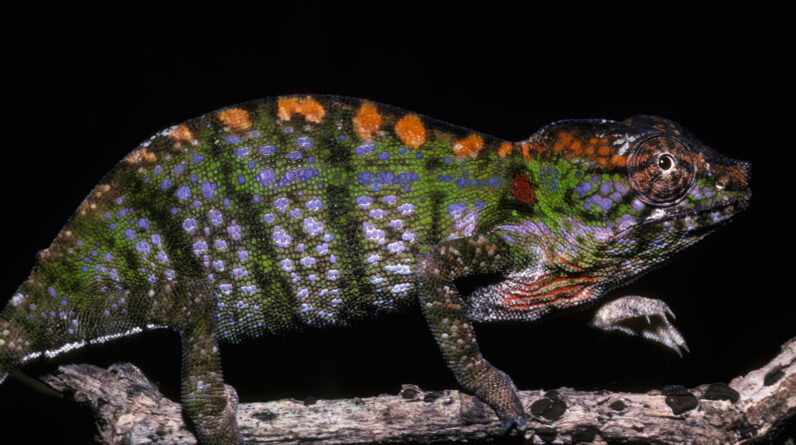
Call: Labord’s chameleon (Furcifer labordi
Where it lives: Western Madagascar
What it consumes: Crickets, flies, locusts, insects and stick bugs
Why it’s incredible: Labord’s chameleons live quickly and pass away young. They hold the record for the quickest life-span of all tetrapods– they hatch, grow, mate and pass away in simply 4 to 5 months.
Labord’s chameleons in fact invest more time establishing inside their eggs than they do beyond them. For around 8 to 9 months, the embryos rest below the forest flooring, getting ready for their whirlwind time above ground.
These temporary chameleons grow to around 3.5 inches (9 centimeters) long and are discovered specifically in forests in the lowlands of western Madagascar.
Once they hatch, they grow rapidly and reach sexual maturity at 2 months old.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Their aggressive breeding season starts in January, throughout the damp season, with males fighting increasingly for the possibility at recreating then passing away quickly after.
Women then put all their energy into producing eggs, which they lay in February. They have a reasonably high reproductive rate to make up for their brief adult life-span, with each female laying up to 11 eggsHours after laying their eggs, the women pass away.
This suggests that for two-thirds of the year, the whole types exists in eggs buried underground.
This uncommon– and apparently dangerous– lifecycle is believed to be a survival adjustment to the extreme seasonal environment of western Madagascar. The area experiences unique damp and dry seasons, with the rainy season offering the needed resources for survival, such as food and water, while these ended up being more limited in the dry season. Lots of tropical areas experience damp and dry seasons, the environment of Madagascar is very variable and ecological unpredictability is much higher than other tropical locations.
To line up with these conditions, the chameleons have actually developed to invest the majority of the year as embryos in their eggs– emerging throughout the quick rainy season to mate and lay more eggs.
By compressing their whole adult presence into the damp season, the chameleons optimize their possibilities of discovering food and mates. This method likewise minimizes competitors for resources, as a lot of grownups pass away before the next generation hatches (although throughout uncommonly long rainy seasons, women can endure for a 2nd breeding season.
Chameleons are understood for their capability to alter color, and Labord’s chameleons are no various. Their skin modifications color by broadening and contracting unique cells which contain nanocrystals, which changes how they show light. They do not do it to camouflage themselves. Rather, they utilize it to interact with other chameleons– for instance, to bring in mates — and in reaction to feelings.
Female Chameleon Erupts with Color Before Death – YouTube
Enjoy On
In a 2024 PBS documentary recorded in the Kirindy Forest in western Madagascar, a Labord’s chameleon burglarized a dynamic, pulsating display screen of color simply minutes before its death. This is the outcome of the nerve systems continuing to send out signals to skin cells, leading to a significant “technicolor fireworks display,” according to the specialists in the documentary.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.