Paleontologists have actually explained a brand-new genus and types of carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur based upon representations of the now-destroyed specimen from the Bahariya Formation in Egypt.
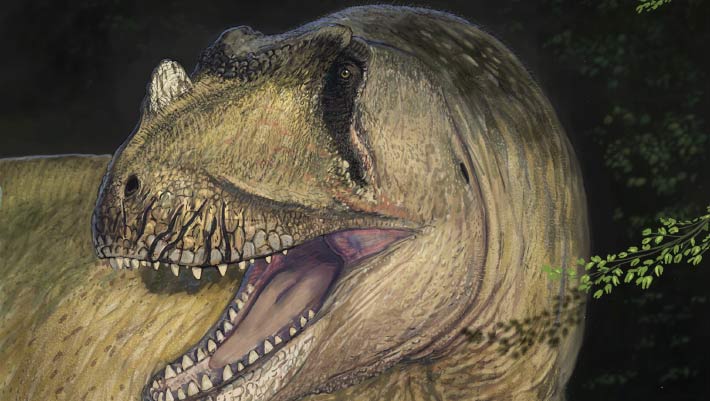
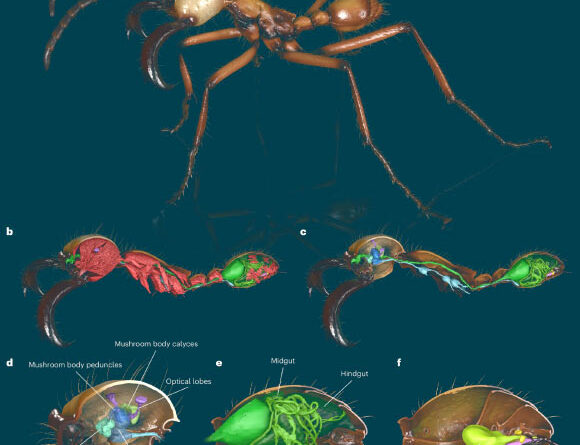
Life restoration of Tameryraptor markgrafiImage credit: Joschua Knüppe.
The newly-identified dinosaur resided in what is now Africa throughout the Cretaceous duration, some 95 million years earlier.
Called Tameryraptor markgrafithe ancient types belongs to a group of meat-eating theropod dinosaurs called Carcharodontosauridae.
The dinosaur’s fossilized remains were discovered in 1914 roughly 2 km (1.2 miles) from Ain Gedid on the Western foot of the Gebel Harra of the Bahariya Formation.
The fossils were very first explained in 1931 by the German paleontologist Ernst Stromer von Reichenbach as the carcharodontosaurid types Carcharodontosaurus saharicus
“In 1931, Stromer explained the very first partial carcharodontosaurid skeleton from the Cretaceous of Northern Africa,” stated lead author Dr. Maximilian Kellermann and his coworkers from the Staatliche Naturwissenschaftliche Sammlungen Bayerns-Bayerische Staatssammlung für Paläontologie und Geologie and the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität.
“The specimen originated from the Bahariya Formation, from a region in the northern part of the Bahariya Oasis in Egypt and consisted of skull pieces (maxillae, nasals, partial braincase), vertebrae, partial pubis and ischium, thigh, and a fibula.”
“Realizing typical functions of an associated tooth, Stromer referred the specimen to Dryptosaurus saharicushowever proposed a brand-new genus name, Carcharodontosaurusfor this types.”
According to the authors, the initial specimen was damaged throughout the World War II.
The only enduring information include Stromer’s descriptions and representations of the specimen, in addition to an endocast of the braincase, presently housed in Berlin.
“What we saw in the historic images amazed all of us,” Dr. Kellermann stated.
“The Egyptian dinosaur fossil portrayed there varies substantially from more current Carcharodontosaurus discovers in Morocco.”
“Stromer’s initial category was therefore inaccurate. We determined an entirely various, formerly unidentified predatory dinosaur types here and called it Tameryraptor markgrafi“
Tameryraptor markgrafi was almost 10 m (33 feet) long, had in proportion teeth and a popular nasal horn.
“We discovered that the dinosaur was carefully associated to the North African and South American carcharodontosaurs, in addition to a group of predatory dinosaurs from Asia, the metriacanthosaurs,” stated Dr. Oliver Rauhut, senior author of the research study.
“Presumably, the dinosaur animals of North Africa was a lot more varied than we formerly believed.”
“This work reveals that it can be beneficial for paleontologists to dig not just in the ground, however likewise in old archives.”
“However, a more extensive evaluation of the Cretaceous predatory dinosaur animals from the Bahariya Oasis would need the healing of more fossils from the website.”
The group’s work was released in the journal PLoS ONE
_____
M. Kellermann et al2025. Re-evaluation of the Bahariya Formation carcharodontosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) and its ramifications for allosauroid phylogeny. PLoS ONE 20 (1 ): e0311096; doi: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0311096
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.