New information from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and ESO’s Very Large Telescope offer proof that outbursts from supermassive great voids can assist cool off gas to feed themselves.
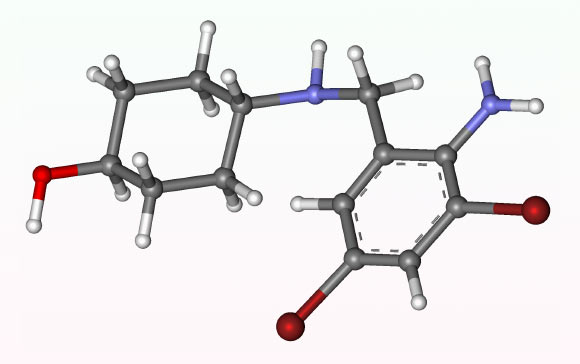
These images reveal 2 of the galaxy clusters in the research study, the Perseus Cluster and the Centaurus Cluster. Chandra information represented in blue expose X-rays from filaments of hot gas, and VLT information reveal cooler filaments in red. Image credit: NASA/ CXC/ SAO/ Olivares et al/ DSS/ CFHT/ SITELLE/ ESA/ STScI/ ESO/ VLT/ MUSE/ N. Wolk.
In a brand-new research study, Dr. Valeria Olivares from the Universidad de Santiago de Chile and her associates evaluated deep observations of 7 galaxy clusters that show popular multiphase filamentary structures: Perseus, M87, Centaurus, Abell 2597, Abell 1795, Hydra-A, and PKS 0745-191.
“The centers of galaxy clusters include deep space’s most enormous galaxies, which harbor substantial great voids with masses varying from millions to 10s of billions of times that of the Sun,” they stated.
“Jets from these great voids are driven by the great voids delighting in gas.”
Their outcomes support a design where outbursts from the great voids set off hot gas to cool and form narrow filaments of warm gas.
Turbulence in the gas likewise plays a crucial function in this setting off procedure.
According to the design, a few of the warm gas in these filaments must then stream into the centers of the galaxies to feed the great voids, triggering an outburst.
The outburst triggers more gas to cool and feed the great voids, resulting in more outbursts.
The design anticipates there will be a relationship in between the brightness of filaments of hot and warm gas in the centers of galaxy clusters.
More particularly, in areas where the hot gas is brighter, the warm gas ought to likewise be brighter.
“Our outcomes supply brand-new understanding of these gas-filled filaments, which are essential not simply for feeding great voids however likewise for triggering brand-new stars to form,” the astronomers stated.
“This advance was enabled by an ingenious strategy that separates the hot filaments in the Chandra X-ray information from other structures, consisting of big cavities in the hot gas developed by the great void’s jets.”
“The freshly discovered relationship for these filaments reveals exceptional resemblance to the one discovered in the tails of jellyfish galaxies, which have actually had gas removed away from them as they take a trip through surrounding gas, forming long tails.”
“This resemblance exposes an unforeseen cosmic connection in between the 2 things and suggests a comparable procedure is happening in these items.”
The group’s paper was released in the journal Nature Astronomy
_____
V. Olivares et alAn Hα-X-ray surface-brightness connection for filaments in cooling-flow clusters. Nat Astronreleased online January 27, 2025; doi: 10.1038/ s41550-024-02473-8
Learn more
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.