(Image credit: Diego Fernandez)
Human beings have actually discovered lead beneficial for countless years, however the metal’s harmful results didn’t end up being popular till the 20th century. Now, utilizing historic hair samples, scientists have actually revealed that guidelines targeting heavy-metal contamination were very reliable at minimizing the general public’s direct exposure to lead as soon as its threats were understood.
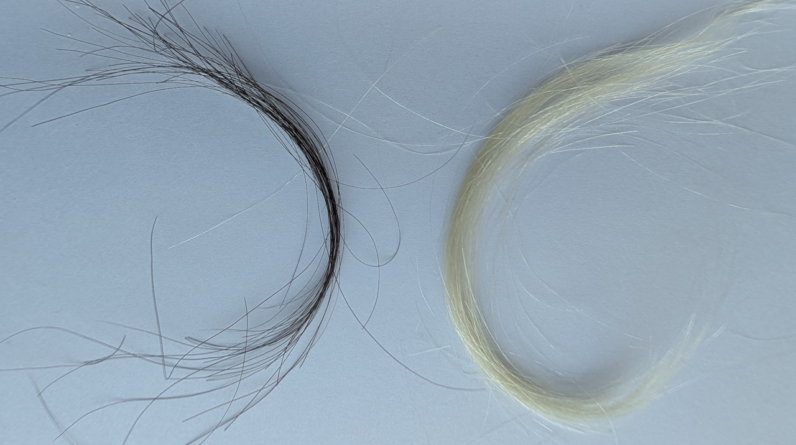
“We have hair samples spanning about 100 years,” research study co-author Ken Smitha demographer at the University of Utah, stated in a declaration. The research study concentrated on individuals residing in Utah.
In the brand-new research study, released Monday(Feb. 2 )in the journal PNASthe scientists detailed their analysis of hair samples from 47 individuals who resided in the Greater Salt Lake City area as kids and as grownups. The research study individuals supplied locks of their child hair that had actually been maintained in household scrapbooks, along with an existing hair sample. The scientists evaluated the hair for lead utilizing mass spectrometry, a method that determines chemical substances in a sample.
Lead direct exposure is damaging to human healthtriggering damage to the nerve system that can cause developmental hold-ups, seizures and discovering issues, while likewise raising the danger of fertility problems and hypertensionThere is no recognized safe level of lead direct exposure, the scientists composed in the research study.
A significant source of harmful lead direct exposure in the very first half of the 20th century was leaded gas. In the 1920s, tetraethyl lead– a substance consisting of carbon and lead– was contributed to fuel to lower engine “knocking,” the pinging noise brought on by the early ignition of fuel. The U.S. Public Health Service recognized as early as 1925 that leaded gas was triggering health concerns, the fuel additive was not totally prohibited in the U.S. till 1996.
Crucial policies on lead were developed before the 1990s. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which was produced by then-President Richard Nixon in 1970 to resolve several air and contamination issues, led to an instant decrease in lead direct exposure, the scientists discovered in the brand-new research study.
Get the world’s most remarkable discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
Concentrations of lead in human hair from the Salt Lake City area were incredibly high from 1916 to 1969, in part due to an absence of EPA guideline and in part due to the fact that of 2 active lead smelter websites in the location. From the 1970s to the 1990s, after the EPA was developed and the smelting plants were shuttered, the typical worths decreased by 2 orders of magnitude.
The U.S. Mining and Smelting Co. plant in Midvale, Utah, photographed in 1906. (Image credit: Utah Historical Society)”Current concentrations of lead in hair from this population average almost 100 times lower than before the establishment of the Environmental Protection Agency,” the scientists composed.
One caution is that the worths of lead in hair do not correspond precisely to levels in the bloodwhich is doctors’common requirement for determining individuals who require treatment for lead toxicity.
A hair sample “doesn’t really record that internal blood concentration that your brain is seeing, but it tells you about that overall environmental exposure,” research study co-author Thure Cerlinga geologist at the University of Utah, stated in the declaration. In general, the research study revealed that individuals were taking in a considerably bigger quantity of lead prior to 1970.
“It’s just coming out of the tailpipe, goes up in the air and then it comes down,” Cerling stated. Lead remains in the air for days and “it absorbs into your hair, you breathe it, and it goes into your lungs.”
The scientists kept in mind that, although their research study shows the efficiency of ecological policies in managing harmful toxins, such as lead, these policies are now in threat of being rolled back.
Particularly, the scientists indicated a March 12, 2025, statement by the EPA and President Donald Trump that would decontrol a number of the EPA’s arrangements that presently guarantee U.S. homeowners have tidy air, land and water. Lead contamination is not particularly pointed out, specialists have actually recommended that the statement is a “roadmap” for rolling back policies on air contamination in the production sector and wastewater from coal plants, to name a few things. A minimum of one federal claim has actually currently been submitted to reverse “presidential exemptions” to the EPA’s Clean Air Act.
“We should not forget the lessons of history,” Cerling stated. “Those regulations have been very important,” as evidenced by the EPA having “really, really positive effects” rather not long after it was developed.
The historical hair research study reveals that the lax ecological requirements of previous years led to unhealthy lead levels however that these levels can be controlled with “science-based regulations,” the scientists composed.
Cerling, T.E., Fernandez, D.P., & & Smith, K.R. (2026 ). Lead in archived hair files a decrease in lead direct exposure to human beings considering that the facility of the United States Environmental Protection Agency. PNAS, 123, e2525498123. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2525498123
IN CONTEXT
Nowadays in the U.S., lead direct exposure tends to posture the most significant danger in low-income neighborhoods and in Northeast and Midwest cities with older real estate– specifically, real estate constructed before 1978, the year lead-based paints were prohibited. Other typical sources of direct exposure consist of soil infected by historic sources of lead, like mining; polluted pipelines and pipes products; infected fashion jewelry, toys or sweets; and lead dust tracked into the
home from offices. Kids under 6 are especially prone to lead poisoning, as their growing bodies soak up the metal extremely effectively.Table of elements of components test: How lots of aspects can you call in 10 minutes?
Kristina Killgrove is a personnel author at Live Science with a concentrate on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her short articles have actually likewise appeared in places such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological sociology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, along with a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was previously a university teacher and scientist. She has actually gotten awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science composing.
You should verify your show and tell name before commenting
Please logout and after that login once again, you will then be triggered to enter your screen name.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.