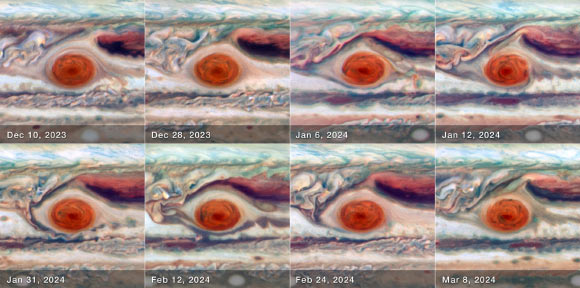
Astronomers utilizing the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope observed Jupiter’s many distinguishing characteristic, the Great Red Spot, with on 8 dates over a single, 90-day oscillation cycle from December 2023 to March 2024.
Simon et aldetermined the Great Red Spot’s size, shape, brightness, color, and vorticity over one complete oscillation cycle. Image credit: NASA/ ESA/ Amy Simon, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/ Joseph DePasquale, STScI.
“While we understood its movement differs somewhat in its longitude, we didn’t anticipate to see the size oscillate,” stated Dr. Amy Simon, an astronomer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight.
“As far as we understand, it’s not been determined before.”
“This is truly the very first time we’ve had the appropriate imaging cadence of the Great Red Spot.”
“With Hubble’s high resolution we can state that the Great Red Spot is definitively squeezing in and out at the very same time as it moves faster and slower.”
“That was really unanticipated, and at present there are no hydrodynamic descriptions.”
Dr. Simon and associates utilized Hubble to focus on the Great Red Spot for an in-depth take a look at its size, shape, and any subtle color modifications.
“When we look carefully, we see a great deal of things are altering from day to day,” Dr. Simon stated.
“This consists of ultraviolet-light observations revealing that the unique core of the storm gets brightest when the Great Red Spot is at its biggest size in its oscillation cycle.”
“This suggests less haze absorption in the upper environment.”
“As it speeds up and slows down, the Great Red Spot is pressing versus the windy jet streams to the north and south of it,”stated Dr. Mike Wong, an astronomer at the University of California at Berkeley.
“It’s comparable to a sandwich where the pieces of bread are required to bulge out when there’s excessive filling in the middle.”
The authors contrasted this to Neptune, where dark areas can wander extremely in latitude without strong jet streams to hold them in location.
The Great Red Spot has actually been held at a southern latitude, caught in between the jet streams, for the degree of Earth-bound telescopic observations.
The astronomers forecast it will keep diminishing before handling a steady, less-elongated, shape.
“Right now it’s over-filling its latitude band relative to the wind field,” Dr. Simon stated.
“Once it diminishes inside that band the winds will truly be holding it in location.”
“We forecast that the Great Red Spot will most likely support in size, however for now Hubble just observed it for one oscillation cycle.”
The group’s outcomes were released in the Planetary Science Journal
_____
Amy A. Simon et al2024. A Detailed Study of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot over a 90-day Oscillation Cycle. World. Sci. J 5, 223; doi: 10.3847/ PSJ/ad71d1
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.