A brand-new genus and types of nimravid from the middle Oligocene date has actually been determined from the fossilized remains discovered in northern China. The discovery fills a space in understanding about the Nimravidae household in the eastern part of Eurasia.
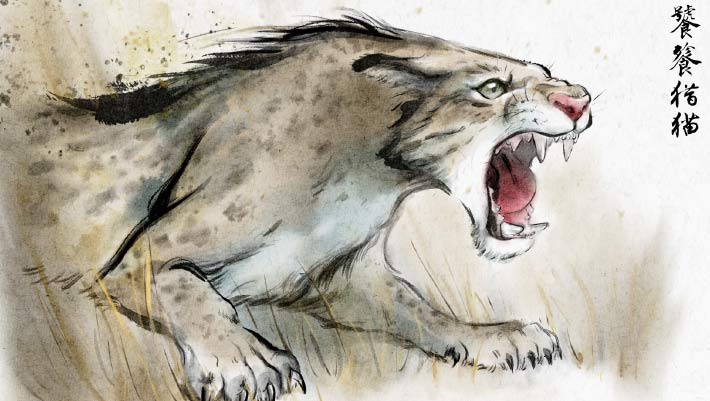
Life restoration of Taotienimravus songi in Chinese painting design. Image credit: Yuefeng Song.
Taotienimravus songi resided in what is now China throughout the middle Oligocene, roughly 28 million years back.
The ancient types comes from Nimravidae, an extinct household of saber-toothed hypercarnivores, often called incorrect saber-toothed felines.
“The order Carnivora shows among the best varieties of body size variety within Mammalia, covering from around 50 g for the least weasel Mustela nivalis to approximately over 3 lots in the pinniped Mirounga,” stated Dr. Qigao Jiangzuo from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences and associates.
“With couple of exceptions such as Ursidae, large-bodied terrestrial predators– especially those surpassing 20 kg– usually embrace a macrocarnivorous diet plan, taking advantage of big animals of equivalent or higher size.”
“The household Nimravidae, typically described as incorrect sabertooths, represents among the earliest diverging family trees of Carnivora, defined by big body size, hypercarnivorous craniodental morphology and most likely a macrocarnivorous diet plan,” they included.
“The earliest verified fossil records of the household in the center Eocene come from currently extremely specialized types with felid-like craniodental morphology.”
“Nimravidae went through a radiation throughout the Eocene-Oligocene, with the best-preserved records discovered in North America, where various skulls and total skeletons have actually been found.”
“Fossil stays are likewise plentiful in Eurasia however are less well maintained.”
“As the very first family tree of Carnivora to develop big body size, Nimravidae is a perfect group to study expedition of the early macrocarnivorous specific niche by Carnivora in an ecological context greatly various from that of the modern-day world.”
The skeletal remains of Taotienimravus songi were found in the Qingshuiying Formation in northern China.
The analysis of the specimens reveals that the brand-new types represents a non-sabertooth ecomorph type with preliminary bone-cracking adjustment– a special kind amongst the Nimravidae gamily.
The animal most likely had a killing habits that was various from any other felid-like predators however most likely utilized a tearing bite as seen in hyenas.
“The most unique characters of the brand-new nimravid are the really brief and robust upper dog and the general broad palatal area,” the paleontologists stated.
“The rostrum is really large, most likely among the best amongst the recognized nimravids.”
“Unlike in numerous other felid-like predators, the premolars are not decreased in size however rather bigger, leaving no diastema in between the canine and the cheek teeth.”
“This contrasts with the condition in a lot of felid-like carnivorans, where a diastema is practically usually present.”
“We analyze this space as associated with a strong canine bite and utilizing dogs to deeply pierce into the victim.”
The group’s phylogenetic analysis locations Taotienimravus songi within Nimravinae, where it forms the sis family tree to European and North American Nimravus and Dinaelurus
This clade is sis to the European family tree Eofelis + Dinailurictis + Quercylurus
“A boost in body size amongst Nimravidae appears to have actually accompanied the death of Oxyaenidae, another meat-eating clade in the Paleogene,” the scientists stated.
“The preliminary introduction of macrocarnivorous adjustment of Carnivora by a felid-like ecomorph most likely shows competitors characteristics.”
“Nimravidae effectively inhabited numerous eco-friendly specific niches that were not made use of by Felidae, most likely owing to the absence of competitors within Carnivora throughout much of their evolutionary history.”
“Our research study highlights the function of both abiotic and biotic consider forming specific niche accessibility for these animals, highlighting the requirement for conversations on specific niche modification and development to be grounded in these factors to consider.”
A paper explaining this discovery was released on November 26, 2025 in the Procedures of the Royal Society B
_____
Qigao Jiangzuo et al2025. A brand-new ecomorph of Nimravidae, and the early macrocarnivorous specific niche expedition in Carnivora. Proc Biol Sci 292 (2059 ): 20251686; doi: 10.1098/ rspb.2025.1686
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.