scientists are recognizing increasingly more that Earth’s lava has plenty of unusual blobsconsisting of some that were believed to be missing out on and have showed up in unanticipated locations
And it’s not simply Earth– expeditions of Mars, too, have exposed blobs of all sizes and shapes hiding listed below the world’s surface area.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Discover more amazing locationswhere we highlight the great history and science behind a few of the most remarkable landscapes in the world.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.