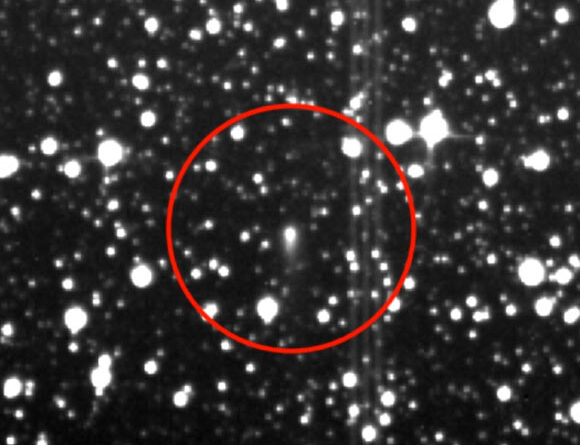
(Image credit: Cenker Atila )
Dark-brown flakes found inside a 1,900-year-old Roman glass vial are the very first direct proof for making use of human feces for medical functions, a brand-new chemical analysis exposes. The feces were blended with thyme to mask the odor, and the mixture might have been utilized to deal with swelling or infection.
“While working in the storage rooms of the Bergama Museum, I noticed that some glass vessels contained residues,” Cenker Atilaan archaeologist at Sivas Cumhuriyet University in Turkey, informed Live Science in an e-mail. “Residues were found in a total of seven different vessels, but only one yielded conclusive results.”
“When we opened the unguentarium, there was no bad smell,” Atila stated. Throughout its remain in storage, nevertheless, “the residue inside it was overlooked. I noticed it and immediately initiated the analysis process.”
The scientists utilized gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MSto recognize the natural substances in the dark-brown residue they had actually scraped from inside the glass unguentarium. 2 of the recognized substances– coprostanol and 24-ethylcoprostanol– are normally discovered in the gastrointestinal systems of animals that metabolize cholesterol.
Scientist studied the contents of a second-century glass vial found in ancient Pergamon, Turkey. (Image credit: Cenker Atila)”The consistent identification of stanols — validated fecal biomarkers — strongly suggests that the Roman unguentarium originally contained fecal material,” the scientists composed in the research study. They might not conclusively figure out the origin of the feces, the scientists kept in mind that the ratio of coprostanol to 24-ethylcoprostanol recommends it was human.
Another significant discovery in the residue was carvacrol, a fragrant natural substance present in necessary oils made from specific herbs.
Get the world’s most interesting discoveries provided directly to your inbox.
“In this sample, we identified human feces mixed with thyme,” Atila stated. “Because we are well-acquainted with ancient textual sources, we immediately recognized this as a medicinal preparation used by the famous Roman physician Galen.”
Throughout the 2nd and 3rd centuries, Pergamon was called a significant center for Roman medication, thanks to the doctor and anatomist Galen of Pergamonwhose concepts would concern control Western medical science for centuries.
There were numerous popular feces-based solutions in Roman medication that were indicated to deal with conditions varying from swelling and infection to reproductive conditions, the scientists composed. In one exampleGalen discussed the healing worth of the feces of a kid who had actually consumed vegetables, bread and white wine. Since ancient doctors understood their clients would turn down foul-smelling medications, they frequently promoted for masking them with fragrant herbs, red wine or vinegar.
“This study provides the first direct chemical evidence for the medicinal use of fecal matter in Greco-Roman antiquity,” the scientists composed, along with direct proof that the smell of the excrement was masked with strong-smelling herbs. “These findings closely align with formulations described by Galen and other classical authors, suggesting that such remedies were materially enacted, not merely textually theorized.”
Atila, C., Demirbolat, İ., & & Çelebi, R. B. (2026 ). Feces, scent and medication chemical proof of ancient rehabs in a Roman unguentarium. Journal of Archaeological Science Reports, 70, 105589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2026.105589
Roman emperor test: Test your understanding on the rulers of the ancient empire
Kristina Killgrove is a personnel author at Live Science with a concentrate on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her short articles have actually likewise appeared in places such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological sociology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, in addition to a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was previously a university teacher and scientist. She has actually gotten awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science composing.
You should verify your show and tell name before commenting
Please logout and after that login once again, you will then be triggered to enter your display screen name.
Find out more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.